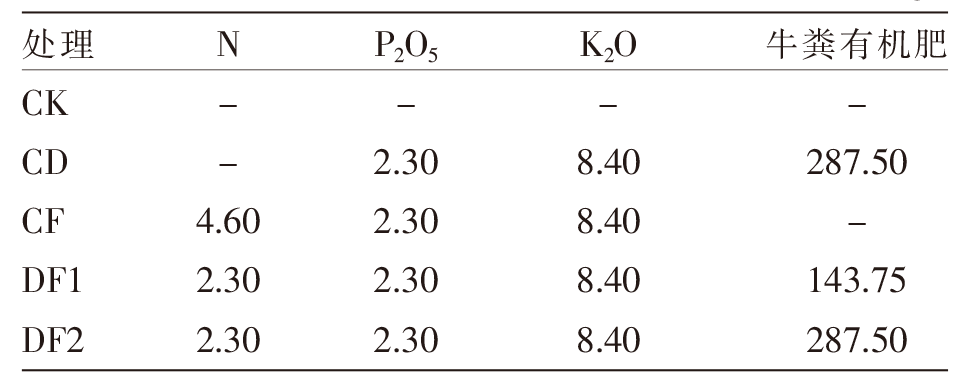
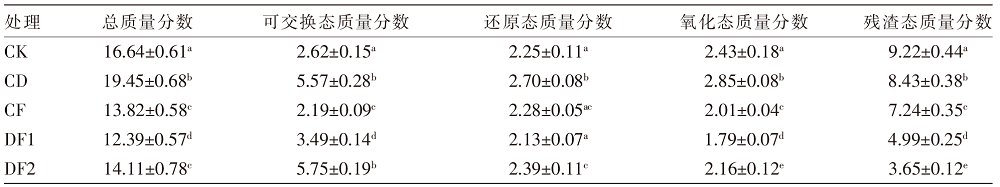
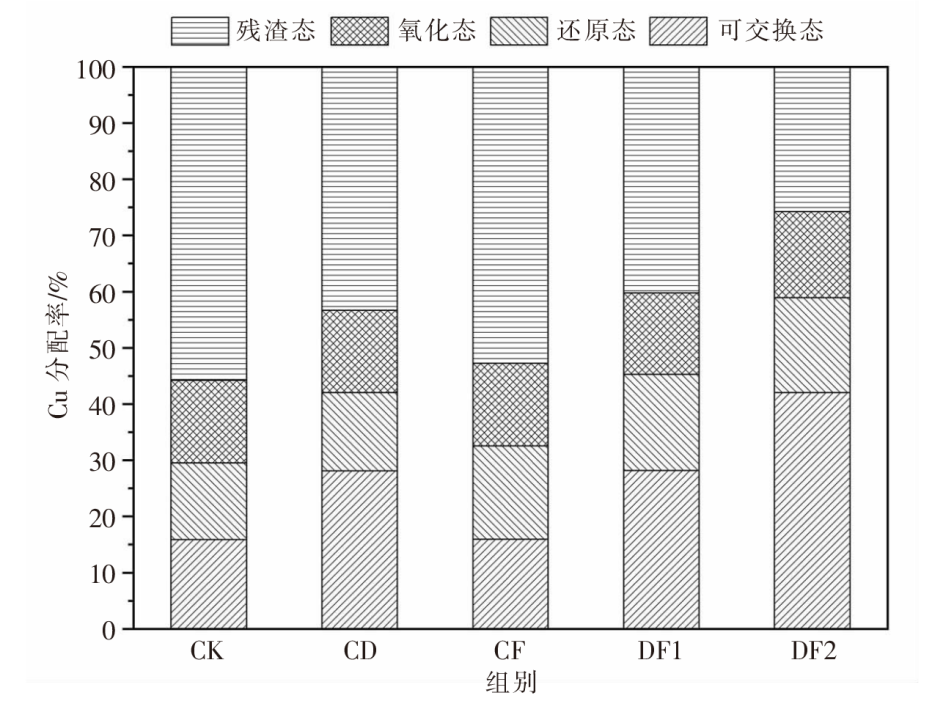
| [1] |
刘晨阳, 马广旭, 刘春, 等. 畜禽粪便资源化利用研究综述与对策建议——基于供给与需求二维度视角[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2022(2): 13-17.
|
| [2] |
路剑, 刘振涛. 效率和公平视角下畜禽粪污肥料化利用碳减排潜力测度——基于河北省县域经验数据[J]. 河北农业大学学报(社会科学版), 2023, 25(1): 50-61.
|
| [3] |
刘春, 刘晨阳, 王济民, 等. 我国畜禽粪便资源化利用现状与对策建议[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2021, 41(2): 35-43.
|
| [4] |
陈守亮. 畜禽粪污资源化处理的现状与改进措施[J]. 养殖与饲料, 2021, 20(1): 112-114.
|
| [5] |
李庆, 秦文杰, 曹秀芳, 等. 基于黑水虻转化的畜禽粪便资源化利用研究进展[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2022, 41(6): 169-175.
|
| [6] |
潘世优, 黎贞崇, 韦宇拓. 禽畜粪便资源化利用技术的研究进展[J]. 广西科学院学报, 2022, 38(3): 222-235.
|
| [7] |
陆则基, 周敏, 左媛媛, 等. 三种畜禽粪污资源化利用模式对比[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2023, 40(1): 52-54,64.
|
| [8] |
王祎, 杨磊, 屈博. 全国畜禽粪污还田试点典型模式分析[J]. 养殖与饲料, 2023, 22(1): 109-111.
|
| [9] |
袁立, 王占哲, 刘春龙. 国内外牛粪生物质资源利用的现状与趋势[J]. 中国奶牛, 2011(5): 3-9.
|
| [10] |
郭龙, 李陈, 刘佩诗, 等. 牛粪有机肥替代化肥对茶叶产量、品质及茶园土壤肥力的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2021, 35(6): 264-269.
|
| [11] |
YIN L. Analysis of assessment methods of heavy metal pollution in soil[J]. Scientific Journal of Economics and Management Research, 2022, 4(4): 11-18.
|
| [12] |
ZHANG X. Study on harm and technology of heavy metal pollution in soil[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2019(11): 93-95.
|
| [13] |
罗乐, 王金霞, 周皓. 优化BCR法-ICP-MS在土壤重金属化学形态分析中的应用[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2019, 45(2): 88-92.
|
| [14] |
张朝阳, 彭平安, 宋建中, 等. 改进BCR法分析国家土壤标准物质中重金属化学形态[J]. 生态环境学报, 2012, 21(11): 1881-1884.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906(2012)11-1881-04
|
| [15] |
中华人民共和国生态环境部. 土壤和沉积物铜、锌、铅、镍、铬的测定火焰原子吸收分光光度法:HJ 491—2019[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团, 2019.
|
| [16] |
中华人民共和国生态环境部. 土壤有机碳的测定重铬酸钾氧化-分光光度法:HJ 615—2011[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2011.
|
| [17] |
王小霞. 天津市北京排污灌区土壤中重金属形态的空间分布及影响因素研究[D]. 天津: 天津师范大学, 2012.
|
| [18] |
丁疆华, 温琰茂, 舒强. 土壤环境中镉、锌形态转化的探讨[J]. 城市环境与城市生态, 2001, 14(2): 47-49.
|
| [19] |
刘霞, 刘树庆, 王胜爱. 河北主要土壤中Cd和Pb的形态分布及其影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2003(3): 393-400.
|
| [20] |
陈璐, 刘宇斌, 党秀丽, 等. 牛粪与秸秆配施对棕壤镉赋存形态及玉米吸收镉的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(5): 313-317,324.
|
| [21] |
李晓宁, 高明, 慈恩. 重庆市植烟土壤有效态微量元素含量评价[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2007(3): 25-28.
|
| [22] |
韩春梅, 王林山, 巩宗强, 等. 土壤中重金属形态分析及其环境学意义[J]. 生态学杂志, 2005(12): 1499-1502.
|
| [23] |
杨潞. 养猪粪污土地利用中土壤重金属累积迁移转化规律研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018.
|
| [24] |
王洋, 刘景双, 郑娜. 土壤pH值对冻融黑土重金属锌赋存形态的影响[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2010, 24(1): 163-167.
|
| [25] |
钟晓兰, 周生路, 黄明丽, 等. 土壤重金属的形态分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(4): 1266-1273.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906(2009)04-1266-08
|
| [26] |
刘霞, 刘树庆, 王胜爱. 河北主要土壤中重金属镉、铅形态与土壤酶活性的关系[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2002(1): 33-37,60.
|
| [27] |
戴树桂. 环境化学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006:265-302.
|
| [28] |
HARTER R D, NAIDU R. An assessment of environmental and solution parameter impact on trace‐metal sorption by soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2001, 65(3): 597-612.
doi: 10.2136/sssaj2001.653597x
|