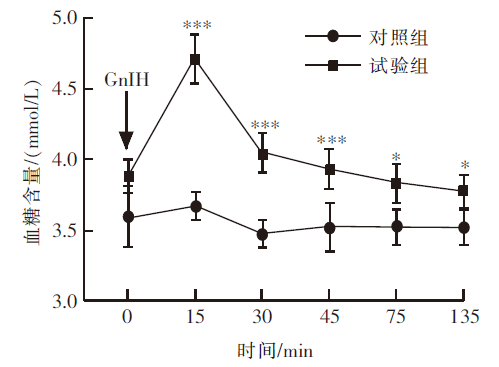
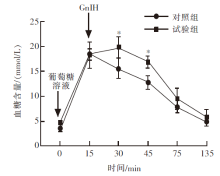
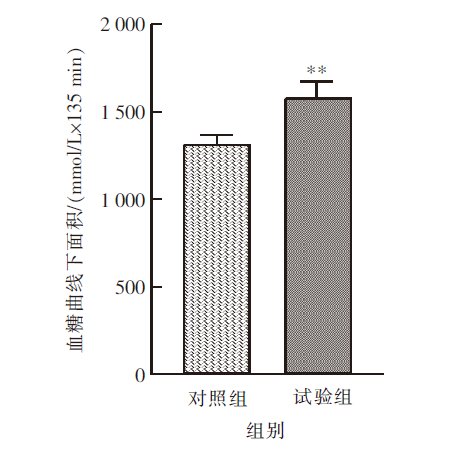
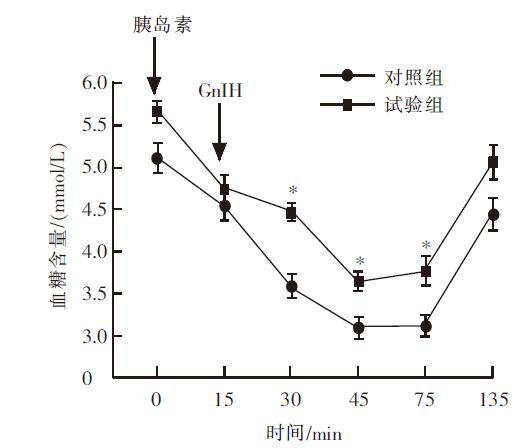
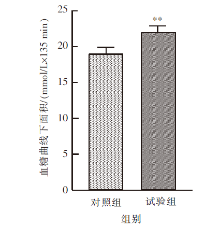
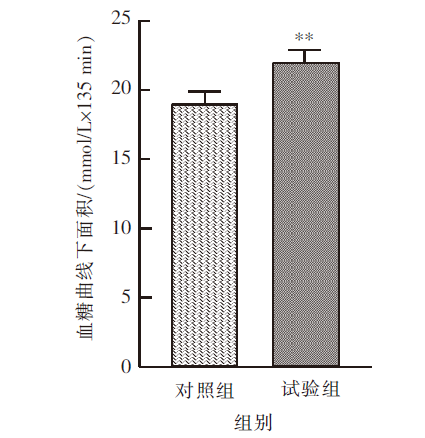
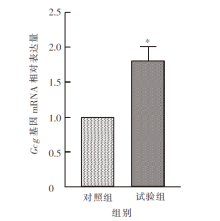
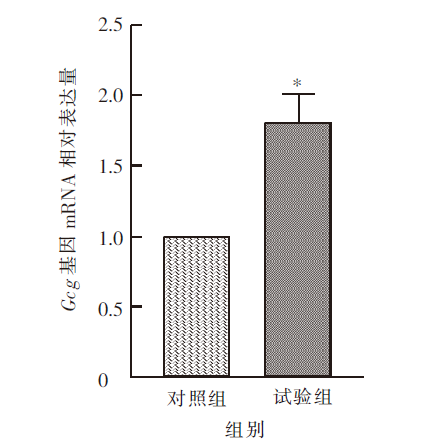
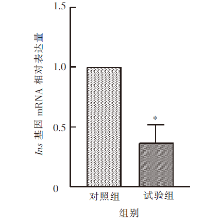
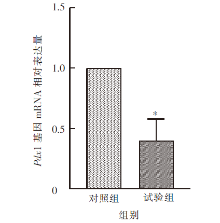
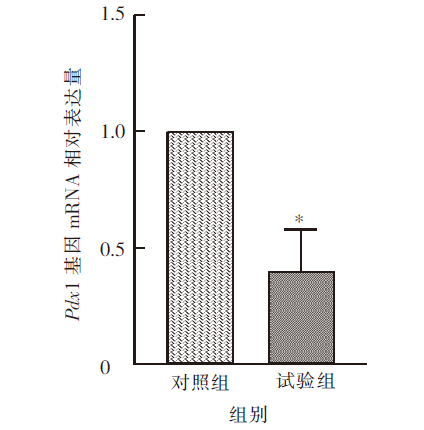
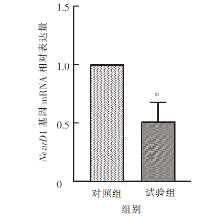
| [1] |
TSUTSUI K, SAIGOH E, UKENA K, et al. A novel avian hypothalamic peptide inhibiting gonadotropin release[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2000, 275(2):661-667.
doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3350
pmid: 10964719
|
| [2] |
CLARKE I J, QI Y, PUSPITA S I, et al. Evidence that RF-amide related peptides are inhibitors of reproduction in mammals[J]. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 2009, 30(3):371-378.
doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2009.04.001
pmid: 19362107
|
| [3] |
TSUTSUI K. A new key neurohormone controlling reproduction, gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH):Biosynthesis, mode of action and functional significance[J]. Progress in Neurobiology, 2009, 88(1):76-88.
doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.02.003
|
| [4] |
TSUTSUI K, UBUKA T. GnIH control of feeding and reproductive behaviors[J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2016, 7:170.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00170
pmid: 28082949
|
| [5] |
SCHWARTZ M W, WOODS S C, PORTE D Jr, et al. Central nervous system control of food intake[J]. Nature, 2000, 404(6778):661-671.
doi: 10.1038/35007534
|
| [6] |
UKENA K, TSUTSUI K. Distribution of novel RFamide-related peptide-like immunoreactivity in the mouse central nervous system[J]. Neuroscience Letters, 2001, 300(3):153-156.
pmid: 11226634
|
| [7] |
JOHNSON M A, TSUTSUI K, FRALEY G S. Rat RFamide-related peptide-3 stimulates GH secretion, inhibits LH secretion, and has variable effects on sex behavior in the adult male rat[J]. Hormones and Behavior, 2007, 51(1):171-180.
doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2006.09.009
pmid: 17113584
|
| [8] |
UBUKA T, LAI H, KITANI M, et al. Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone identification, cDNA cloning, and distribution in rhesus macaque brain[J]. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 2009, 517(6):841-855.
doi: 10.1002/cne.22191
pmid: 19844991
|
| [9] |
QI Y, OLDFIELD B J, CLARKE I J. Projections of RFamide-related peptide-3 neurones in the ovine hypothalamus, with special reference to regions regulating energy balance and reproduction[J]. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, 2009, 21(8):690-697.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2009.01886.x
pmid: 19500220
|
| [10] |
CLARKE I J, SMITH J T, HENRY B A, et al. Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone is a hypothalamic peptide that provides a molecular switch between reproduction and feeding[J]. Neuroendocrinology, 2012, 95(4):305-316.
doi: 10.1159/000332822
pmid: 22286004
|
| [11] |
HOU K, LI X, HU W, et al. RFRP-3, the mammalian ortholog of GnIH, is a novel modulator involved in food intake and glucose homeostasis[J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2020, 11:194.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00194
pmid: 32328034
|
| [12] |
沈兆艳, 彭佛友, 程秋根, 等. 微胶囊包膜缓释植物精油在蛋鹌鹑上的应用效果及使用方案研究[J]. 广东饲料, 2019, 28(5):23-27.
|
| [13] |
AYALA J E, SAMUEL V T, MORTON G J, et al. Standard operating procedures for describing and performing metabolic tests of glucose homeostasis in mice[J]. Disease Models and Mechanisms, 2010, 3(9/10):525-534.
doi: 10.1242/dmm.006239
|
| [14] |
FU S H, CHEN Y T, CHIANG C H, et al. Enhancing engraftment of neonatal porcine xenoislet with CTLA4Ig and nordihydroguaiaretic acid[J]. Transplantation Proceedings, 2006, 38(10):3283-3285.
pmid: 17175250
|
| [15] |
SCHNEIDER J E, WISE J D, BENTON N A, et al. When do we eat? Ingestive behavior, survival, and reproductive success[J]. Hormones and Behavior, 2013, 64(4):702-728.
doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2013.07.005
pmid: 23911282
|
| [16] |
FRALEY G S, COOMBS E, GEROMETTA E, et al. Distribution and sequence of gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone and its potential role as a molecular link between feeding and reproductive systems in the Pekin duck (Anas platyrhynchos domestica)[J]. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 2013, 184:103-110.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2012.11.026
pmid: 23354058
|
| [17] |
TACHIBANA T, SATO M, TAKAHASHI H, et al. Gonadotropin-inhibiting hormone stimulates feeding behavior in chicks[J]. Brain Research, 2005, 1050(1/2):94-100.
doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.05.035
|
| [18] |
曹旭. 胰岛素抵抗的分子机制研究进展[J]. 医学新知杂志, 2004(2):114-116.
|
| [19] |
JUNG S H, JUNG C H, REAVEN G M, et al. Adapting to insulin resistance in obesity: Role of insulin secretion and clearance[J]. Diabetologia, 2018, 61(3):681-687.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4511-0
|
| [20] |
李卉, 罗明秀, 宋辉. GnIH基因在小鼠各个组织中的表达[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2017, 58(10):24-26.
|
| [21] |
霍孔林, 胡浩, 李建华, 等. GnIH在陆川仔公猪中枢神经系统的分布与定位[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2015, 45(10):1072-1077.
|
| [22] |
LIU X D, RUAN J X, XIA J H, et al. The study of regulatory effects of Pdx-1, MafA and NeuroD1 on the activity of porcine insulin promoter and the expression of human islet amyloid polypeptide[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 2014, 394(1/2):59-66.
doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2081-8
|
| [23] |
SHAO S, LIU Z, YANG Y, et al. SREBP-1c, Pdx-1, and GLP-1R involved in palmitate-EPA regulated glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in INS-1 cells[J]. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 2010, 111(3):634-642.
doi: 10.1002/jcb.22750
pmid: 20589757
|
| [24] |
BELL G I, POLONSKY K S. Diabetes mellitus and genetically programmed defects in beta-cell function[J]. Nature, 2001, 414(6865):788-791.
doi: 10.1038/414788a
|