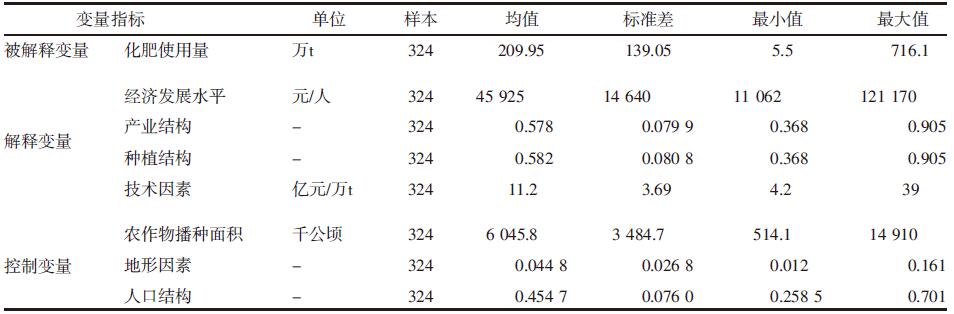
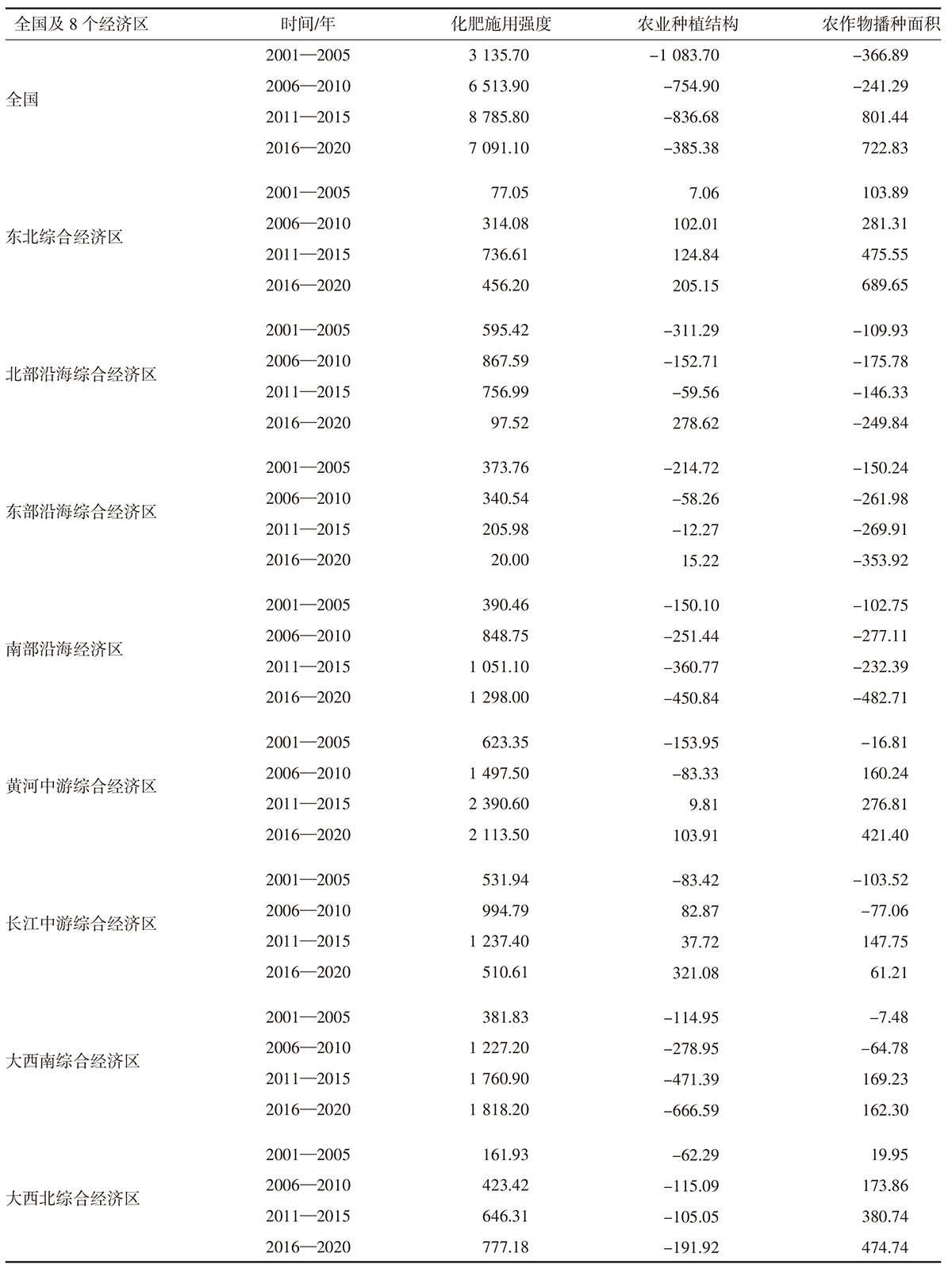
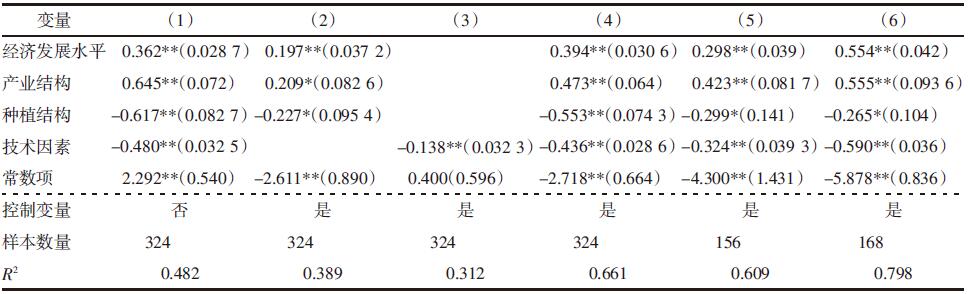
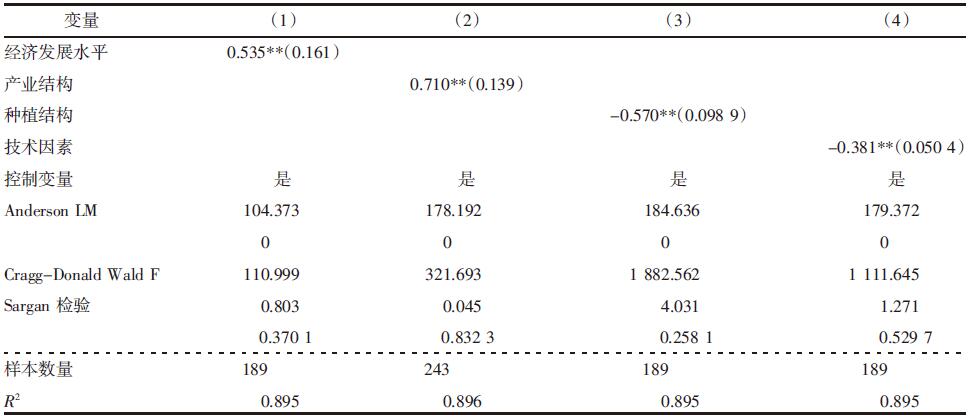
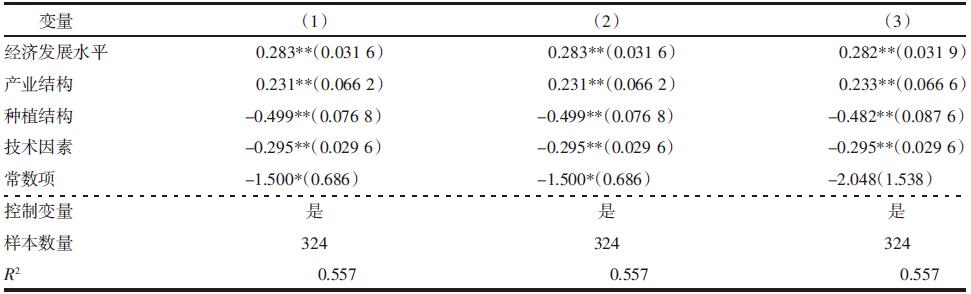
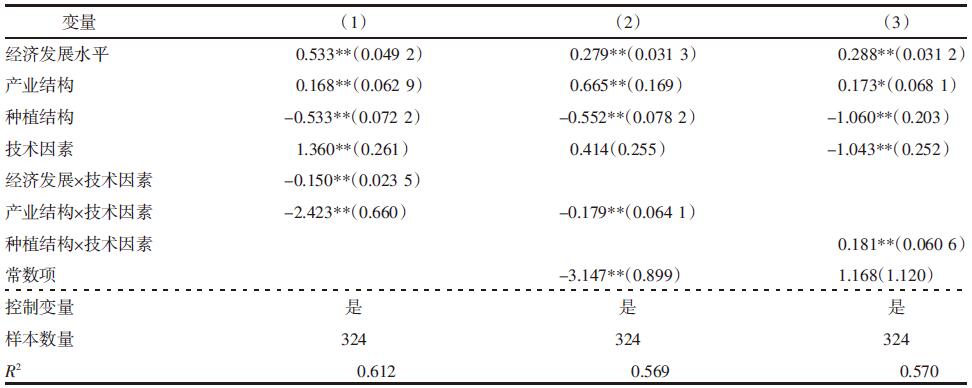
| [1] |
林源, 马骥. 农户粮食生产中化肥施用的经济水平测算——以华北平原小麦种植户为例[J]. 农业技术经济, 2013(1):25-31.
|
| [2] |
仇焕广, 栾昊, 李瑾, 等. 风险规避对农户化肥过量施用行为的影响[J]. 中国农村经济, 2014(3):85-96.
|
| [3] |
郑微微, 何在中, 徐雪高. 江苏主要粮食生产中化肥过量施用评价及影响因素研究[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2017, 38(4):666-672.
|
| [4] |
刘文倩, 费喜敏, 王成军. 化肥经济过量施用行为的影响因素研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2018, 34(8):726-732.
|
| [5] |
史常亮, 郭焱, 朱俊峰. 中国粮食生产中化肥过量施用评价及影响因素研究[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2016, 37(4):671-679.
|
| [6] |
何浩然, 张林秀, 李强. 农民施肥行为及农业面源污染研究[J]. 农业技术经济, 2006(6):2-10.
|
| [7] |
麻坤, 刁钢. 化肥对中国粮食产量变化贡献率的研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2018, 24(4):1113-1120.
|
| [8] |
张福锁, 张卫峰, 陈新平. 对我国肥料利用率的分析[C]. //第二届全国测土配方施肥技术研讨会论文集. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2007:10-12.
|
| [9] |
新华网. 农业农村部曾衍德:我国化肥使用量首次减少[EB/OL].(2017-03-26). http://www.xinhuanet.com//food/2017-03/26/c_1120696660.htm.
|
| [10] |
JORGENSON A K, KUYKENDALL K A. Globalization,foreign investment dependence and agriculture production:Pesticide and fertilizer use in less-developed countries,1990-2000[J]. Social Forces, 2008, 87(1):529-560.
doi: 10.1353/sof.0.0064
|
| [11] |
ZHU Z L, CHEN D L. Nitrogen fertilizer use in China—Contributions to food production,impacts on the environment and best management strategies[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2002, 63(2/3):117-127.
doi: 10.1023/A:1021107026067
|
| [12] |
石文香, 陈盛伟. 中国化肥面源污染排放驱动因素分解与EKC检验[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(5):1-7.
|
| [13] |
栾江, 仇焕广, 井月, 等. 我国化肥使用量持续增长的原因分解及趋势预测[J]. 自然资源学报, 2013, 28(11):1869-1878.
doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2013.11.004
|
| [14] |
王珊珊, 张广胜, 李秋丹, 等. 我国粮食主产区化肥使用量增长的驱动因素分解[J]. 农业现代化研究, 2017, 38(4):658-665.
|
| [15] |
龚琦, 王雅鹏. 我国农用化肥施用的影响因素——基于省际面板数据的实证分析[J]. 生态经济, 2011, 21(2):33-38.
|
| [16] |
赵明正, 赵翠萍, 李天祥, 等. “零增长”行动背景下中国化肥使用量下降的驱动因素研究——基于LMDI分解和面板回归分析[J]. 农业技术经济, 2019(12):118-130.
|
| [17] |
韩峰, 庄宗武, 阳立高. 中国制造业出口价值攀升的空间动力来源——基于要素供给和市场需求的综合视角[J]. 中国工业经济, 2021(3):61-79.
|
| [18] |
张卫峰, 季玥秀, 马骥, 等. 中国化肥消费需求影响因素及走势分析 Ⅱ 种植结构[J]. 资源科学, 2008, 30(1):31-36.
|
| [19] |
付浩然, 李婷玉, 曹寒冰, 等. 我国化肥减量增效的驱动因素探究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(3):561-580.
|
| [20] |
杨莉莎, 朱俊鹏, 贾智杰. 中国碳减排实现的影响因素和当前挑战——基于技术进步的视角[J]. 经济研究, 2019, 54(11):118-132.
|
| [21] |
胡婉玲, 张金鑫, 王红玲. 中国农业碳排放特征及影响因素研究[J]. 统计与决策, 2020, 36(5):56-62.
|
| [22] |
田云, 尹忞昊. 技术进步促进了农业能源碳减排吗?——基于回弹效应与空间溢出效应的检验[J]. 改革, 2021(12):45-58.
|