畜牧与饲料科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 1-8.doi: 10.12160/j.issn.1672-5190.2023.02.001
• 科技创新支撑畜牧业高质量发展专栏——畜禽粪污无害化处理及资源化利用专题 • 下一篇
黑龙江省畜牧业粪污的时空分布及集聚特征分析
董依博1,张武鑫1,林秀蔚2,韦春波1
- 1.黑龙江八一农垦大学动物科技学院/农业农村部东北平原农业绿色低碳重点实验室,黑龙江 大庆 163319
2.黑龙江省农业科学院畜牧兽医分院,黑龙江 齐齐哈尔 161000
Temporal and Spatial Distribution and Aggregation Characteristics of Livestock and Poultry Manures in Heilongjiang Province
DONG Yibo1,ZHANG Wuxin1,LIN Xiuwei2,WEI Chunbo1
- 1. College of Animal Science and Technology,Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University/Key Laboratory of Low-carbon Green Agriculture in Northeastern China,Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs,Daqing 163319,China
2. Branch of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary,Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Qiqihar 161000,China
摘要:
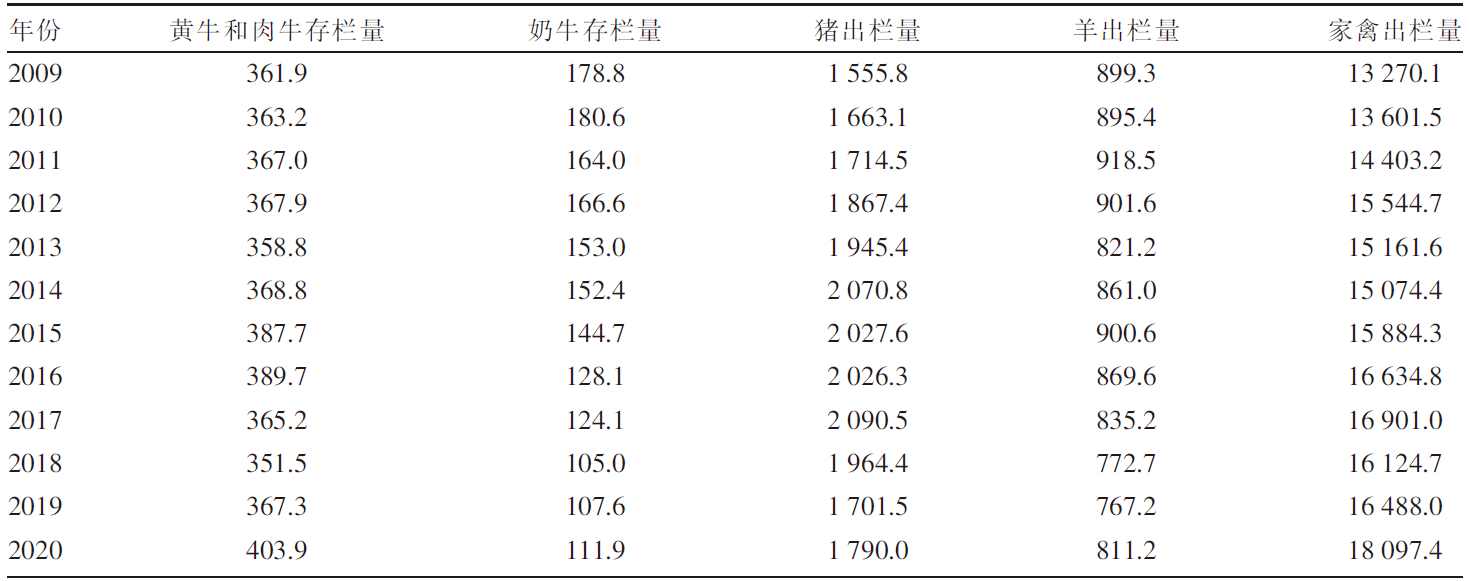
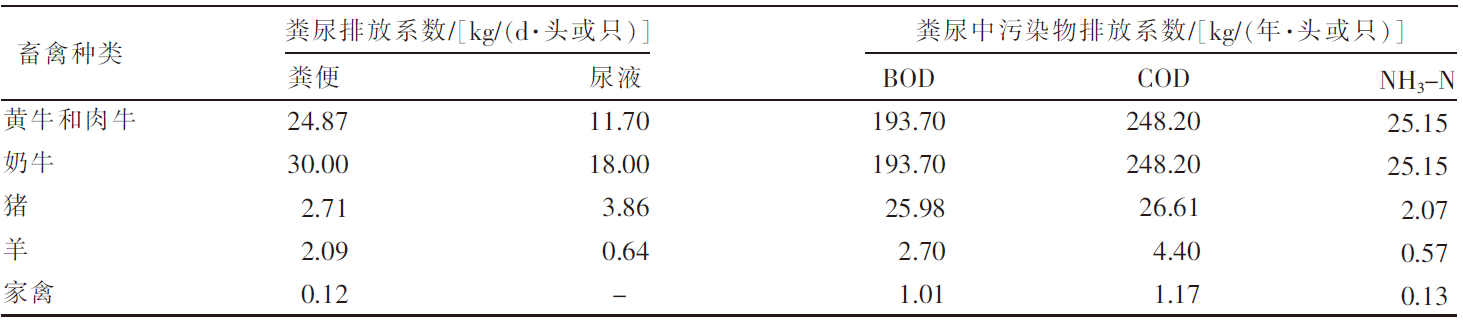
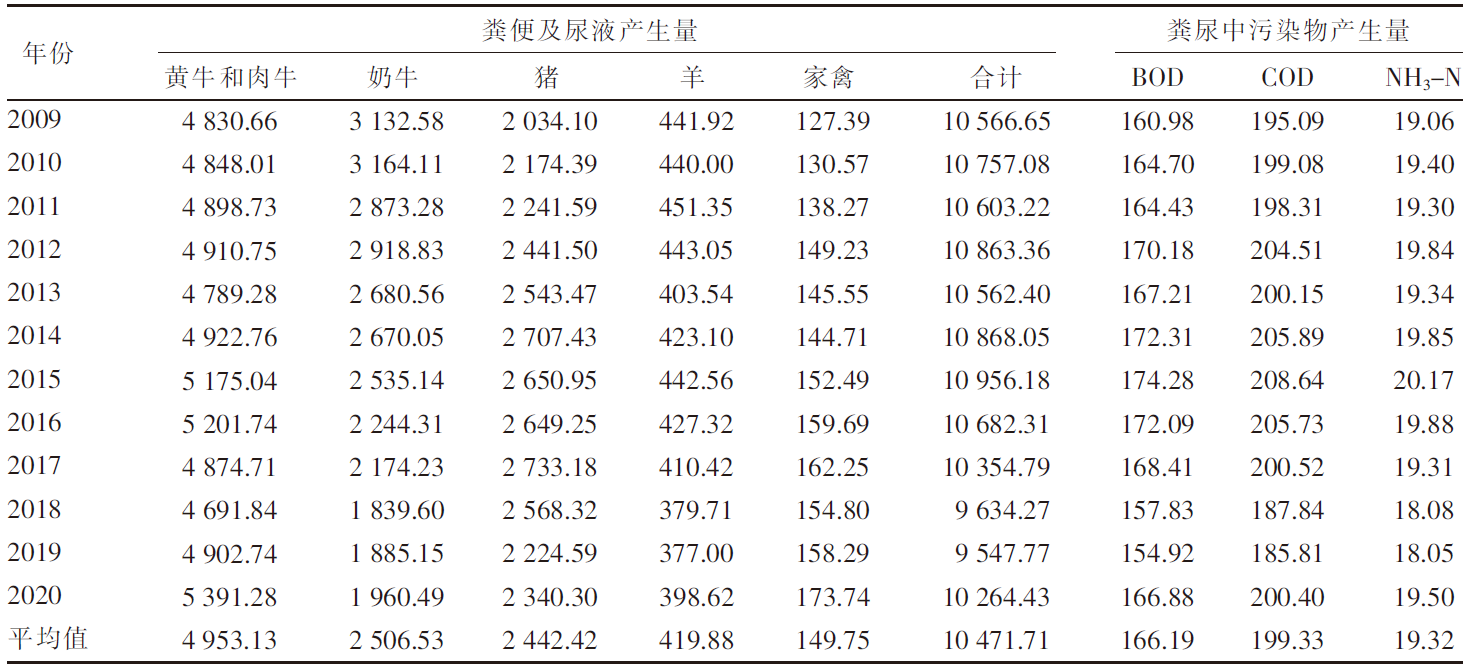
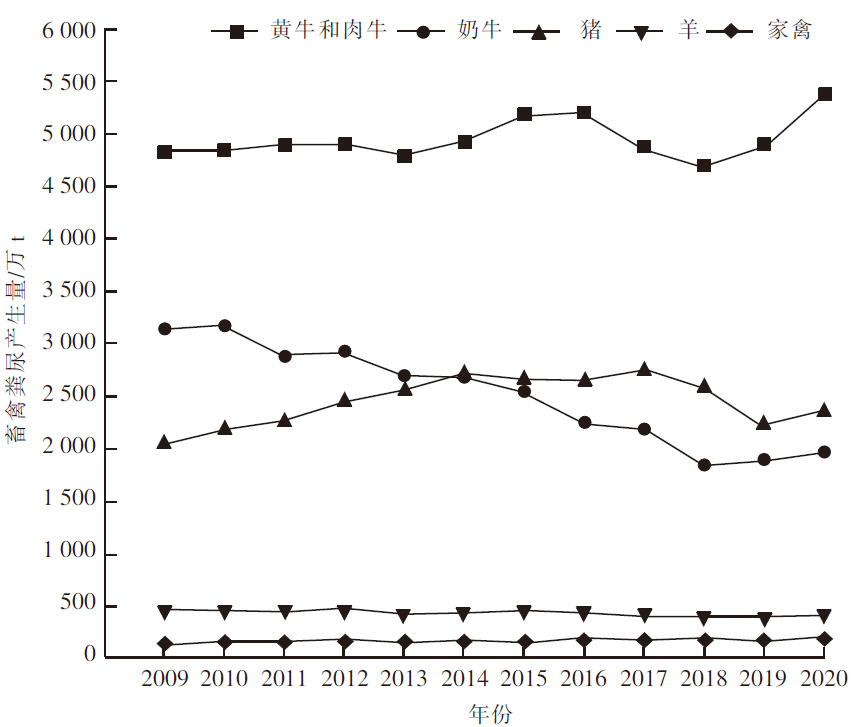
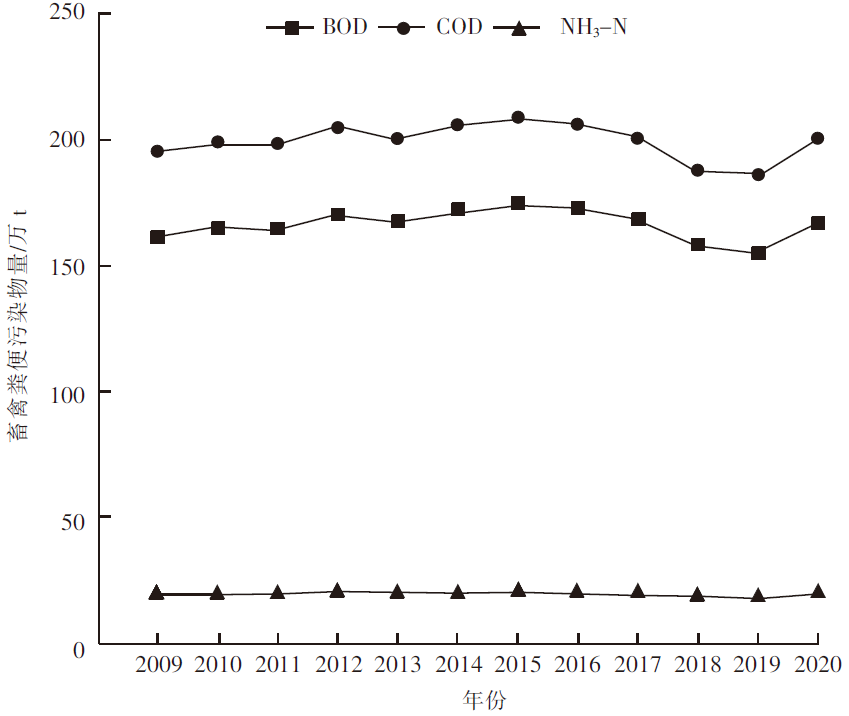
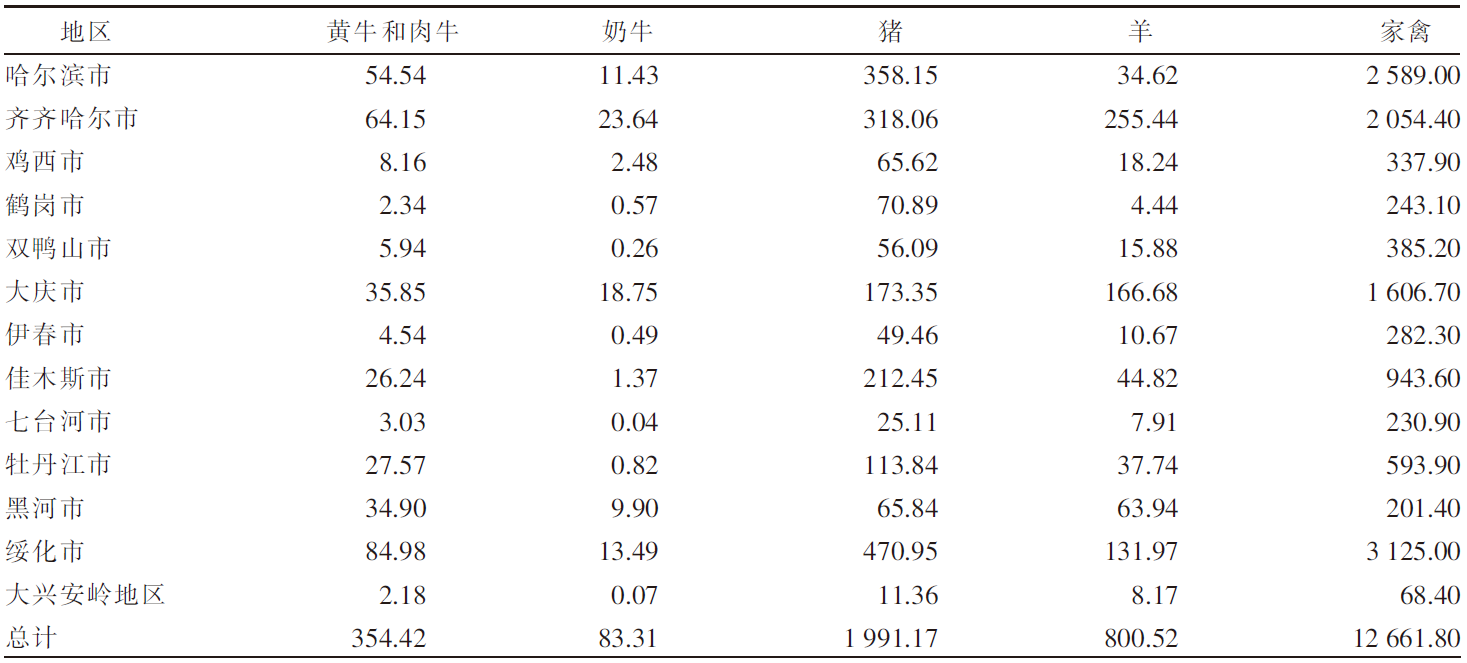
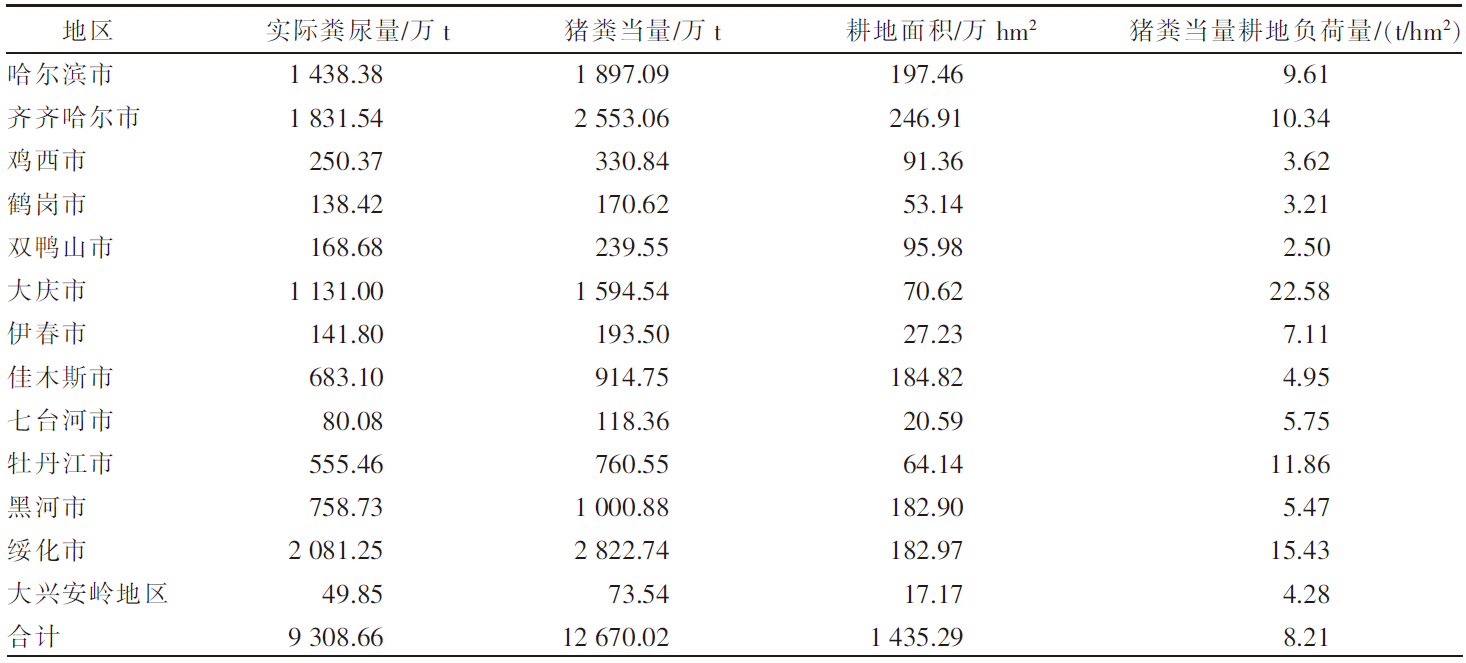
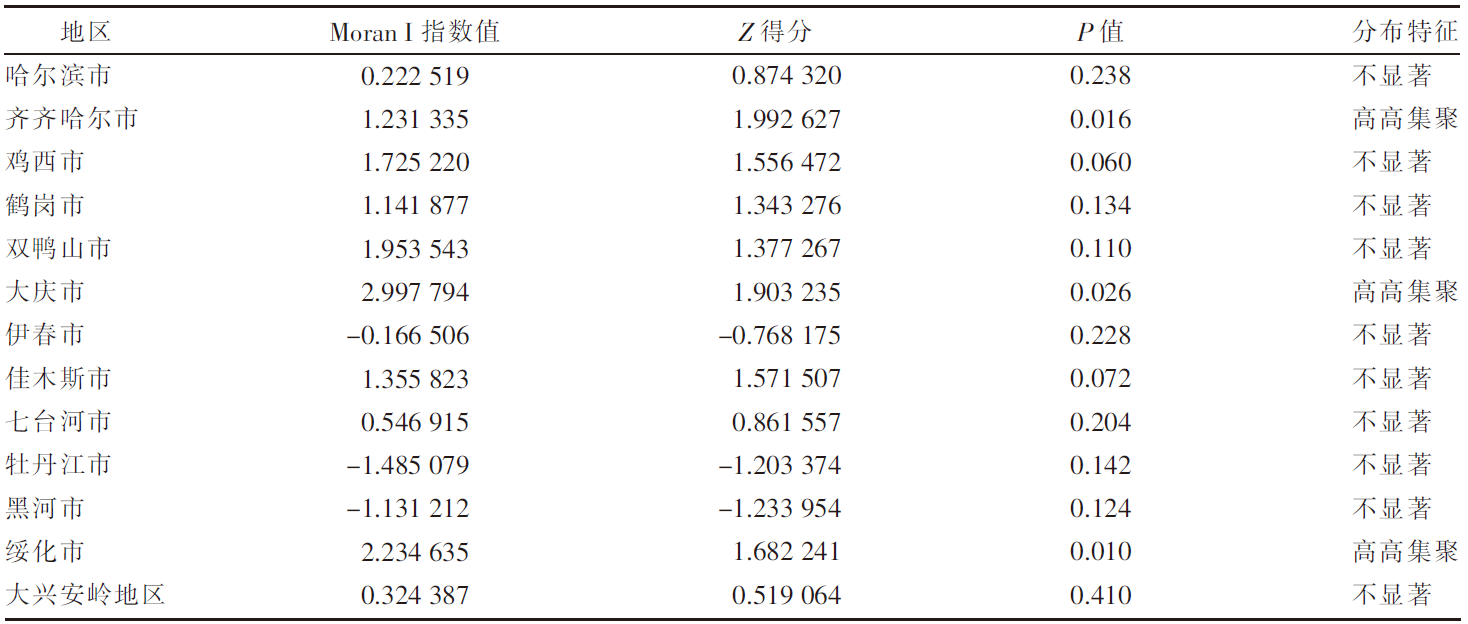
[目的]探究黑龙江省畜牧业粪污的时空分布及集聚特征。[方法]以《黑龙江省统计年鉴》为数据来源,利用畜禽粪污排放系数及计算模型,对黑龙江省2009—2020年畜牧业粪污[粪便、尿液以及粪污污染物生化需氧量(BOD)、化学需氧量(COD)、氨态氮(NH3-N)]排放量进行测算,运用Excel软件中的总体标准偏差函数和均值函数计算变异系数,评价该省畜禽粪尿总排放量的变化幅度。以2019年为例,对该省13个地区(绥化市、大庆市、哈尔滨市、齐齐哈尔市、牡丹江市、佳木斯市、双鸭山市、鸡西市、鹤岗市、黑河市、伊春市、七台河市、大兴安岭地区)的猪、羊、家禽、奶牛、黄牛和肉牛的饲养量进行调查分析;采用猪粪当量土地负荷量计算方法,对13个地区畜禽粪尿产生量及耕地负荷量进行分析;运用ArcGIS软件,采用空间自相关法对该省畜禽粪污量空间集聚特征进行分析。[结果]2009—2020年黑龙江省畜禽粪尿总排放量的变异系数为4.20%,表明畜禽粪尿总排放量有一定波动但年际变化幅度不大;粪尿总排放量由2009年的10 566.65万t下降到2020年的10 264.43万t,下降了2.86%;不同畜禽的粪尿排放量差异较大,黄牛和肉牛的粪尿排放量最多,家禽的最少;由于2020年畜牧业生产结构及规模的变动,畜禽粪污污染物BOD、COD、NH3-N排放量与2009年相比分别增加了3.67%、2.72%、2.31%。空间分布上,黑龙江省的畜牧业发展以绥化市、哈尔滨市和齐齐哈尔市为重点区域,主要养殖区域集中在该省西南地区,而东部、中部和北部地区的畜禽养殖量较少;该省13个地区的畜禽粪尿排泄量与畜禽粪尿猪粪当量排列顺序大致相同,绥化市、哈尔滨市、齐齐哈尔市是排名前三的地区;该省猪粪当量耕地负荷量平均值为8.21 t/hm2,大庆市猪粪当量耕地负荷量在13个地区中最高,为22.58 t/hm2,二者均低于我国土地最适宜负荷量;该省各地区的猪粪当量耕地负荷量呈现一定的集聚性,其中,大庆市、绥化市和齐齐哈尔市呈现出高高集聚的分布特征。[结论]黑龙江省畜禽生产和粪污排放的空间分布不平衡,但畜禽粪污的耕地负荷并未对环境产生不利影响。随着黑龙江省畜牧业的快速发展以及畜牧生产布局的动态变化,畜禽养殖污染问题也应引起更多关注。
中图分类号: