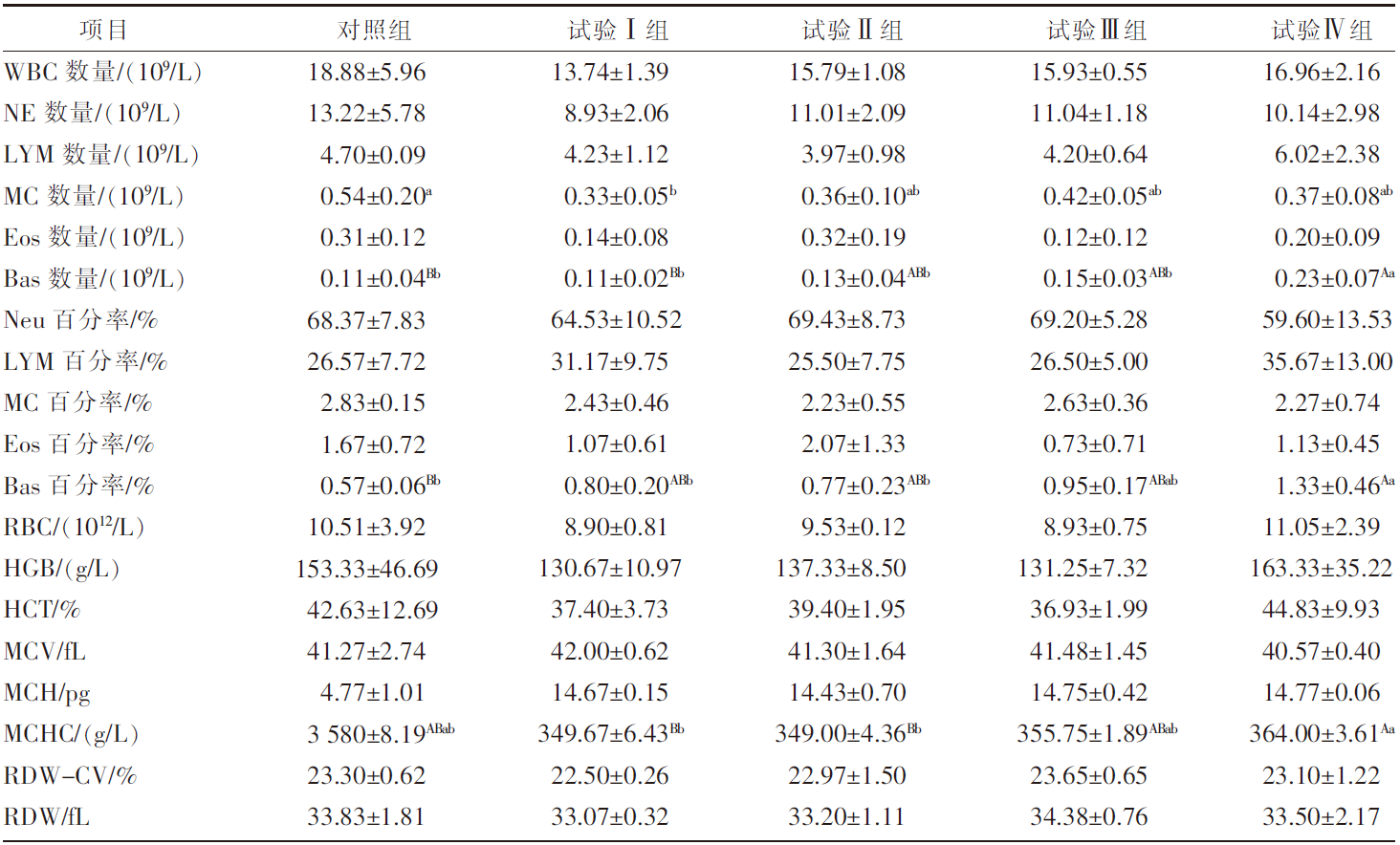
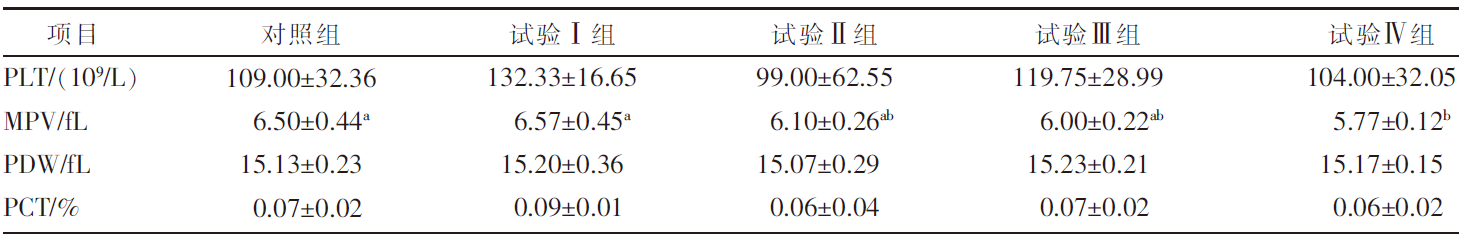
| [1] |
中华人民共和国农业农村部. 伊犁马:NY/T 2831—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.
|
| [2] |
杨光友. 动物寄生虫病学[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社, 2005.
|
| [3] |
SHEFERAW D, ALEMU M. Epidemiological study of gastrointestinal helminths of equines in Damot-Gale district,Wolaita zone,Ethiopia[J]. Journal of Parasitic Diseases, 2015, 39(2):315-320.
doi: 10.1007/s12639-013-0352-z
|
| [4] |
孔繁瑶. 家畜寄生虫学[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2010.
|
| [5] |
HINNEY B, WIRTHERLE N C, KYULE M, et al. Prevalence of helminths in horses in the state of Brandenburg,Germany[J]. Parasitology Research, 2011, 108(5):1083-1091.
doi: 10.1007/s00436-011-2362-z
|
| [6] |
王美玲. 新疆昭苏马消化道寄生虫动态调查及临床驱虫实验[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2015.
|
| [7] |
明·乌尔娜. 新疆昭苏县马消化道常见寄生虫感染情况调查及驱虫效果评价[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2016.
|
| [8] |
马亭. 吡喹酮治疗牛血吸虫病效果观察[J]. 中国畜禽种业, 2021, 17(10):130-131.
|
| [9] |
邓海峰, 李晓斌, 马军, 等. 碘醚柳胺对6月龄伊犁马驹驱虫效果的研究[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2016, 43(11):3066-3072.
|
| [10] |
索勋, 杨晓野. 高级寄生虫学实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2005.
|
| [11] |
EYSKER M, BAKKER J, VAN DEN BERG M, et al. The use of age-clustered pooled faecal samples for monitoring worm control in horses[J]. Veterinary Parasitology, 2008, 151(2/3/4):249-255.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.10.008
|
| [12] |
李国清. 兽医寄生虫学:双语版[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2006.
|
| [13] |
图尔荪·萨迪尔. 新疆部分地区马属动物常见寄生虫病的流行病学调查[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2016.
|
| [14] |
赛迪拉木, 呼尔查, 吾力江, 等. 冬季新疆普氏野马消化道寄生虫感染情况及驱虫试验[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2020(14):70-72,151.
|
| [15] |
SLOCOMBE J O D, HEINE J, BARUTZKI D, et al. Clinical trials of efficacy of praziquantel horse paste 9% against tapeworms and its safety in horses[J]. Veterinary Parasitology, 2007, 144(3/4):366-370.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.09.038
|
| [16] |
李麟, 付党华, 黄薇, 等. 某动物园斑马和野马肝片吸虫感染的诊断与治疗[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2012, 44(S2):119.
|
| [17] |
梁颖欣, 陈泽加, 李继超, 等. 广东省部分地区马肠道寄生虫感染情况调查[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2022, 49(7):2725-2734.
|
| [18] |
明·乌尔娜, 斯清, 李海, 等. 昭苏马夏秋季感染消化道寄生虫病的动态观察[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2016(21):156-157,161.
|
| [19] |
王玉琴, 赵有璋. 波德代羊主要生理生化指标的测定和分析[J]. 甘肃畜牧兽医, 2003, 33(3):2-4.
|
| [20] |
刘幸君. 不同羊品种血液细胞计数、生化指标和脂肪酸含量的比较研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2012.
|
| [21] |
何生虎, 王明成, 晁向阳, 等. 银川地区小尾寒羊血常规生理指标的测定[J]. 甘肃畜牧兽医, 2004, 34(6):17-18.
|
| [22] |
薛艳, 邓显佑, 王嘉福, 等. 3个马群感染马泰勒虫的分子病原学调查[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2016, 43(4):1086-1091.
|
| [23] |
张忠花. 枣庄地区主要绵、山羊血液生理指标的分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2016.
|
| [24] |
REIMERT C M, FITZSIMMONS C M, JOSEPH S, et al. Eosinophil activity in Schistosoma mansoni infections in vivo and in vitro in relation to plasma cytokine profile pre- and posttreatment with praziquantel[J]. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology, 2006, 13(5):584-593.
doi: 10.1128/CVI.13.5.584-593.2006
|
| [25] |
冯辉, 顾艳华, 尹志群. 一起羊注射伊维菌素同时口服阿苯达唑毒副反应分析[J]. 兽医导刊, 2021(19):126-127.
|
| [26] |
钟文伟, 李京阳, 耿丽婷, 等. 嗜碱性粒细胞在过敏性疾病中研究进展及临床应用展望[J]. 临床儿科杂志, 2022, 40(8):566-572.
|
| [27] |
杨芳. 马圆线虫病的治疗[J]. 养殖技术顾问, 2014(12):223.
|
| [28] |
肖锋, 杨凌宸. 一例泰迪犬血小板减少症的诊疗体会[J]. 湖南畜牧兽医, 2021(1):34-40.
|
| [29] |
何宝强, 李晓梅. 急性心肌梗死患者平均血小板体积变化的意义[J]. 心血管病学进展, 2018, 39(2):235-238.
|