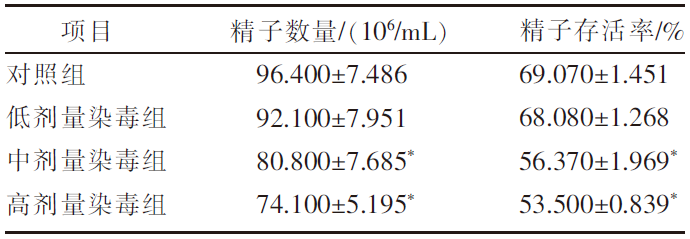
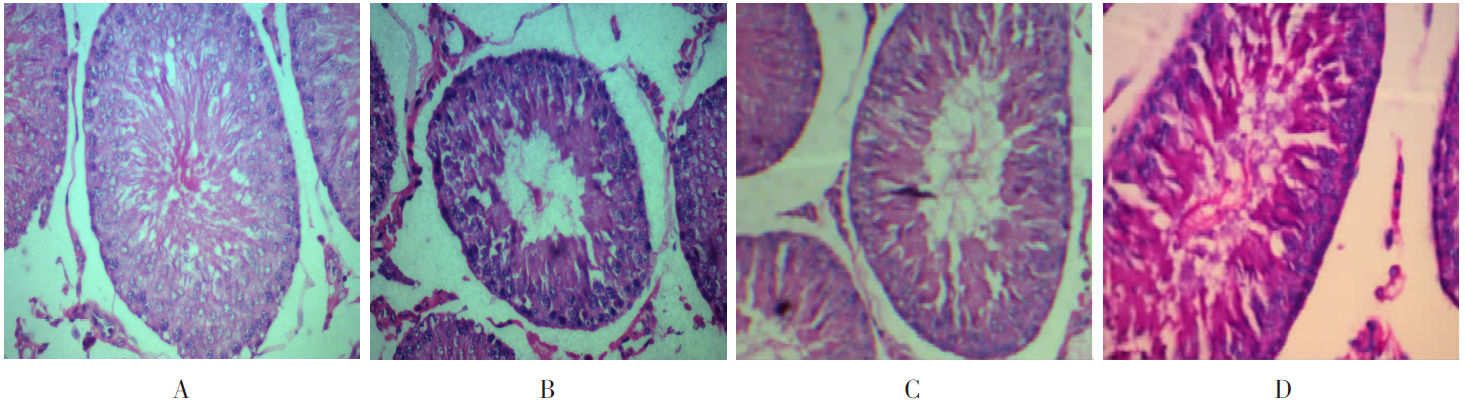
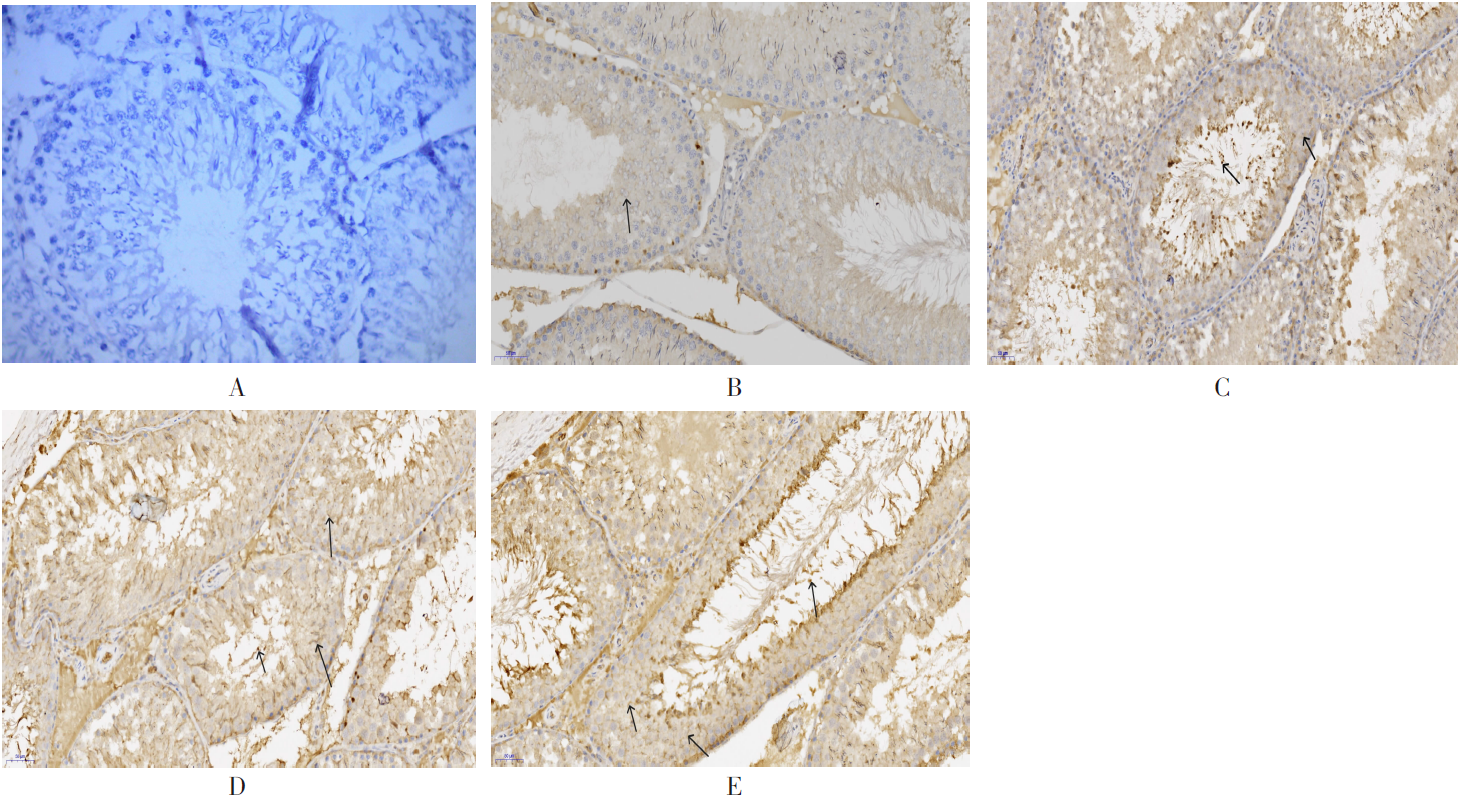
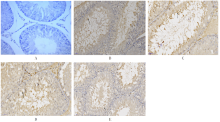
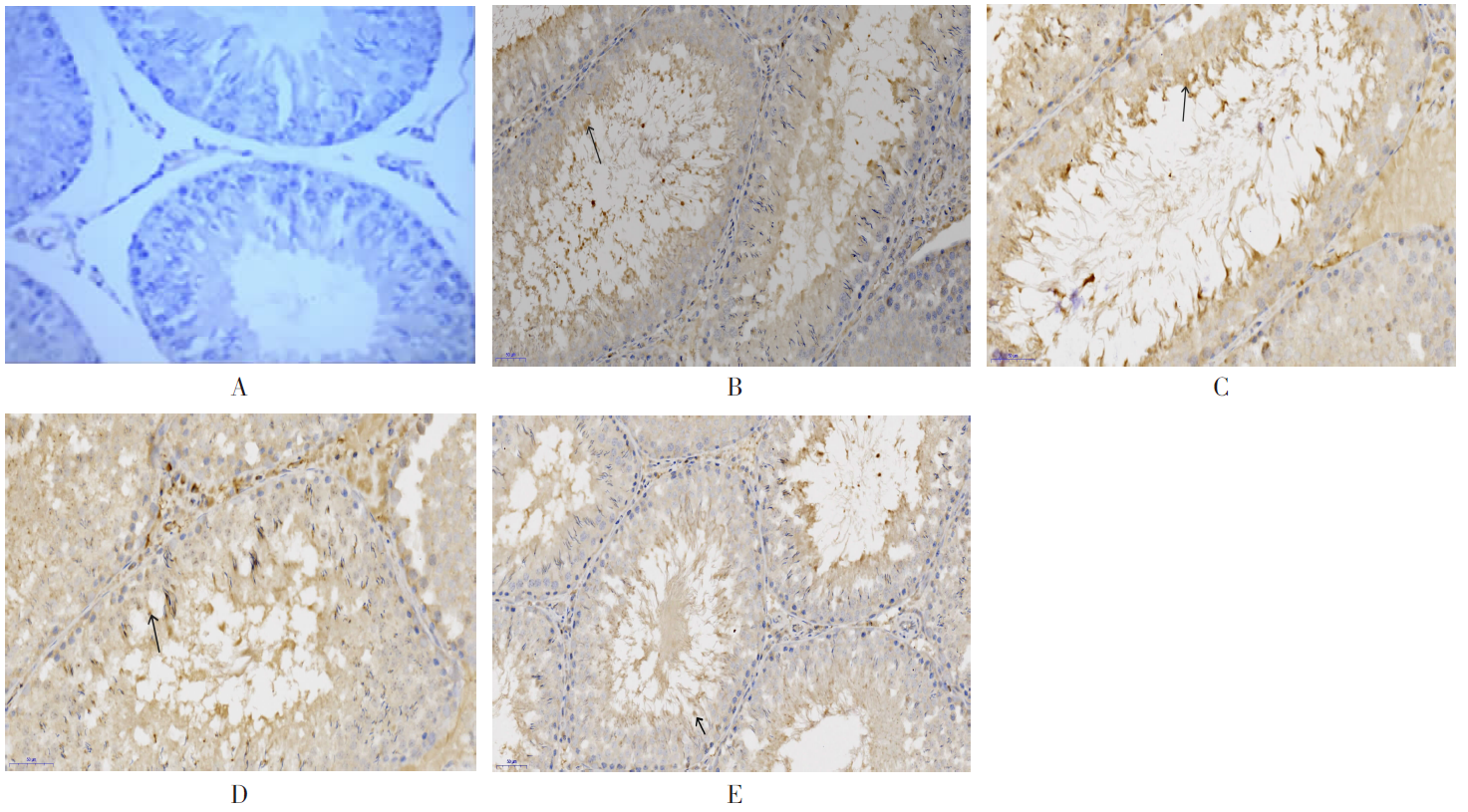
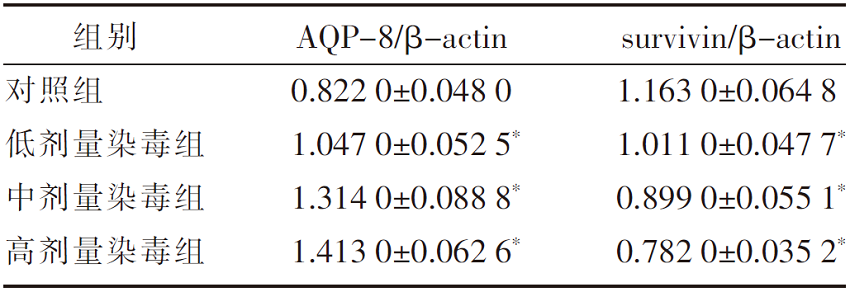
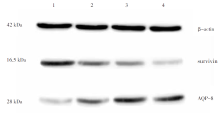
| [1] |
孙欣, 袁业锋, 李海雁, 等. 小鼠睾丸、附睾和前列腺组织细胞外囊泡蛋白质组分的鉴定及功能分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(6):8-17.
|
| [2] |
COUTO-SANTOS F, SOUZA A C F, BASTOS D S S, et al. Prepubertal exposure to arsenic alters male reproductive parameters in pubertal and adult rats[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2020, 409:115304.
doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115304
|
| [3] |
何佳, 许博闻, 高文博, 等. 三氧化二砷对肝癌细胞HepG2迁移侵袭和凋亡的影响[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2020, 37(1):105-111.
|
| [4] |
崔思远, 解荣燕, 于丽明, 等. 三氧化二砷对人多发性骨髓瘤KM3细胞凋亡和染色体区域稳定蛋白mRNA表达的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(6):2407-2411.
|
| [5] |
戴研平, 高晓勤, 马晓萍, 等. 慢性砷染毒对大鼠附睾上皮细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2016, 33(9):788-791.
|
| [6] |
鞠晶昀, 陈刚. 禁食引起小鼠多组织砷吸收增加及其机制研究[C]// 中国环境科学学会.中国环境科学学会2010年学术年会论文集(第四卷). 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2010:4302-4306.
|
| [7] |
ROUSTON V G D, SHAABAN A A A, ABD ALLAH D M, et al. Survivin and caspase-3 cannot predict recurrence for urinary bladder carcinoma[J]. SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine, 2021, 3:2292-2300.
doi: 10.1007/s42399-021-01052-6
|
| [8] |
SHARMA G, KUMAR M. Arsenic induced histological alterations in testis of Swiss albino mice and protection by Chlorophytum borivilianum[J]. Asian Pacific Journal of Reproduction, 2014, 3(4):282-287.
doi: 10.1016/S2305-0500(14)60040-3
|
| [9] |
JAHAN S, IFTIKHAR N, ULLAH H, et al. Alleviative effect of quercetin on rat testis against arsenic: A histological and biochemical study[J]. Systems Biology in Reproductive Medicine, 2015, 61(2):89-95.
doi: 10.3109/19396368.2014.998350
pmid: 25539033
|
| [10] |
ZENG Q, YI H, HUANG L, et al. Reduced testosterone and Ddx3y expression caused by long-term exposure to arsenic and its effect on spermatogenesis in mice[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2018, 63:84-91.
doi: S1382-6689(18)30248-5
pmid: 30189373
|
| [11] |
STROCCHIO L, GURNARI C, SANTORO N, et al. Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid treatment for childhood acute promyelocytic leukaemia[J]. British Journal of Haematology, 2019, 185(2):360-363.
doi: 10.1111/bjh.15507
pmid: 30028005
|
| [12] |
陈锦锋, 马瑜婷. 砷剂调控肿瘤细胞命运的机制及激活抗肿瘤免疫的潜力[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2021, 48(21):1113-1119.
|
| [13] |
IKAGA R, NAMEKATA I, KOTIADIS V N, et al. Knockdown of aquaporin-8 induces mitochondrial dysfunction in 3T3-L1 cells[J]. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports, 2015, 4:187-195.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.09.009
pmid: 29124204
|
| [14] |
SQUILLACIOTI C, MIRABELLA N, LIGUORI G, et al. Aquaporins are differentially regulated in canine cryptorchid efferent ductules and epididymis[J]. Animals, 2021, 11(6):1539.
doi: 10.3390/ani11061539
|
| [15] |
YYEUNG C H, CALLIES C, TÜTTELMANN F, et al. Aquaporins in the human testis and spermatozoa-identification, involvement in sperm volume regulation and clinical relevance[J]. International Journal of Andrology, 2010, 33(4):629-641.
|
| [16] |
KHAIRUL I, WANG Q Q, JIANG Y H, et al. Metabolism, toxicity and anticancer activities of arsenic compounds[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(14):23905.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14733
pmid: 28108741
|
| [17] |
HOONJAN M, JADHAV V, BHATT P. Arsenic trioxide: Insights into its evolution to an anticancer agent[J]. Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry, 2018, 23:313-329.
doi: 10.1007/s00775-018-1537-9
pmid: 29396610
|
| [18] |
VEERAVARMAL V, AUSTIN R D, SIDDAVARAM N, et al. Caspase-3 expression in normal oral epithelium, oral submucous fibrosis and oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, 2016, 20(3):445.
pmid: 27721610
|
| [19] |
SHIN S, SUNG B J, CHO Y S, et al. An anti-apoptotic protein human survivin is a direct inhibitor of caspase-3 and-7[J]. Biochemistry, 2001, 40(4):1117-1123.
doi: 10.1021/bi001603q
|
| [20] |
HU X, LI H, IP T K Y, et al. Arsenic trioxide targets Hsp60, triggering degradation of p53 and survivin[J]. Chemical Science, 2021, 12(32):10893-10900.
doi: 10.1039/d1sc03119h
pmid: 34476069
|