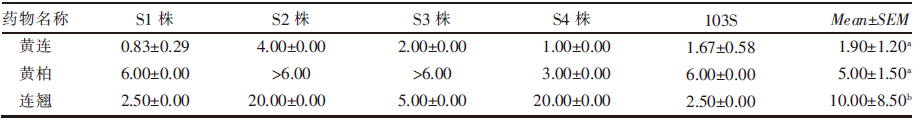
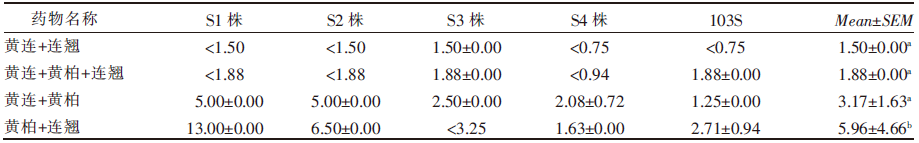
| [1] |
GIGUÈRE S, BERGHAUS L J, LEE E A. Activity of 10 antimicrobial agents against intracellular Rhodococcus equi[J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2015, 178(3/4):275-278.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.05.019
|
| [2] |
WITKOWSKI L, RZEWUSKA M, TAKAI S, et al. Molecular characterization of Rhodococcus equi isolates from horses in Poland:PVapA characteristics and plasmid new variant, 85 kb type V[J]. BMC Veterinary Research, 2017, 13(1):35.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-017-0954-2
|
| [3] |
HILLIDGE C J. Use of erythromycin-rifampin combination in treatment of Rhodococcus equi pneumonia[J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 1987, 14(3):337-342.
doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90121-0
|
| [4] |
ÁLVAREZ-NARVÁEZ S, GIGUÈRE S, COHEN N, et al. Spread of multidrug-resistant Rhodococcus equi, United States[J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 2021, 27(2):529-537.
doi: 10.3201/eid2702.203030
|
| [5] |
LIU H M, WANG Y T, YAN J, et al. Appearance of multidrug-resistant virulent Rhodococcus equi clinical isolates obtained in China[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 2014, 52(2):703.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.02925-13
|
| [6] |
EFSA Panel on Animal Health and Welfare AHAW, NIELSEN S S, BICOUT D J, et al. Assessment of listing and categorisation of animal diseases within the framework of the Animal Health Law [Regulation (EU) No2016/429]: Antimicrobial-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in cattle and horses[J]. EFSA Journal European Food Safety Authority, 2022, 20(5):e07312.
|
| [7] |
中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴(2021)[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2021.
|
| [8] |
冼欣彤. 马红球菌流行病学调查及其分离株特性的初步研究[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2018.
|
| [9] |
张谦, 刘一尘, 徐进, 等. 加味白头翁散发酵产物对肉仔鸡大肠杆菌病的防治效果及对其肠道菌群的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2018, 46(21):177-180.
|
| [10] |
刘敏杰, 杨立军, 汪金萍, 等. 5种中草药提取物对奶牛乳房炎致病菌的体外抑制效果[J]. 中兽医医药杂志, 2022, 41(4):74-77.
|
| [11] |
戴悦, 江源誉, 张腾月, 等. 9种中草药对沙门菌和金黄色葡萄球菌体外抑制作用[J]. 中兽医医药杂志, 2022, 41(1):81-84.
|
| [12] |
李昭融. 13味中草药及八正散对泌尿系感染致病菌体外抑菌作用研究[D]. 天津: 天津中医药大学, 2021.
|
| [13] |
中国畜牧兽医学会兽医药理毒理学分会,CLSI. 动物源细菌抗菌药物敏感性试验纸片法与稀释法执行标准(CLSI授权翻译,内部交流)[Z]. 北京: 中国畜牧兽医学会兽医药理毒理学分会, 2013.
|
| [14] |
唐金蓉, 李盛, 张曼俐, 等. 黄芩、黄连和黄柏对CRKP的抑菌作用研究[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2022, 35(14):2469-2471.
|
| [15] |
张腾月, 黄思涵, 戴悦, 等. 白头翁散与其他中药联合对大肠杆菌的体外抑菌效果[J]. 中兽医医药杂志, 2022, 41(2):78-81.
|
| [16] |
张瑞麟, 范敏, 周桂玲. 新疆中草药的产业优势与发展策略[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2004, 41(4):208-212.
|
| [17] |
朱晓萍, 庄智威, 叶泽铭, 等. 黄连等中草药对常见病原菌体外抑菌效果的研究[J]. 饲料研究, 2021, 44(7):98-101.
|
| [18] |
穆廷杰, 杨芬兰, 金海红, 等. 连翘等中草药对肺炎克雷伯菌抑菌作用的实验研究及临床应用[J]. 西部中医药, 2015, 28(9):19-21.
|
| [19] |
张雪宁, 马方芳, 郑艳秋, 等. 苦寒类中药抑菌作用及机制的现状与思考展望[J]. 中外医学研究, 2020, 18(14):180-182.
|
| [20] |
胡诚毅, 莫志贤. 黄连素的药理作用及机制研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017, 23(20):213-219.
|
| [21] |
张天锡, 史磊, 刘雯, 等. 连翘化学成分、药理活性现代研究[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2016, 18(12):222-224.
|
| [22] |
CHU M, DING R, CHU Z Y, et al. Role of berberine in anti-bacterial as a high-affinity LPS antagonist binding to TLR4/MD-2 receptor[J]. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2014, 14:89.
doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-89
pmid: 24602493
|
| [23] |
徐硕超. 不同类型清热中药的抑菌作用特点比较及应用研究[D]. 广州: 广东药科大学, 2017.
|