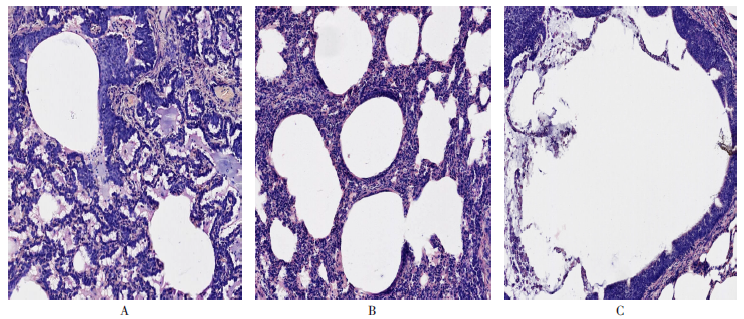
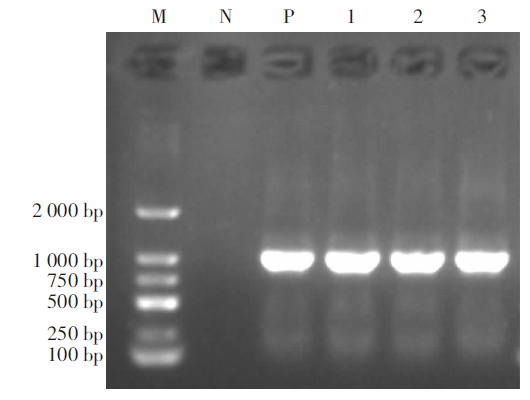
| [1] |
ZHAO Z X, WU G H, YAN X M, et al. Development of duplex PCR for differential detection of goatpox and sheeppox viruses[J]. BMC Veterinary Research, 2017, 13(1):278.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-017-1179-0
pmid: 28859636
|
| [2] |
YANG Y, QIN X D, ZHANG X L, et al. Development of real-time and lateral flow dipstick recombinase polymerase amplification assays for rapid detection of goatpox virus and sheeppox virus[J]. Virology Journal, 2017, 14(1):131.
doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0792-7
pmid: 28716095
|
| [3] |
STANFORD M M, MCFADDEN G, KARUPIAH G, et al. Immunopathogenesis of poxvirus infections:Forecasting the impending storm[J]. Immunology Cell Biology, 2007, 85(2):93-102.
doi: 10.1038/sj.icb.7100033
|
| [4] |
LIU S W, KATSAFANAS G C, LIU R K, et al. Poxvirus decapping enzymes enhance virulence by preventing the accumulation of dsRNA and the induction of innate antiviral responses[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2015, 17(3):320-331.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.02.002
|
| [5] |
ROY P, PURUSHOTHAMAN V, SREEKUMAR C, et al. Sheeppox disease outbreaks in Madras Red and Mechery breeds of indigenous sheep in Tamilnadu,India[J]. Research in Veterinary Science, 2008, 85(3):617-621.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2008.03.011
|
| [6] |
BHANUPRAKASH V, INDRANI B K, HOSAMANI M, et al. The current status of sheeppox disease[J]. Comparative Immunology Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 2006, 29(1):27-60.
doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2005.12.001
|
| [7] |
TULMAN E R, AFONSO C L, LU Z, et al. The genomes of sheeppox and goatpox viruses[J]. Journal of Virology, 2002, 76(12):6054-6061.
doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.12.6054-6061.2002
pmid: 12021338
|
| [8] |
HOSAMANI M, BHANUPRAKASH V, KALLESH D J, et al. Cell culture adapted sheeppox virus as a challenge virus for potency testing of sheeppox vaccine[J]. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 2008, 46(10):685-689.
pmid: 19024165
|
| [9] |
周建宏. 山羊痘综合防治[J]. 中国畜禽种业, 2015(11):130-131.
|
| [10] |
CHU Y F, YAN X M, GAO P C, et al. Molecular detection of a mixed infection of goatpox virus,Orf virus,and Mycoplasma capricolum subsp. capripneumoniae in goats[J]. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation, 2011, 23(4):786-789.
doi: 10.1177/1040638711407883
|
| [11] |
切环. 山羊痘病毒NM株的分离鉴定[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2013, 40(7):179-181.
|
| [12] |
程振涛, 岳筠, 徐春志, 等. 山羊痘病毒贵州株的分离与鉴定[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2008(3):59-61.
|
| [13] |
易成功, 朱相儒, 满成连, 等. 江苏地区2株山羊痘病毒的分离与鉴定[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2017, 39(4):322-324.
|
| [14] |
丁玉春, 林玲, 罗林, 等. 重庆地区山羊痘病毒分离鉴定及其动物模型构建[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2018, 38(3):39-42.
|
| [15] |
杨世发, 朱瑞良, 崔国林, 等. 规模化羊场山羊痘病毒的分离鉴定及其P32基因的分析[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2014(S1):333-335.
|
| [16] |
KITCHING R P, CARN V M. Sheeppox and goatpox[M]// OIE. OIE Manual of Standards for Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines. 3rd ed. Paris, France:OIE, 1996:119-127.
|
| [17] |
杨俊, 聂福平, 周庆, 等. 绵羊痘病毒和山羊痘病毒实时荧光重组酶聚合酶检测方法的建立[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2019, 49(5):544-550.
|
| [18] |
殷俊磊, 周碧君, 文明, 等. 山羊痘病毒P32基因重组真核表达载体的构建与鉴定[J]. 河南农业科学, 2010(9):132-134.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3268.2010.09.035
|
| [19] |
白艳艳, 张斌, 郝玉青, 等. 山羊痘病毒PCR检测方法的建立及应用[J]. 动物医学进展, 2017, 38(9):10-13.
|
| [20] |
BARMAN D, CHATTERJEE A, GUHA C, et al. Estimation of post vaccination antibody titre against goatpox and determination of protective antibody titre[J]. Small Ruminant Research, 2010, 93(2/3):76-78.
doi: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2010.04.028
|