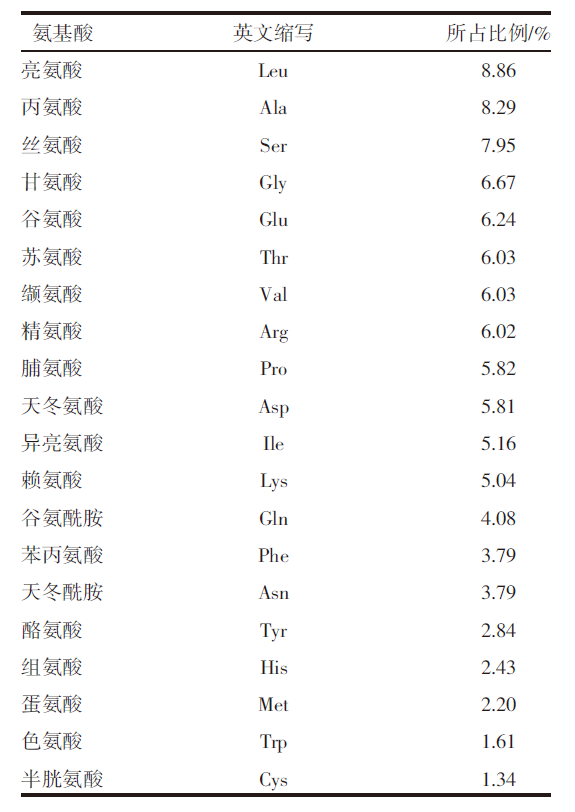
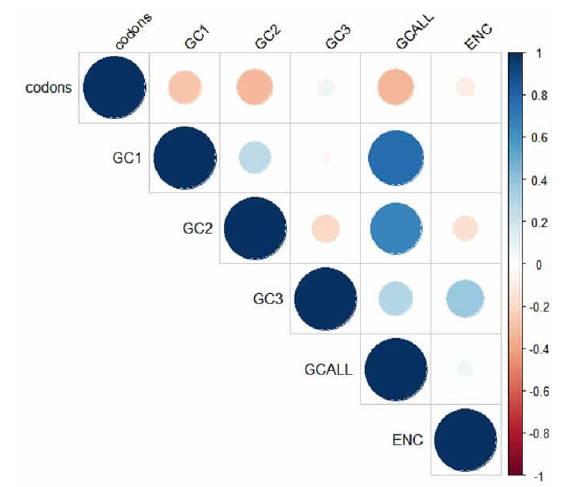
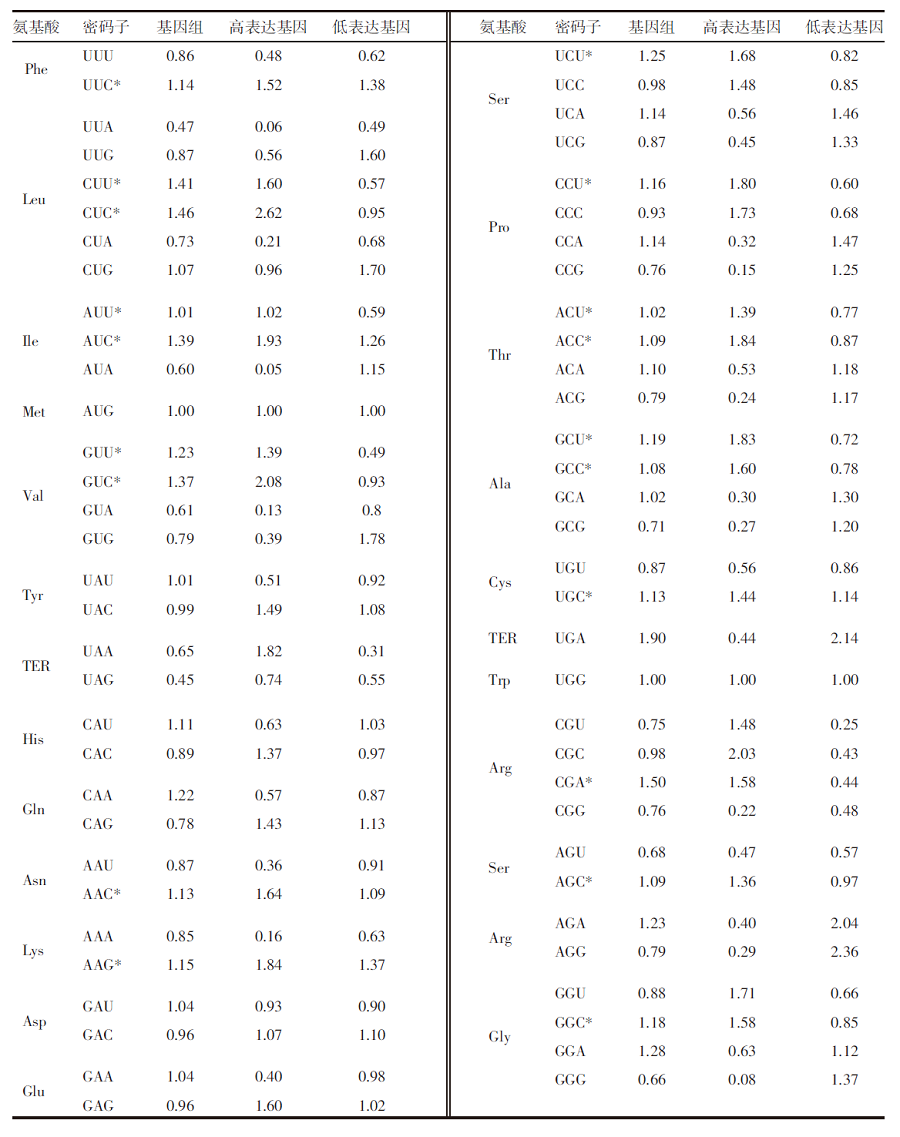
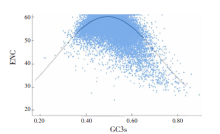
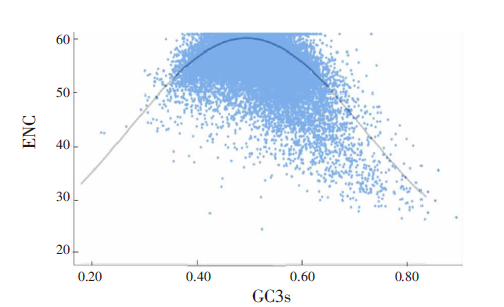
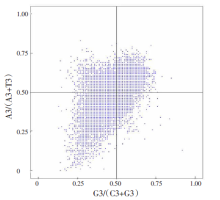
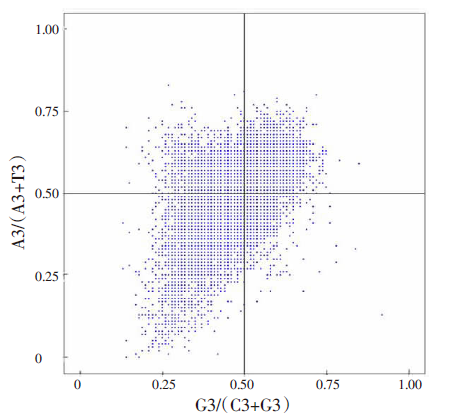
| [1] |
王宇鹏, 杨帆, 赵华. 致病性尖孢镰刀拮抗菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 中国酿造, 2018, 37(9):94-99.
|
| [2] |
MA L J, VAN DER DOES H C, BORKOVICH K A, et al. Comparative genomics reveals mobile pathogenicity chromosomes in Fusarium[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7287):367-373.
doi: 10.1038/nature08850
|
| [3] |
DEAN R, VAN KAN A L, PRETORIUS Z A, et al. The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology:Top 10 fungal pathogens[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2012, 13(4):414-430.
doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00783.x
pmid: 22471698
|
| [4] |
MICHIELSE C B, REP M. Pathogen profile update:Fusarium oxysporum[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2009, 10(3):311-324.
doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00538.x
|
| [5] |
THATCHER L F, GAO L L, SINGH K B. Jasmonate signalling and defence responses in the model legume Medicago truncatula—A focus on responses to Fusarium wilt disease[J]. Plants, 2016, 5(1):11.
doi: 10.3390/plants5010011
|
| [6] |
PAULET D, DAVID A, RIVALS E. Ribo-seq enlightens codon usage bias[J]. DNA Research, 2017, 24(3):303-310.
doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsw062
pmid: 28168289
|
| [7] |
李易聪, 蒲飞洋, 王慧慧, 等. 同义密码子使用偏嗜性对mRNA半衰期及翻译调控的影响[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(3):882-892.
|
| [8] |
蒋玮, 吕贝贝, 何建华, 等. 草菇密码子偏好性分析[J]. 生物工程学报, 2014, 30(9):1424-1435.
|
| [9] |
黄晓星. 银耳密码子偏好性分析及启动子克隆[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2011.
|
| [10] |
陈奕钊, 李晓宇, 吴家来, 等. 金针菇高表达基因的密码子偏好性及特征分析[J]. 菌物学报, 2022, 41(6):939-951.
|
| [11] |
韩利红, 田雪莲, 李雪梅, 等. 蛹虫草基因组密码子使用偏性分析[J]. 食用菌学报, 2021, 28(2):26-35.
|
| [12] |
韩利红, 贾欣楠, 陈仁欢, 等. 药用真菌茯苓基因组密码子使用偏性分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(1):83-90.
doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0827
|
| [13] |
杨云彭, 马晓焉, 霍毅欣. 密码子优化策略在异源蛋白表达中的应用[J]. 生物工程学报, 2019, 35(12):2227-2237.
|
| [14] |
霍莹莹, 李甜甜, 杨静, 等. 尖孢镰刀菌相关致病因子与挥发油抑制尖孢镰刀菌的潜力研究进展[J]. 农药, 2022, 61(2):79-86.
|
| [15] |
陈星彤, 杜春梅. 植物激素调控植物与尖孢镰刀菌的互作研究进展[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2021, 27(3):816-822.
|
| [16] |
刘泽. 不同唐菖蒲品种根系分泌物对尖孢镰刀菌影响的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2014.
|
| [17] |
杜琳, 范淑英, 刘文睿, 等. 瓜类寄主与尖孢镰刀菌互作的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2012, 39(9):1767-1772.
|
| [18] |
HE B, DONG H, JIANG C, et al. Analysis of codon usage patterns in Ginkgo biloba reveals codon usage tendency from A/U-ending to G/C-ending[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:35927.
doi: 10.1038/srep35927
|
| [19] |
LIU K, WANG R, GUO X X, et al. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of complete chloroplast genomes in eragrostideae(Chloridoideae,Poaceae)[J]. Plants, 2021, 10(1):109.
doi: 10.3390/plants10010109
|
| [20] |
WRIGHT F. The‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene[J]. Gene, 1990, 87(1):23-29.
doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90491-9
|
| [21] |
SUEOKA N. Near homogeneity of PR2-bias fingerprints in the human genome and their implications in phylogenetic analyses[J]. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 2001, 53(4/5):469-476.
doi: 10.1007/s002390010237
|
| [22] |
SONG H, LIU J, SONG Q Y, et al. Comprehensive analysis of codon usage bias in seven Epichloe species and their peramine-coding genes[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2017, 8:1419.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01419
|
| [23] |
DURET L, MOUCHIROUD D. Expression pattern and,surprisingly,gene length shape codon usage in Caenorhabditis,Drosophila,and Arabidopsis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1999, 96(8):4482-4487.
|
| [24] |
张瑞芝, 陈章宝, 陈德敏, 等. 球孢白僵菌基因组密码子使用模式及其影响因素分析[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 40(5):66-74.
|
| [25] |
周显臻, 曹支敏, 于丹. 落叶松-杨栅锈菌基因组密码子使用偏好分析[J]. 菌物学报, 2020, 39(2):289-297.
|