Animal Husbandry and Feed Science ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 75-82.doi: 10.12160/j.issn.1672-5190.2023.03.011
• Animal Husbandry Resource and Environment • Previous Articles Next Articles
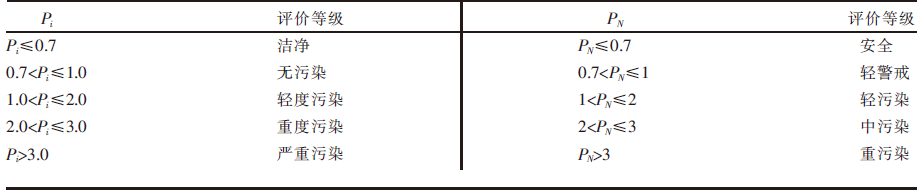
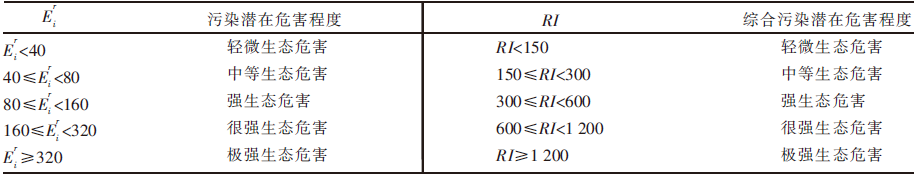
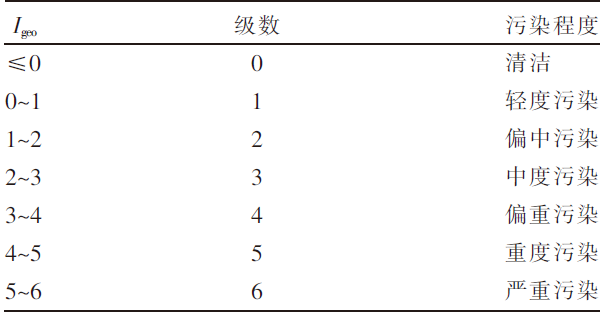
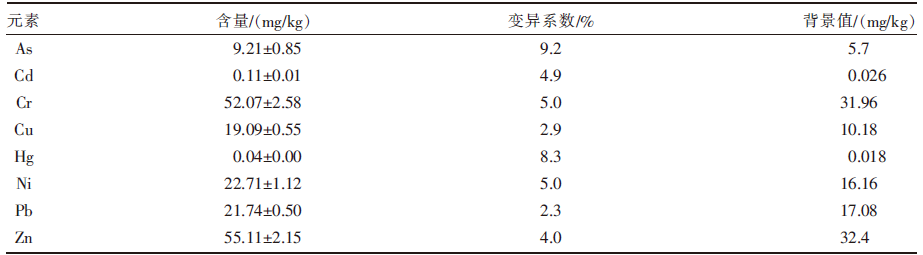
Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals in Roadside Grassland in Central Inner Mongolia
HE Yimin1,2,Hongyu 1,2,WANG Yang1,2,HUA Yao1
- 1. College of Life Science and Technology,Inner Mongolia Normal University,Hohhot 010022,China
2. Key Laboratory of Biodiversity Conservation and Sustainable Utilization for College and University of Inner Mongolia,Hohhot 010022, China
-
Received:2023-03-14Online:2023-05-30Published:2023-07-12
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HE Yimin, Hongyu , WANG Yang, HUA Yao. Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals in Roadside Grassland in Central Inner Mongolia[J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2023, 44(3): 75-82.
share this article
| [1] | 谢龙涛, 潘剑君, 白浩然, 等. 基于GIS的农田土壤重金属空间分布及污染评价:以南京市江宁区某乡镇为例[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(2):316-325. |
| [2] |
JIANG Y F, CHEN S C, HU B F, et al. A comprehensive framework for assessing the impact of potential agricultural pollution on grain security and human health in economically developed areas[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 263:114653.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114653 |
| [3] | 柴磊, 王新, 马良, 等. 基于PMF模型的兰州耕地土壤重金属来源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(9):3919-3929. |
| [4] |
YUAN X H, XUE N D, HAN Z G. A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 101:217-226.
doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.08.013 pmid: 33334517 |
| [5] |
SUN T, HUANG J L, WU Y Y, et al. Risk assessment and source apportionment of soil heavy metals under different land use in a typical estuary alluvial island[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(13):4841.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph17134841 |
| [6] |
FINZGAR N, LESTAN D. The two-phase leaching of Pb,Zn and Cd contaminated soil using EDTA and electrochemical treatment of the washing solution[J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 73(9):1484-1491.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.043 |
| [7] |
GU Y G, LIN Q, GAO Y P. Metals in exposed-lawn soils from 18 urban parks and its human health implications in Southern China′s largest city, Guangzhou[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 115:122-129.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.12.031 |
| [8] |
CHEN H Y, TENG Y G, LU S J, et al. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 512/513: 143-153.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025 |
| [9] |
GUO G H, WU F C, XIE F Z, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in urban soils from southwest China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2012, 24(3):410-418.
pmid: 22655353 |
| [10] |
SHI T R, WANG Y H. Heavy metals in indoor dust:Spatial distribution, influencing factors,and potential health risks[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 755:142367.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142367 |
| [11] |
YANG Y, WU J P, CHRISTAKOS G. Prediction of soil heavy metal distribution using Spatiotemporal Kriging with trend model[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2015, 56:125-133.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.03.034 |
| [12] |
GANUGAPENTA S, NADIMIKERI J, CHINNAPOLLA S R R B, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution from the sediment of Tupilipalem Coast,southeast coast of India[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2018, 33(3):294-302.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijsrc.2018.02.004 |
| [13] |
TRAN Q B, LOHITNAVY M, PHENRAT T. Assessing potential hydrogen cyanide exposure from cyanide-contaminated mine tailing management practices in Thailand′s gold mining[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 249:109357.
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109357 |
| [14] | 韩琳, 徐夕博. 基于PMF模型及地统计的土壤重金属健康风险定量评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(11):5114-5124. |
| [15] |
周旭, 吕建树. 山东省广饶县土壤重金属来源、分布及生态风险[J]. 地理研究, 2019, 38(2):414-426.
doi: 10.11821/dlyj020171151 |
| [16] | 张军, 梁青芳, 高煜. 宝鸡市绿植叶片重金属空间分布及污染特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(10):4504-4513. |
| [17] | 庄洋, 赵娜, 赵吉. 内蒙古草地碳汇潜力估测及其发展对策[J]. 草业科学, 2013, 30(9):1469-1474. |
| [18] | 刘梦梅, 王利军, 王丽, 等. 西安市不同功能区土壤重金属含量及生态健康风险评价[J]. 土壤通报, 2018, 49(1):167-175. |
| [19] | 孙变变, 赵银鑫, 常丹, 等. 银川市城市绿地土壤重金属分布特征及其生态风险评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(6):262-268,277. |
| [20] | 张俊辉, 林青, 姜珊, 等. 宝鸡市植被叶子重金属分布规律及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(2):978-986. |
| [21] | 黄钟霆, 易盛炜, 陈贝贝, 等. 典型锰矿区周边农田土壤-农作物重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(2):975-984. |
| [22] | 沈良辰, 胡文勇, 张丽娟, 等. 典型废弃锰矿厂渣库土壤重金属污染特征与评价[J]. 有色金属工程, 2022, 12(8):187-197. |
| [23] | 姚玉玲, 代力, 舒荣波, 等. 赣南某未开发离子型稀土矿区土壤环境质量评价[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(4):152-156,161. |
| [24] | 许璐, 周春海, 刘梅, 等. 石灰海泡石钝化后两种轮作模式对重度镉污染农田土壤的利用及修复[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(6):3299-3307. |
| [25] | 丁永福, 班玲. 广西土壤环境背景值应用开发初探[J]. 中国环境监测, 1993, 9(3):41-42. |
| [26] |
ODEWANDE A A, ABIMBOLA A F. Contamination indices and heavy metal concentrations in urban soil of Ibadan metropolis,southwestern Nigeria[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2008, 30(3):243-254.
doi: 10.1007/s10653-007-9112-2 |
| [27] | 顾永瑞, 张彤, 白红玉. 内蒙土壤环境背景值属性分类[J]. 内蒙古环境保护, 1995, 7(1):6-9. |
| [28] | 唐哲, 王琪, 申亚兰, 等. 湖库型铁山水库饮用水水源地水资源评价[J]. 人民长江, 2017, 48(S2):104-107,192. |
| [29] | HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control:A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8):975-1001. |
| [30] |
FABER J H, VAN WENSEM J. Elaborations on the use of the ecosystem services concept for application in ecological risk assessment for soils[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 415:3-8.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.05.059 |
| [31] | 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等. 潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(2):112-115. |
| [32] | 孙锐, 舒帆, 郝伟, 等. 典型Pb/Zn矿区土壤重金属污染特征与Pb同位素源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(4):1146-1153. |
| [33] | MULLER G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River[J]. GeoJournal, 1969, 2:108-118. |
| [34] | 赖书雅, 董秋瑶, 宋超, 等. 南阳盆地东部山区土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(11):5500-5509. |
| [35] | 王玉军, 刘存, 周东美, 等. 一种农田土壤重金属影响评价的新方法:土壤和农产品综合质量指数法[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(7):1225-1232. |
| [36] | 廖启林, 任静华, 姜丽, 等. 江苏典型地区河流沉积物重金属元素分布特征及其污染来源[J]. 地质学刊, 2018, 42(4):651-661. |
| [37] |
易文利, 董奇, 杨飞, 等. 宝鸡市不同功能区土壤重金属污染特征、来源及风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(11):2142-2149.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2018.11.022 |
| [38] |
SUZUKI K, YABUKI T, ONO Y. Roadside Rhododendron pulchrum leaves as bioindicators of heavy metal pollution in traffic areas of Okayama, Japan[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2009, 149(1/2/3/4): 133-141.
doi: 10.1007/s10661-008-0188-7 |
| [39] |
CHEN X, XIA X H, ZHAO Y, et al. Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing,China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 181(1/2/3):640-646.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.060 |
| [40] | 崔崴, 张菲, 珊丹, 等. 草原矿区土壤重金属累积效应与潜在风险评价[J]. 能源与环境, 2023(1):2-5,22. |
| [41] | 杨晓杰, 崔向新, 珊丹, 等. 荒漠草原金矿周边土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 北方园艺, 2022(19):78-86. |
| [42] | 李贺, 姜霞, 王书航, 等. 寒旱区草原湖泊沉积物重金属地球化学基线构建:以达里诺尔湖为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(12):5803-5813. |
| [43] |
周会程, 周恒, 肖海龙, 等. 三江源区不同退化梯度高寒草原土壤重金属含量及其与养分和酶活性的变化特征[J]. 草地学报, 2020, 28(3):784-792.
doi: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2020.03.024 |
| [44] |
VIARD B, PIHAN F, PROMEYRAT S, et al. Integrated assessment of heavy metal (Pb,Zn,Cd) highway pollution: Bioaccumulation in soil, Graminaceae and land snails[J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 55(10):1349-1359.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.01.003 |
| [45] |
ZHAO Y, ZHAO C. Concentration and distribution analysis of heavy metals in total suspended particulates along Shanghai-Nanjing expressway[J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2012, 13:1405-1411.
doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2012.01.133 |
| [46] |
ZHANG H, ZHANG Y L, WANG Z F, et al. Traffic-related metal(loid) status and uptake by dominant plants growing naturally in roadside soils in the Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 573: 915-923.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.128 |
| [47] | SZYCZEWSKI P, SIEPAK J, NIEDZIELSKI P, et al. Research on heavy metals in Poland[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2009, 18(5):755-768. |
| [48] | 张前进, 刘华, 陈永生, 等. 合肥老城区土壤重金属分布格局及树木富集重金属潜力[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(12):4140-4147. |
| [49] | JEONG H, CHOI J Y, LEE J, et al. Heavy metal pollution by road-deposited sediments and its contribution to total suspended solids in rainfall runoff from intensive industrial areas[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020,265(Pt A):115028. |
| [50] | 李仰征, 马建华. 高速公路旁土壤重金属污染及不同林带防护效应比较[J]. 水土保持学报, 2011, 25(1):105-109. |
| [51] | 秦兵, 陈代庚, 任利民, 等. 成都盆地浅层土壤中砷来源的多元统计分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2006, 13(3):23-28. |
| [52] | 黄益宗, 石孟春, 招礼军. 水稻根系吸收砷的动力学特征及硅的缓解机制[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2010, 5(3):433-438. |
| [1] | ZHANG Xiaoyan, ZHANG Jian, CHEN Xiang, Chao Lemeng, XI Yaqin, JIN Jing, FENG Caixia, Hunusitu, ZHANG Tianyu, WANG Yaru. Effects of Different Remediation Measures on the Restoration of Degraded Grassland [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2024, 45(2): 45-49. |
| [2] | ZHANG Qingqing, LIU Xuejiao, ZHANG Bo, ZHANG Peng, HE Jia, HAN Haibo, Chao Lemeng, ZHENG Shuhua. CiteSpace Based Analysis of Research Hotspots and Evolution Trend of Grassland Ecological Protection Compensation in China [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2024, 45(2): 50-57. |
| [3] | Yeruhan, Xijiritana, CHANG Hong, LIU Sibo, ZHANG Pujin, LIU Xinchao, YIN Guomei, WEN Chao, SHAN Yumei, LIU Guixiang. Research Progress on the Response of Soil and Vegetation to Extreme Drought in Grassland Ecosystems [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2024, 45(2): 58-72. |
| [4] | WANG Dinghui, WANG Xin, WANG Yunying, PEI Weiwei, DU Yangong. Comparative Study on Soil Organic Carbon Contents and the Influencing Factors of Five Types of Alpine Deserts in Qinghai Province [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2023, 44(4): 70-75. |
| [5] | ZHANG Limei,GUO Jun,YE Le,LIU Yujia,LIU Xiaoqi,GUO Lingzhi. Determination and Evaluation on Visceral Selenium Content in Hulun Buir Grassland Short-tailed Sheep in Inner Mongolia [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2023, 44(4): 101-108. |
| [6] | DU Yangong,ZHANG Xiangyun,WANG Yunying,FAN Bo. Effects of Alfalfa Cultivation on Physiochemical Properties of Farmland Soil [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2023, 44(2): 98-102. |
| [7] | WANG Jing-xuan, DING Ji. Research on the Problems and Strategies of the High-quality Development of Grassland Animal Husbandry in Inner Mongolia under the Background of Rural Revitalization [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2023, 44(1): 1-6. |
| [8] | MA Fu-ming, ZHANG Xiang-yun, WANG Yun-ying, DU Yan-gong. Effects of Alfalfa on Soil Available Nitrogen Content in Different Land Uses and Analysis of the Driven Factors [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2023, 44(1): 91-96. |
| [9] | CAO Yan, LI Bao-he, XU Zhen-peng, LIU Kai, LI Xiu-ping, LI Yan-fang, ZHAO Yi-wen, DI Cai-xia. Nutrient Contents Evaluation of Soil and Vegetation in Typical Grasslands in Inner Mongolia at Different Periods [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2022, 43(6): 77-87. |
| [10] | CHANG Hong, WANG Yang, LIU Ya-hong, YAN Xiao-hong, SHI Lei, SUN Hai-lian. Evaluation of Coordinated Development of Relationship Between Human and Lands in Pastoral Areas of Inner Mongolia [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2022, 43(3): 88-95. |
| [11] | LI Chang-qing, WANG Li, Jinhai, XUE Shu-yuan, GUO Tian-long, WANG Chao, ZHANG Hai-ying, TIAN Feng. Study on Copper Deficiency in Mongolian Sheep Lambs in Gobi Grassland in Spring [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2022, 43(2): 46-50. |
| [12] | AN Chen, DING Hai-rong, TAN Hai-yun, SHI Kai, YANG Zhi-qing, JIN Chong-fu, HOU Fu-yin, CHEN Chang-kuan. Effects of Overturning Three Varieties of Green Manures on Soil Quality after Biogas Slurry Irrigation [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2022, 43(2): 105-110. |
| [13] |
HOU Wei-feng, Qigeqi, DONG Wuyunga, WEN Li, LI Feng-jiao, ZHAO Li-xing, BI Sheng-nan, JIANG Xin-yu.
Effects of Different Nutrient Management Models on Population Characteristics of |
| [14] | YIN Guo-mei, JI Chao, LIU Si-bo, YANG Feng-lan, ZHANG Ying, MU Zong-jie, ZHAO Yi-wen, MA Chun-mei, LU Peng-fei, ZHANG Jin, LIU Yong-lu. Responses of Vegetation Community Characteristics and Species Diversity to Different Ecological Restoration Measures in Mu Us Desertified Grassland [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2022, 43(1): 68-75. |
| [15] | Siqinmenghe, WANG Yu-hui, Xiumei, CHI Lin. Issues and Solutions of Integrated Management of Agriculture and Animal Husbandry under the Grassland Ecological Protection Subsidy and Incentive Policy [J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science, 2022, 43(1): 76-81. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||