| [1] |
赵勇, 李欢, 张昭寰, 等. 食源性致病菌耐药机制研究进展[J]. 生物加工过程, 2018, 16(2):1-10.
|
| [2] |
CHRISTAKI E, MARCOU M, TOFARIDES A. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: Mechanisms, evolution, and persistence[J]. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 2020, 88(1):26-40.
doi: 10.1007/s00239-019-09914-3
pmid: 31659373
|
| [3] |
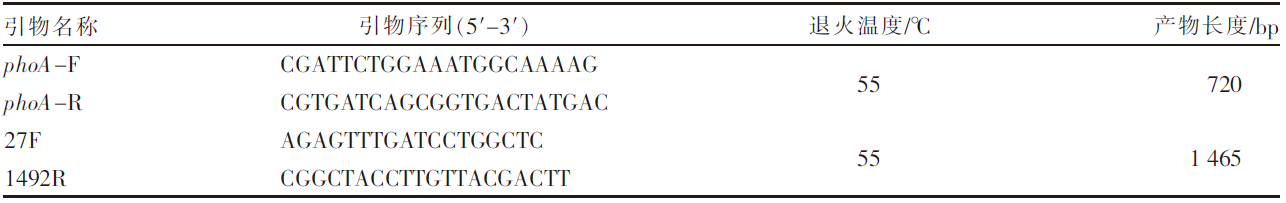
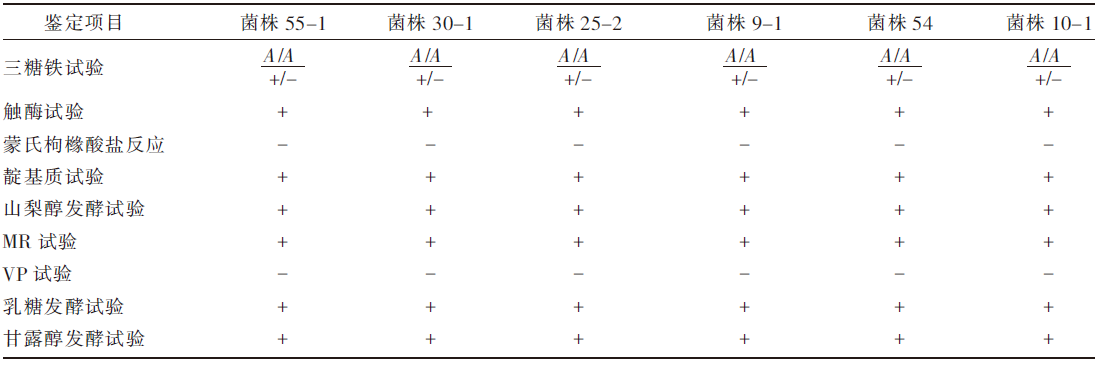
姚火春. 兽医微生物学实验指导[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2002.
|
| [4] |
CLERMONT O, BONACORSI S, BINGEN E, et al. Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(10):4555-4558.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.10.4555-4558.2000
|
| [5] |
孟相秋. 黑龙江省犊牛腹泻粪便中大肠杆菌的毒力基因和耐药性调查[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2014.
|
| [6] |
李铮. 南宁地区动物源sul3阳性大肠杆菌耐药性、致病性及其接合子特性研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2020.
|
| [7] |
刘少昆. 京津部分地区犊牛腹泻大肠杆菌分离鉴定及耐药性分析[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2016.
|
| [8] |
DENAMUR E, CLERMONT O, BONACORSI S, et al. The population genetics of pathogenic Escherichia coli[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2021, 19(1):37-54.
doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0416-x
|
| [9] |
苑晓萌, 赵效南, 李璐璐, 等. 山东地区乳房炎牛奶中大肠杆菌的分离鉴定及耐药性分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2021, 48(1):312-323.
|
| [10] |
DETHA A, SUDARWANTO M, LATIF H, et al. Fractionation and identification antimicrobial activity of Sumba mare milk protein against causative agent of subclinical mastitis[J]. Global Veterinaria, 2013, 11(5):674-680.
|
| [11] |
CLAEYS W L, VERRAES C, CARDOEN S, et al. Consumption of raw or heated milk from different species: An evaluation of the nutritional and potential health benefits[J]. Food Control, 2014, 42:188-201.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.01.045
|
| [12] |
EBRAHIMI A, MOOSAVY M H, KHATIBI S A, et al. A comparative study of the antibacterial properties of milk from different domestic animals[J]. International Journal of Dairy Technology, 2021, 74(2):425-430.
doi: 10.1111/idt.v74.2
|
| [13] |
黄晓英, 李启明, 吴华星, 等. 传统发酵食品中具有抑菌活性乳酸菌筛选及其代谢产物稳定性分析[J]. 现代食品科技, 2021, 37(11):68-78.
|
| [14] |
蔡宏宇, 刘文俊, 沈玲玲, 等. 基于三代测序技术分析新疆鲜马奶和酸马奶中乳酸菌菌群结构[J]. 中国食品学报, 2022, 22(2):291-300.
|
| [15] |
AHMED M O, CLEGG P D, WILLIAMS N J, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in equine faecal Escherichia coli isolates from North West England[J]. Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials, 2010, 9:12.
doi: 10.1186/1476-0711-9-12
|
| [16] |
CHUNG Y S, SONG J W, KIM D H, et al. Isolation and characterization of antimicrobial-resistant Escherichia coli from national horse racetracks and private horse-riding courses in Korea[J]. Journal of Veterinary Science, 2016, 17(2):199-206.
doi: 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.2.199
|
| [17] |
王国艳, 李燕平, 孙乐天, 等. 驴腹泻源大肠杆菌的耐药性分析[J]. 山西农业科学, 2019, 47(12):2199-2201.
|
| [18] |
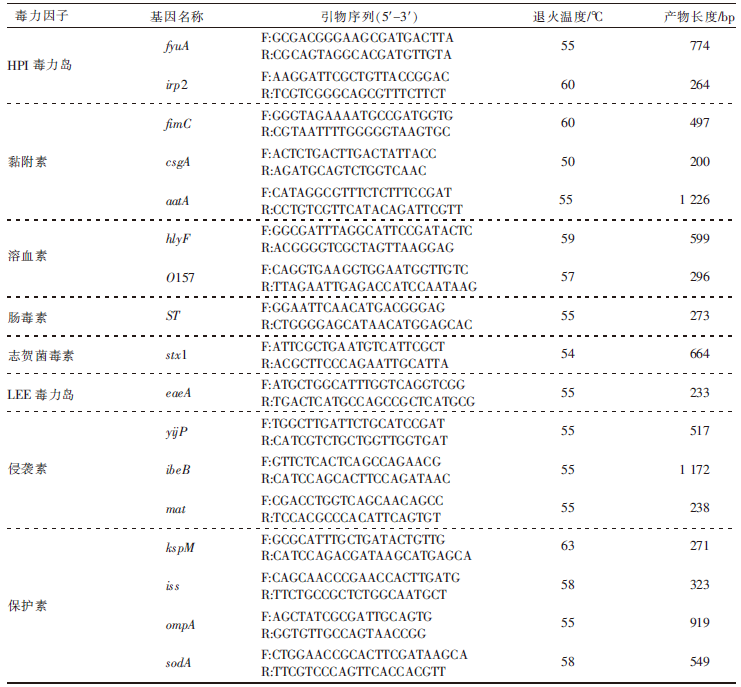
PAKBIN B, BRÜCK W M, ROSSEN J W A. Virulence factors of enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli: A review[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021, 22(18):9922.
doi: 10.3390/ijms22189922
|
| [19] |
SORA V M, MERONI G, MARTINO P A, et al. Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli: Virulence factors and antibiotic resistance[J]. Pathogens, 2021, 10(11):1355.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens10111355
|
| [20] |
ASLAM N, KHAN S U H, USMAN T, et al. Phylogenetic genotyping, virulence genes and antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli isolates from cases of bovine mastitis[J]. The Journal of Dairy Research, 2021, 88(1):78-79.
doi: 10.1017/S002202992100011X
|
| [21] |
BAILEY J K, PINYON J L, ANANTHAM S, et al. Distribution of human commensal Escherichia coli phylogenetic groups[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 2010, 48(9):3455-3456.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.00760-10
|
| [22] |
FARAHAT E M, HASSUNA N A, HAMMAD A M, et al. Distribution of integrons and phylogenetic groups among Escherichia coli causing community-acquired urinary tract infection in Upper Egypt[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2021, 67(6):451-463.
doi: 10.1139/cjm-2020-0292
|
| [23] |
RESHADI P, HEYDARI F, GHANBARPOUR R, et al. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance of potentially human-pathogenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from riding horses[J]. BMC Veterinary Research, 2021, 17(1):131.
doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-02832-x
|