北方农业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 112-118.doi: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2022.05.16
基于遥感信息的植被变化对岱海湖面积的影响
刘凯1,2, 孙丽2,3, 张志成1,4, 张鹏1, 刘金善1, 张存霞1
- 1.乌兰察布市农林科学研究所,内蒙古 乌兰察布 012000
2.农业农村部耕地利用遥感重点实验室,北京 100121
3.农业农村部规划设计研究院,北京 100121
4.内蒙古农业大学,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010018
Influence of vegetation change on the area of Daihai Lake based on remote sensing information
LIU Kai1,2, SUN Li2,3, ZHANG Zhicheng1,4, ZHANG Peng1, LIU Jingshan1, ZHANG Cunxia1
- 1. Ulanqab Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences,Ulanqab 012000,China
2. Key Laboratory of Cultivated Land Use,Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs,Beijing 100121,China
3. Academy of Agriculture Planning and Engineering,Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs,Beijing 100121,China
4. Inner Mongolia Agricultural University,Hohhot 010018,China
摘要:
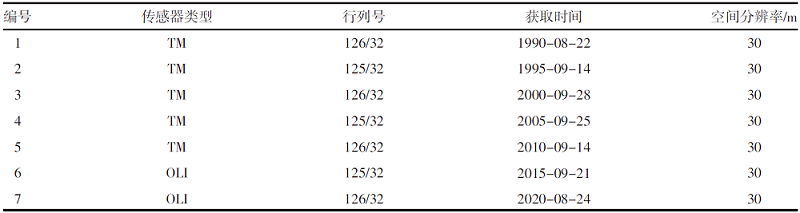
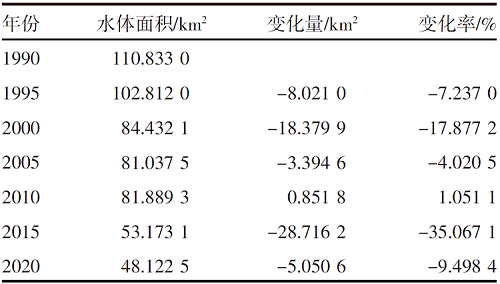
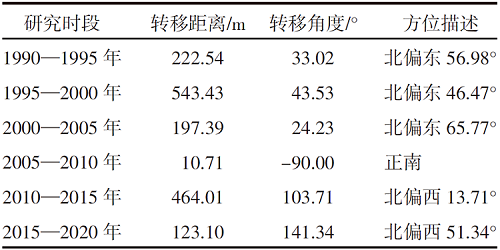
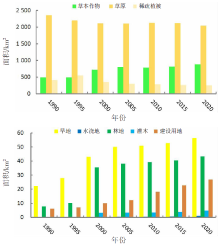
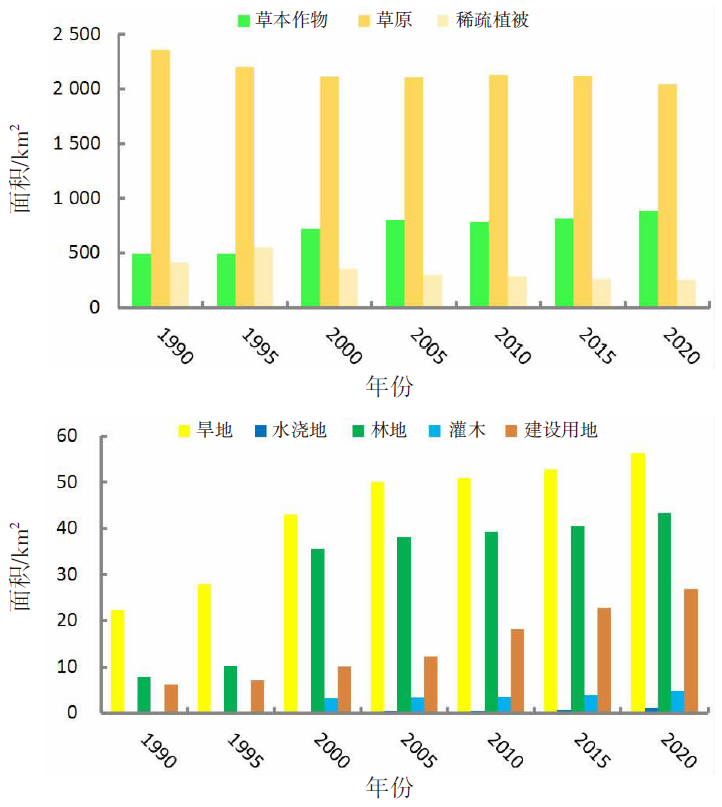
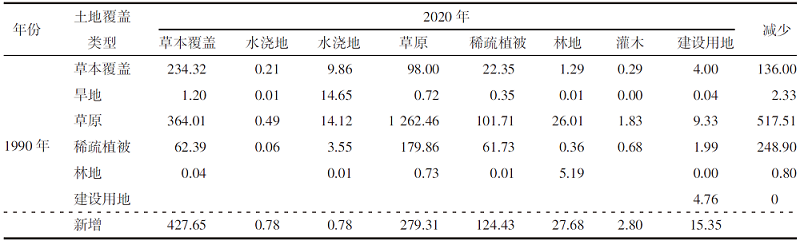
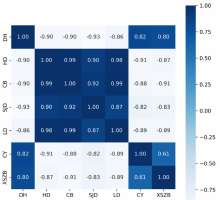
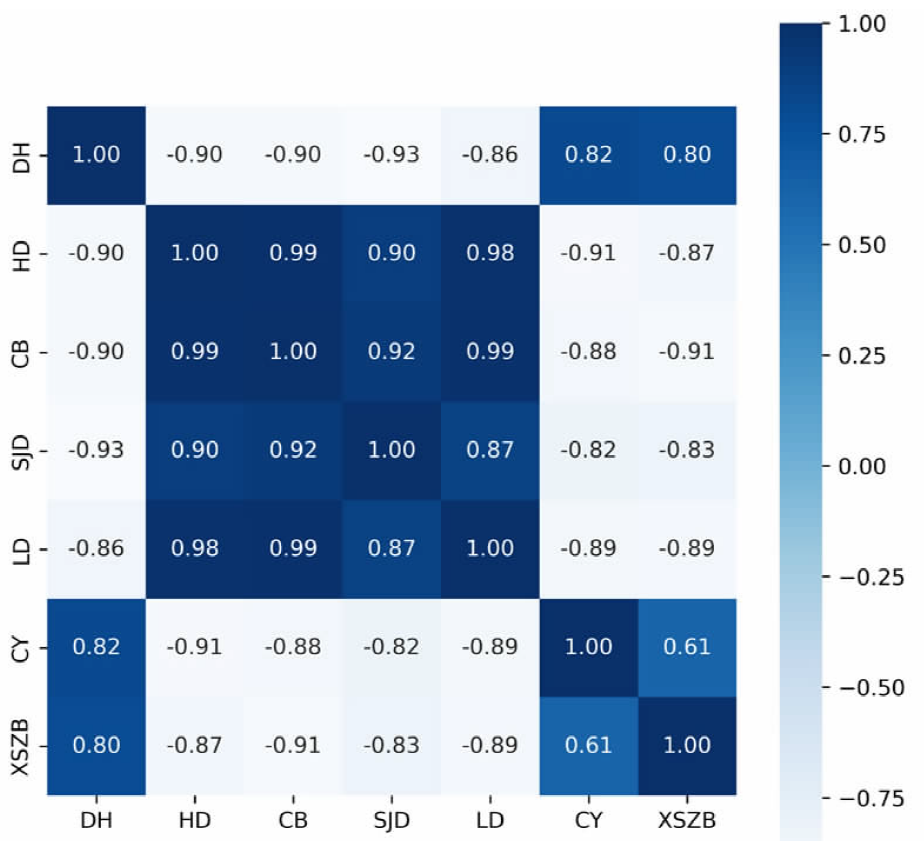
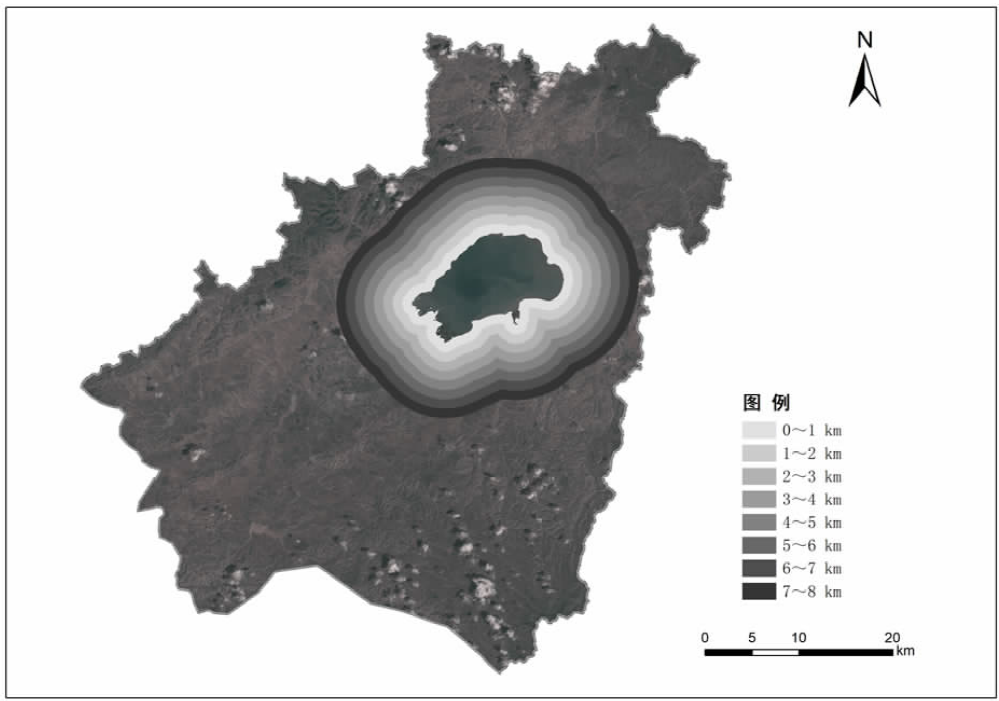
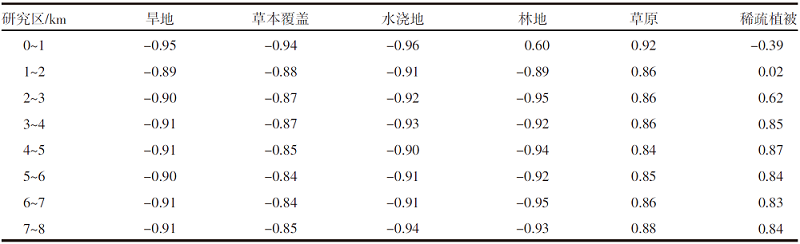
【目的】通过探索植被覆盖变化对岱海湖面积的影响,明确人类生产活动方式及范围与湿地变化的相互关系,为科学制定湖泊保护规划提供理论依据。【方法】研究区域为岱海湖主要支流形成的流域,在获取1990—2020年7期该区域遥感资料的基础上,采用重心迁移分析、土地类型转移矩阵、相关性分析等方法,分析流域内植被变化对岱海湖面积的影响。【结果】1990—2020年岱海湖面积呈下降趋势,1990年为110.833 0 km2,2020年为48.122 5 km2,减小62.710 5 km2,2005年以前湖面重心快速向东北方向转移,2005年以后逐步向北偏西方向迁移;岱海湖面积变化与旱地、草本覆盖、水浇地、林地呈显著负相关,相关系数分别为-0.90、-0.90、-0.93、-0.86;与草原和稀疏植被呈显著正相关,相关系数分别为0.82和0.80;岱海湖周边1 km内旱地、草本覆盖、水浇地、草原的面积与岱海湖面积变化相关性较高,相关系数分别为-0.95、-0.94、-0.96、0.92。【结论】岱海湖周边1 km内的农田开垦对原始草原植被的破坏是岱海湖面积缩减的主要生产活动因素。
中图分类号:
- P343.3