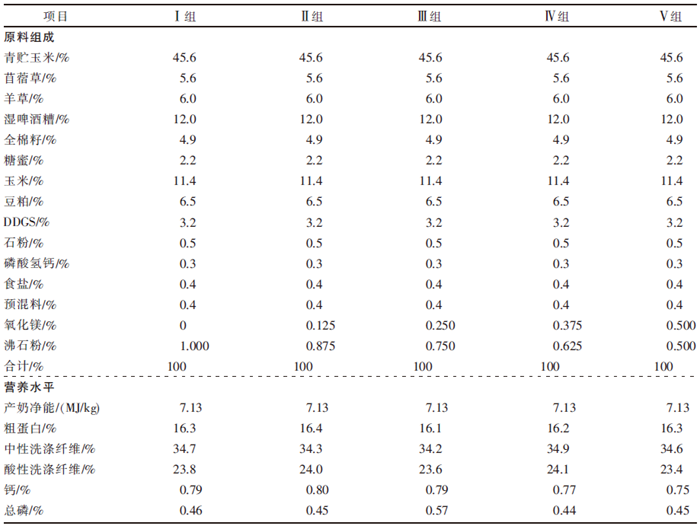
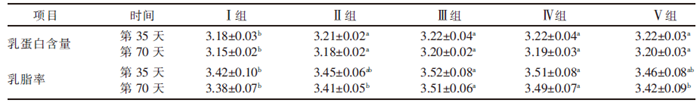
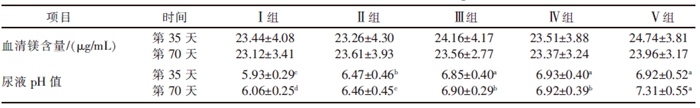
| [1] |
赵超. 豆渣与玉米秸秆混合发酵制备及饲喂奶牛效果的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2021.
|
| [2] |
柳君辉. 酸碱处理高精料日粮中玉米对肉牛瘤胃发酵和菌群、炎症反应和生长性能的影响[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2020.
|
| [3] |
周爽. 发酵全混合日粮降低奶牛瘤胃甲烷产量的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2021.
|
| [4] |
STEFANSKA B, PRUSZYNSK-OSZMALEK E, SZCZEPANKIEWICZ D, et al. Relationship between pH of ruminal fluid during subacute ruminal acidosis and physiological response of the Polish Holstein-Friesian dairy cows[J]. Polish Journal of Veterinary Sciences, 2017, 20(3):551-558.
doi: 10.1515/pjvs-2017-0067
pmid: 29166264
|
| [5] |
IWANIUK M E, ERDMAN R A. Intake, milk production, ruminal, and feed efficiency responses to dietary cation-anion difference by lactating dairy cows[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2015, 98(12):8973-8985.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-9949
pmid: 26409960
|
| [6] |
BACH A, GUASCH I, ELCOSO G, et al. Modulation of rumen pH by sodium bicarbonate and a blend of different sources of magnesium oxide in lactating dairy cows submitted to a concentrate challenge[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2018, 101(11):9777-9788.
doi: S0022-0302(18)30783-5
pmid: 30172393
|
| [7] |
TEBBE A W, WYATT D J, WEISS W P. Effects of magnesium source and monensin on nutrient digestibility and mineral balance in lactating dairy cows[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2018, 101(2):1152-1163.
doi: S0022-0302(17)31162-1
pmid: 29248228
|
| [8] |
LENO B M, LACOUNT S E, RYAN C M, et al. The effect of source of supplemental dietary calcium and magnesium in the peripartum period, and level of dietary magnesium postpartum, on mineral status, performance, and energy metabolites in multiparous Holstein cows[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2017, 100(9):7183-7197.
doi: S0022-0302(17)30674-4
pmid: 28711248
|
| [9] |
AMMERMAN C B, CHICCO C F, MOORE J E, et al. Effect of dietary magnesium on voluntary feed intake and rumen fermentations[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 1971, 54(9):1288-1293.
pmid: 4937669
|
| [10] |
WITWER F, CONTRERAS P A, SILVA N, et al. Efecto de la suplementación con magnesio en alimento y agua sobre el control de tetania hipomagnesémica en rebaños Hereford[J]. Archivos de Medicina Veterinaria, 1997, 29(1):25-33.
|
| [11] |
何宝祥, 杜玉兰, 黄廷富, 等. 高产奶牛血清镁含量分析[J]. 中国奶牛, 2001(4):24-25.
|
| [12] |
ERDMAN R A. Dietary buffering requirements of the lactating dairy cow: A review[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 1988, 71(12):3246-3266.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(88)79930-0
|
| [13] |
敖日格乐, 王纯洁, 张润厚, 等. 缓冲剂在奶牛泌乳前期添加效果的试验[J]. 中国奶牛, 1996(6):16-18.
|
| [14] |
赵书民. 缓冲剂在奶牛生产中的应用[J]. 中国奶牛, 2006(6):61-62.
|
| [15] |
唐洪峰, 余爱英. 氧化镁对奶牛产奶性能的影响[J]. 河南畜牧兽医, 2006, 27(10):9.
|
| [16] |
王宏岩. 奶牛补饲碳酸氢钠和氧化镁对产乳性能的影响[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 1990(2):13-14.
|
| [17] |
张为鹏, 胡昌军, 沈美清. 奶牛饲喂碳酸氢钠与氧化镁的效果[J]. 中国奶牛, 2006(1):22-23.
|
| [18] |
杨蕾. 不同DCAD值日粮钙、镁水平对围产期奶牛血钙稳衡调控的影响[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2009.
|
| [19] |
HAENNI A, OHRVALL M, LITHELL H. Atherogenic lipid fractions are related to ionized magnesium status[J]. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 1998, 67(2):202-207.
doi: 10.1093/ajcn/67.2.202
|
| [20] |
白云龙, 王刚, 吴凌, 等. 酸性尿液的泌乳奶牛血/尿临床病理学变化[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2017, 29(5):21-24.
|
| [21] |
GOFF J P. Mineral absorption mechanisms, mineral interactions that affect acid-base and antioxidant status, and diet considerations to improve mineral status[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2018, 101(4):2763-2813.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13112
|