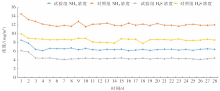
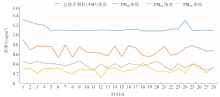
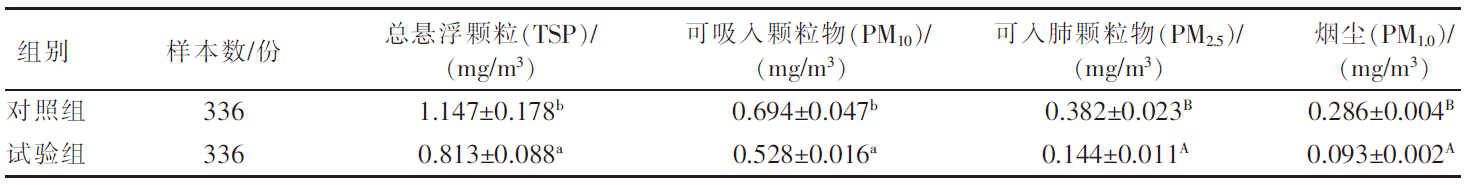
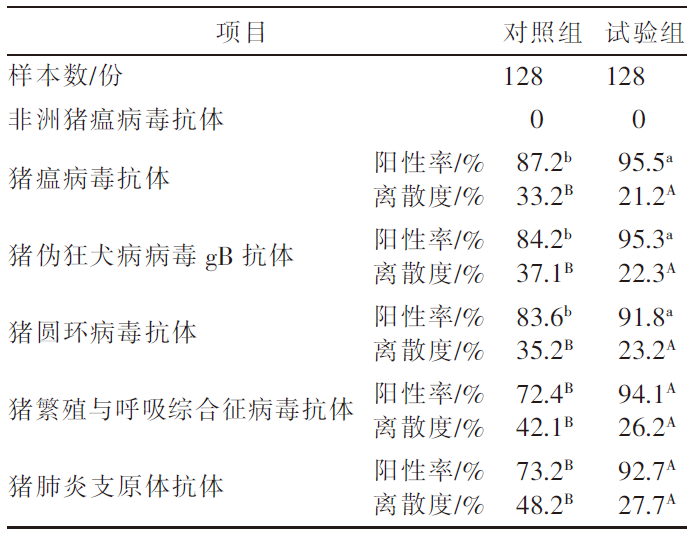
| [1] |
GRINSHPUN S A, CLARK J M. Measurement and characterization of bioaerosols[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2005, 36(5/6):553-555.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2005.03.001
|
| [2] |
SCHIFFMAN S S, AUVERMANN B W, BOTTCHER R W. Health effects of aerial emissions from animal production waste management systems[C]//North Carolina State University. Proceedings of international symposium:Addressing animal production and environmental issues. Raleigh,North Carolina: North Carolina State University, 2011.
|
| [3] |
赵茹仪. 大气生物气溶胶种类及来源概述[J]. 科技经济导刊, 2019, 27(9):127.
|
| [4] |
聂绪明, 杨长明, 李宏伟. 非洲猪瘟传播途径探讨[J]. 当代畜牧, 2019(5):73-74.
|
| [5] |
付典林, 杨卫平, 刘仁鑫, 等. 集约化猪场垂直通风模式分析[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2018(3):137-139.
|
| [6] |
DOUWES J, THORNE P, PEARCE N, et al. Bioaerosol health effects and exposure assessment:Progress and prospects[J]. The Annals of Occupational Hygiene, 2003, 47(3):187-200.
|
| [7] |
迂斌, 朱中平, 张世新, 等. 非洲猪瘟背景下生物安全之空栏清洗消毒与提高猪群非特异性免疫力[J]. 北方牧业, 2019(5):22-23.
|
| [8] |
DUNGAN R S. Fate and transport of bioaerosols associated with livestock operations and manures[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2010, 88(11):3693-3706.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2010-3094
|
| [9] |
CAMBRA-LÓPEZ M, AARNINK A J, ZHAO Y, et al. Airborne particulate matter from livestock production systems:A review of an air pollution problem[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 158(1):1-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.07.011
|
| [10] |
白红杰. 实用养猪大全[M]. 3版. 郑州: 河南科学技术出版社, 2018:174.
|
| [11] |
宋卫东. 空气过滤系统的分类与使用维护[J]. 农业开发与装备, 2018(9):47,49.
|
| [12] |
白红杰, 范磊, 王丽英, 等. 过滤式垂直立体通风系统对改善舍内空气质量和提高生产指标的实践与研究[J]. 上海农业学报, 2021, 37(1):66-70.
|
| [13] |
BLANES V, PEDERSEN S. Ventilation flow in pig houses measured and calculated by carbon dioxide[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2005, 92(4):483-493.
doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2005.09.002
|
| [14] |
陈辉, 仝亚广, 张岩, 等. 雏鸡舍留温新风换气系统设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(11):320-327.
|
| [15] |
ANDERSEN A A. New sampler for the collection,sizing,and enumeration of viable airborne particles[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1958, 76(5):471-484.
doi: 10.1128/jb.76.5.471-484.1958
pmid: 13598704
|
| [16] |
张石锐. 畜禽生产环境中主要有害气体监测方法研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2014.
|
| [17] |
LIU S L, NI J Q, RADCLIFFE J S, et al. Mitigation of ammonia emissions from pig production using reduced dietary crude protein with amino acid supplementation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 233:200-208.
doi: S0960-8524(17)30205-5
pmid: 28279913
|
| [18] |
VRANKEN E, CLAES S, HENDRIKS J, et al. Intermittent measurements to determine ammonia emissions from livestock buildings[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2004, 88(3):351-358.
doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2004.03.011
|
| [19] |
朱丽媛, 卢庆萍, 张宏福, 等. 猪舍中氨气的产生、危害和减排措施[J]. 动物营养学报, 2015, 27(8):2328-2334.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2015.08.003
|
| [20] |
宁芳芳, 施正香, 荆凯凯, 等. 光触媒空气净化器对猪舍空气质量和猪生产性能的影响[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2015, 36(7):47-50.
|
| [21] |
ZHANG G, ZHANG Y P, KIM Y, et al. Field study on the impact of indoor air quality on broiler production[J]. Indoor and Built Environment, 2011, 20(4):449-455.
doi: 10.1177/1420326X11409468
|
| [22] |
HALLOY D J, KIRSCHVINK N A, VINCKE G L, et al. Whole body barometric plethysmography:A screening method to investigate airway reactivity and acute lung injuries in freely moving pigs[J]. The Veterinary Journal, 2004, 168(3):276-284.
doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2003.10.015
|
| [23] |
NEL A. Air pollution-related illness:Effects of particles[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5723):804-806.
doi: 10.1126/science.1108752
|
| [24] |
穆钰, 王美芝, 刘继军, 等. 不同通风方式下猪舍病毒颗粒分布的数值研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(S1):53-58,421.
|
| [25] |
袁文, 柴同杰, 苗增民, 等. 猪舍环境气载需氧菌含量的季节性变化及其健康风险评估[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(5):51-55.
|
| [26] |
DESPRÉS V R, HUFFMAN J A, BURROWS S M, et al. Primary biological aerosol particles in the atmosphere:A review[J]. Tellus B:Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 2012, 64(1):15598.
doi: 10.3402/tellusb.v64i0.15598
|
| [27] |
KALISTE E, LINNAINMAA M, MEKLIN T, et al. Airborne contaminants in conventional laboratory rabbit rooms[J]. Laboratory Animals, 2002, 36(1):43-50.
pmid: 11831738
|
| [28] |
CAMBRA-LÓPEZ M, AARNINK A J, ZHAO Y, et al. Airborne particulate matter from livestock production systems:A review of an air pollution problem[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2009, 158(1):1-17.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.07.011
|
| [29] |
李欣, 张红娜, 李欣贤, 等. 新型猪源H1N1流感病毒的分离鉴定及在实验条件下气源性传播的特点[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2013, 44(3):434-440.
|
| [30] |
黄藏宇, 李永明, 徐子伟, 等. 猪舍内不同季节微生物气溶胶含量及其空气动力学分析[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2016, 37(11):47-51.
|
| [31] |
KIM K Y, KO H J, KIM H T, et al. Association between pig activity and environmental factors in pig confinement buildings[J]. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 2008, 48(5):680.
doi: 10.1071/EA06110
|
| [32] |
LI M F, QI J H, ZHANG H D, et al. Concentration and size distribution of bioaerosols in an outdoor environment in the Qingdao coastal region[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(19):3812-3819.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.06.001
|
| [33] |
何剑. 规模猪场的免疫抗体监测探讨[J]. 中国畜禽种业, 2016, 12(8):84.
|
| [34] |
马琳, 郭建刚, 覃芳芸, 等. 2012—2013年广西部分规模猪场猪瘟群体免疫合格率与抗体离散度监测及免疫效果分析[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(20):68-69.
|