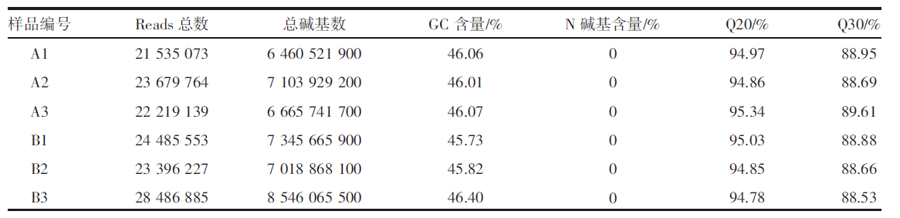
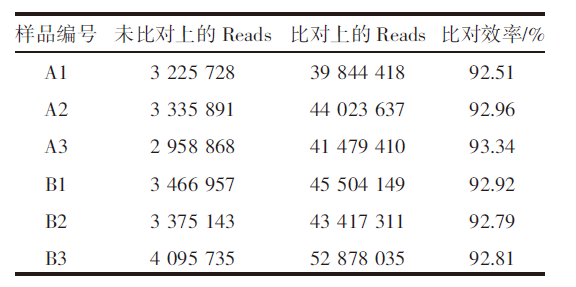
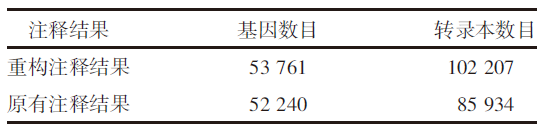
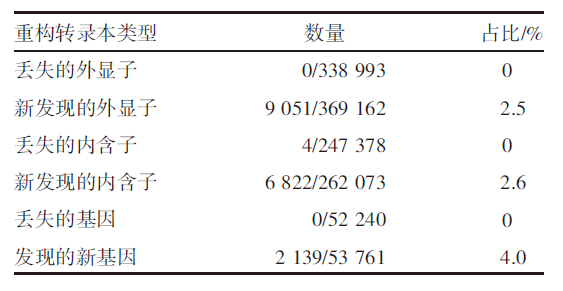
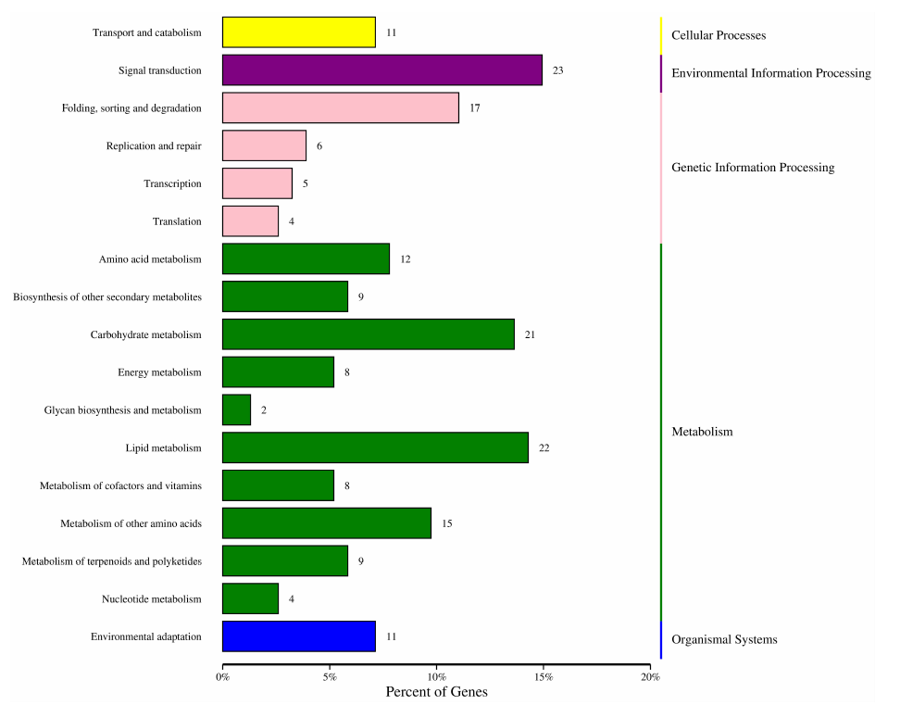
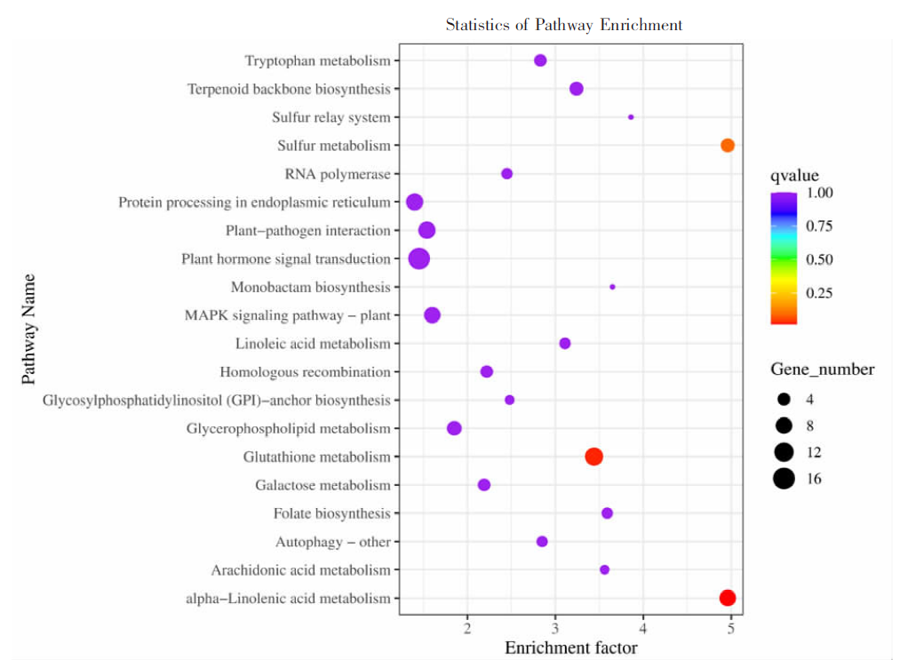
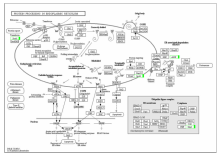
| [1] |
吕慧颖, 王道文, 葛毅强, 等. 大豆育种行业创新动态[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2018, 19(3):464-467.
|
| [2] |
陈锦玲. 大豆油脂和蛋白质合成与累积相关基因的表达及调控研究[D]. 桂林: 广西师范大学, 2020.
|
| [3] |
崔德卿. 对于荏菽和戎菽的再讨论:中国大豆的起源相关联[J]. 中国农史, 2017, 36(4):15-33.
|
| [4] |
石慧. 大豆成为世界性作物的历程探析[J]. 农业考古, 2021(6):71-78.
|
| [5] |
陈慧琳. 中国大豆进口贸易对生态环境的影响[D]. 福州: 福州大学, 2018.
|
| [6] |
杨春燕, 姚利波, 刘兵强, 等. 国内外大豆品质育种研究方法与最新进展[J]. 华北农学报, 2009, 24(S1):75-78.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2009.S1.019
|
| [7] |
谈建中, 楼程富. 大豆种子贮存蛋白基因及其遗传转化的研究进展[J]. 大豆科学, 2000, 19(1):57-62.
|
| [8] |
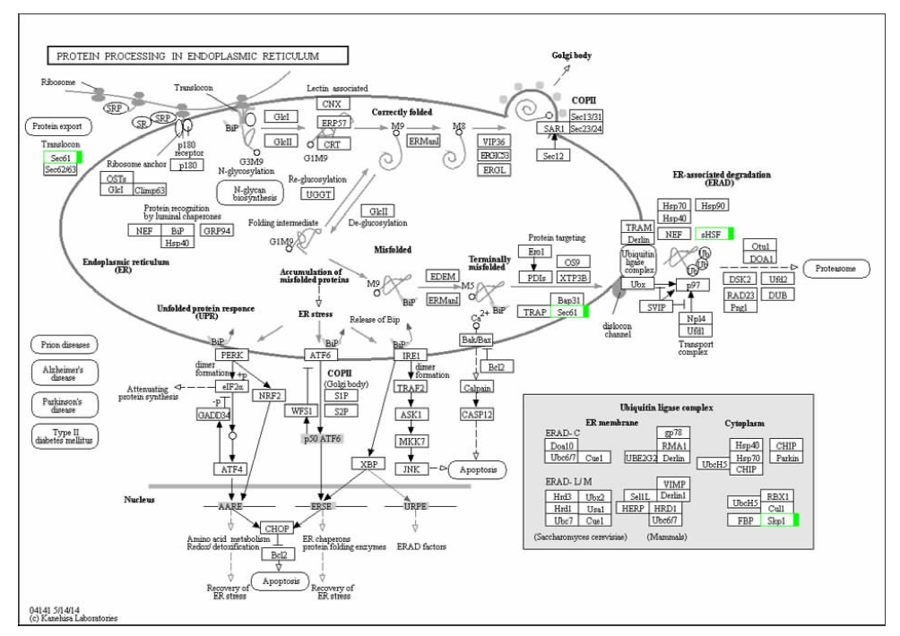
敖雁, 王安, 吴启, 等. 大豆籽粒蛋白代谢途径及相关调控机制研究进展[J]. 大豆科学, 2018, 37(5):794-802.
|
| [9] |
陈欢. 大豆籽粒不同发育时期基因表达谱的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2012.
|
| [10] |
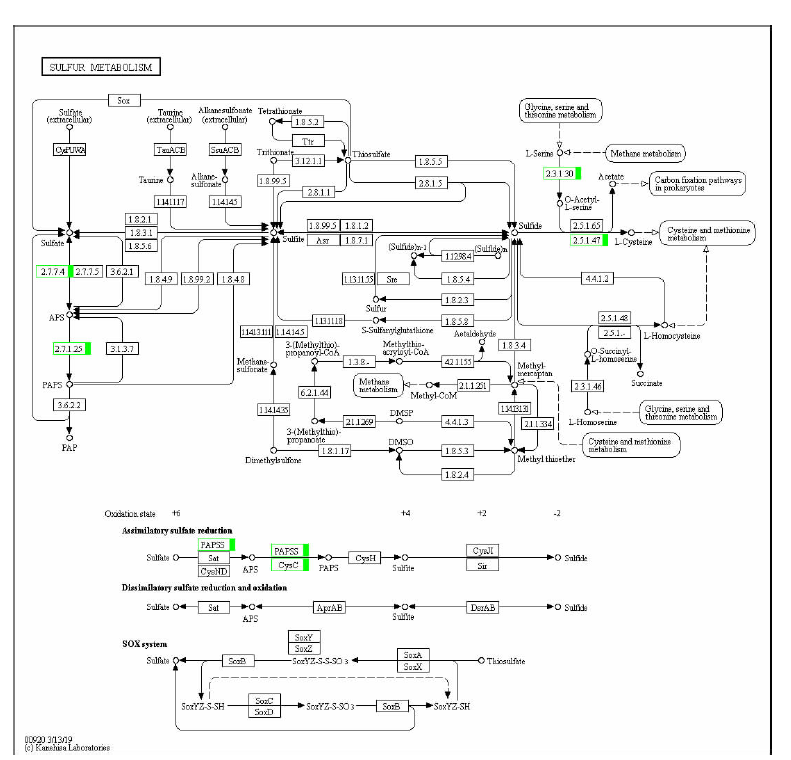
马淑梅. 大豆硫素代谢与蛋白质功能组分的关系[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2010.
|
| [11] |
刘晓, 陈修德, 程宁, 等. 外源脱落酸处理的干旱胁迫下山桃叶片的转录组差异表达分析[J]. 植物生理学报, 2020, 56(12):2755-2766.
|
| [12] |
宋健. 大豆蛋白质代谢关键基因和转录因子的生物信息学预测[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2015.
|
| [13] |
郭静文, 史晓蕾, 刘茜, 等. 基于转录组测序技术挖掘大豆蛋白质合成相关基因[J]. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(1):61-73.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.201751206
|
| [14] |
GOGALA M, BECKER T, BEATRIX B, et al. Structures of the Sec61 complex engaged in nascent peptide translocation or membrane insertion[J]. Nature, 2014, 506(7486):107-110.
doi: 10.1038/nature12950
|
| [15] |
李玉颖. 硫在作物营养平衡中的作用[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 1992(6):37-39.
|
| [16] |
陈坤明, 宫海军, 王锁民. 植物谷胱甘肽代谢与环境胁迫[J]. 西北植物学报, 2004, 24(6):1119-1130.
|
| [17] |
王静, 周祁, 李丽华, 等. 烟草的TMV侵染耐受性与谷胱甘肽代谢途径的关系[J]. 河南农业科学, 2017, 46(2):49-54.
|
| [18] |
KARMOKER J L, CLARKSON D T, SAKER L R, et al. Sulphate deprivation depresses the transport of nitrogen to the xylem and the hydraulic conductivity of barley(Hordeum vulgare L.)roots[J]. Planta, 1991, 185(2):269-278.
|
| [19] |
姜振峰, 杨庆凯, 陈庆山. 东北地区5个大豆品种球蛋白含量的分析及利用[J]. 大豆科学, 2003, 22(2):115-119.
|
| [20] |
周恩远, 刘丽君, 祖伟, 等. 硫肥对大豆蛋白亚基含量的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2006, 37(5):582-587.
|