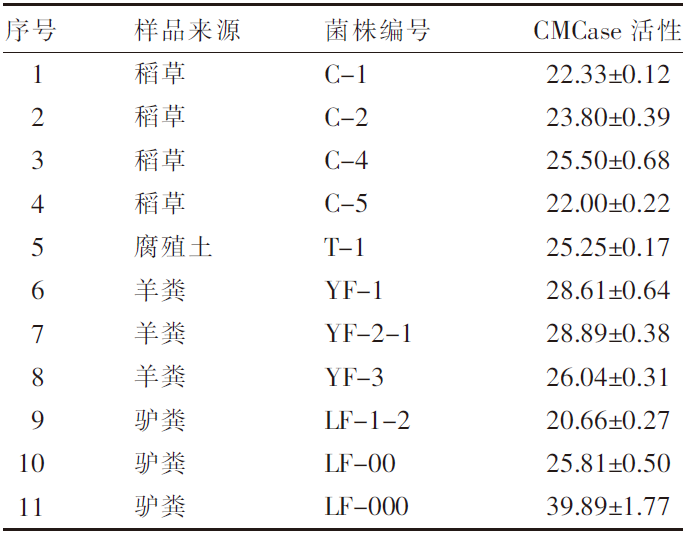
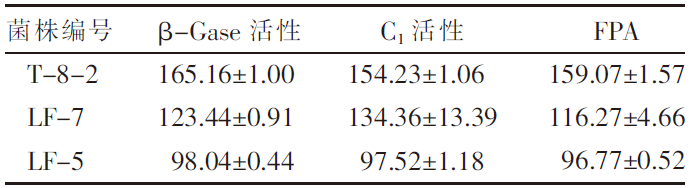
| [1] |
黄国锋, 钟流举, 张振钿, 等. 猪粪堆肥化处理过程中的氮素转变及腐熟度研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(11):1459-1462.
|
| [2] |
黄国锋, 钟流举, 张振钿, 等. 有机固体废弃物堆肥的物质变化及腐熟度评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 2003, 14(5):813-818.
|
| [3] |
BUSTAMANTE M A, PAREDES C, MARHUENDA-EGEA F C, et al. Co-composting of distillery wastes with animal manures carbon and nitrogen transformations in the evaluation of compost stability[J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 72(4):551-557.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.03.030
|
| [4] |
KIM J K, LEE D J, RAVINDRAN B, et al. Evaluation of integrated ammonia recovery technology and nutrient status with an in-vessel composting process for swine manure[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 245:365-371.
doi: S0960-8524(17)31388-3
pmid: 28898832
|
| [5] |
DUAN M L, ZHANG Y H, ZHOU B B, et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on carbon components and microbial functional metabolism during cow manure-straw composting[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 303:122868.
doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122868
|
| [6] |
杨林丽. 纤维素降解菌筛选及混合菌种纤维素降解能力测定[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2013.
|
| [7] |
SELVAM K, SENBAGAM D, SELVANKUMAR T, et al. Cellulase enzyme: Homology modeling, binding site identification and molecular docking[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2017, 1150:61-67.
doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.08.067
|
| [8] |
高星爱, 王鑫, 解娇, 等. 低温秸秆降解复合微生物菌剂的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(4):144-150.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2019-0888
|
| [9] |
宋安东, 张百良, 吴坤, 等. 杂色云芝产木质纤维素酶及对稻草秸秆的降解[J]. 过程工程学报, 2005, 5(4):414-419.
|
| [10] |
付丽, 朱红雨, 杜明楠, 等. 秸秆降解菌株的筛选、鉴定及生物学特性研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2018, 23(12):39-49.
|
| [11] |
BEHERA B C, PARIDA S, DUTTA S K, et al. Isolation and identification of cellulose degrading bacteria from mangrove soil of Mahanadi River delta and their cellulase production ability[J]. American Journal of Microbiological Research, 2014, 2(1):41-46.
doi: 10.12691/ajmr-2-1-6
|
| [12] |
王海滨, 韩立荣, 冯俊涛, 等. 高效纤维素降解菌的筛选及复合菌系的构建[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2015, 23(4):421-431.
|
| [13] |
李静, 张瀚能, 赵翀, 等. 高效纤维素降解菌分离筛选、复合菌系构建及秸秆降解效果分析[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2016, 22(4):689-696.
|
| [14] |
郑丽, 张海鹏, 宋艳培, 等. 纤维素降解菌的筛选、鉴定和糖化水平研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 2017, 44(2):104-111.
|
| [15] |
吴庆珊. 纤维素降解菌筛选及其在羊粪堆肥发酵中的应用[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2018.
|
| [16] |
张必周, 高聚林, 于晓芳, 等. 玉米秸秆低温降解菌的分离与鉴定及复配菌降解效果研究[J]. 玉米科学, 2020, 28(6):168-175.
|
| [17] |
孟建宇, 陈勿力吉玛, 郭慧琴, 等. 常温和低温纤维素降解菌的分离及其降解特性[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2021, 29(1):73-84.
|
| [18] |
董雪丽, 季静, 张松皓, 等. 一株耐低温纤维素降解菌的发酵条件优化和秸秆降解研究[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2022, 30(5):978-989.
|
| [19] |
马欣雨, 孙丽娜, 卢珊, 等. 秸秆降解菌的筛选及对秸秆的降解效果[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(4):1198-1205.
|
| [20] |
孟建宇, 李蘅, 樊兆阳, 等. 低温纤维素降解菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2014, 20(1):152-156.
|
| [21] |
许玉林, 郑月霞, 叶冰莹, 等. 一株纤维素降解真菌的筛选及鉴定[J]. 微生物学通报, 2013, 40(2):220-227.
|
| [22] |
尚晓瑛, 程旭艳, 霍培书, 等. 1株堆肥耐低温纤维素降解菌的筛选、鉴定及生长特性的初步研究[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2012, 31(5):558-562.
|
| [23] |
李娜, 韩永武, 金勋, 等. 一株低温秸秆纤维素降解菌的分离、鉴定及降解特性[J]. 玉米科学, 2019, 27(1):159-163.
|
| [24] |
LI D P, FENG L, LIU K R, et al. Optimization of cold-active CMCase production by psychrotrophic Sphingomonas sp. FLX-7 from the cold region of China[J]. Cellulose, 2016, 23(2): 1335-1347.
doi: 10.1007/s10570-016-0859-4
|
| [25] |
GONG X J, ZOU H T, QIAN C R, et al. Construction of in situ degradation bacteria of corn straw and analysis of its degradation efficiency[J]. Annals of Microbiology, 2020, 70 (1): 1-15.
doi: 10.1186/s13213-020-01552-1
|