畜牧与饲料科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 121-128.doi: 10.12160/j.issn.1672-5190.2023.02.018
• 动物疾病防控 • 上一篇
不同驱虫药对伊犁马驱虫效果及血液生理指标的影响
马玉辉1,2,陈浩南1,蒋硕1,阿依尼尕尔·阿不来提1,李海2,叶斯哈提·胡安2,奴尔兰·阿克亚孜2,杨开伦1
- 1.新疆农业大学动物科学学院,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830052
2.昭苏县西域马业有限责任公司,新疆 昭苏 835600
Efficacy of Different Anthelmintic Drugs and Their Effects on Blood Physiological Parameters in Yili Horses
MA Yuhui1,2,CHEN Haonan1,JIANG Shuo1,Ayinigaer Abulaiti1,LI Hai2,Yeshatti Juan2,Nulan Akyazi2,YANG Kailun1
- 1. College of Animal Science,Xinjiang Agricultural University,Urumqi 830052,China
2. Zhaosu County Western Region Horse Industry Co.,Ltd.,Zhaosu 835600,China
摘要:
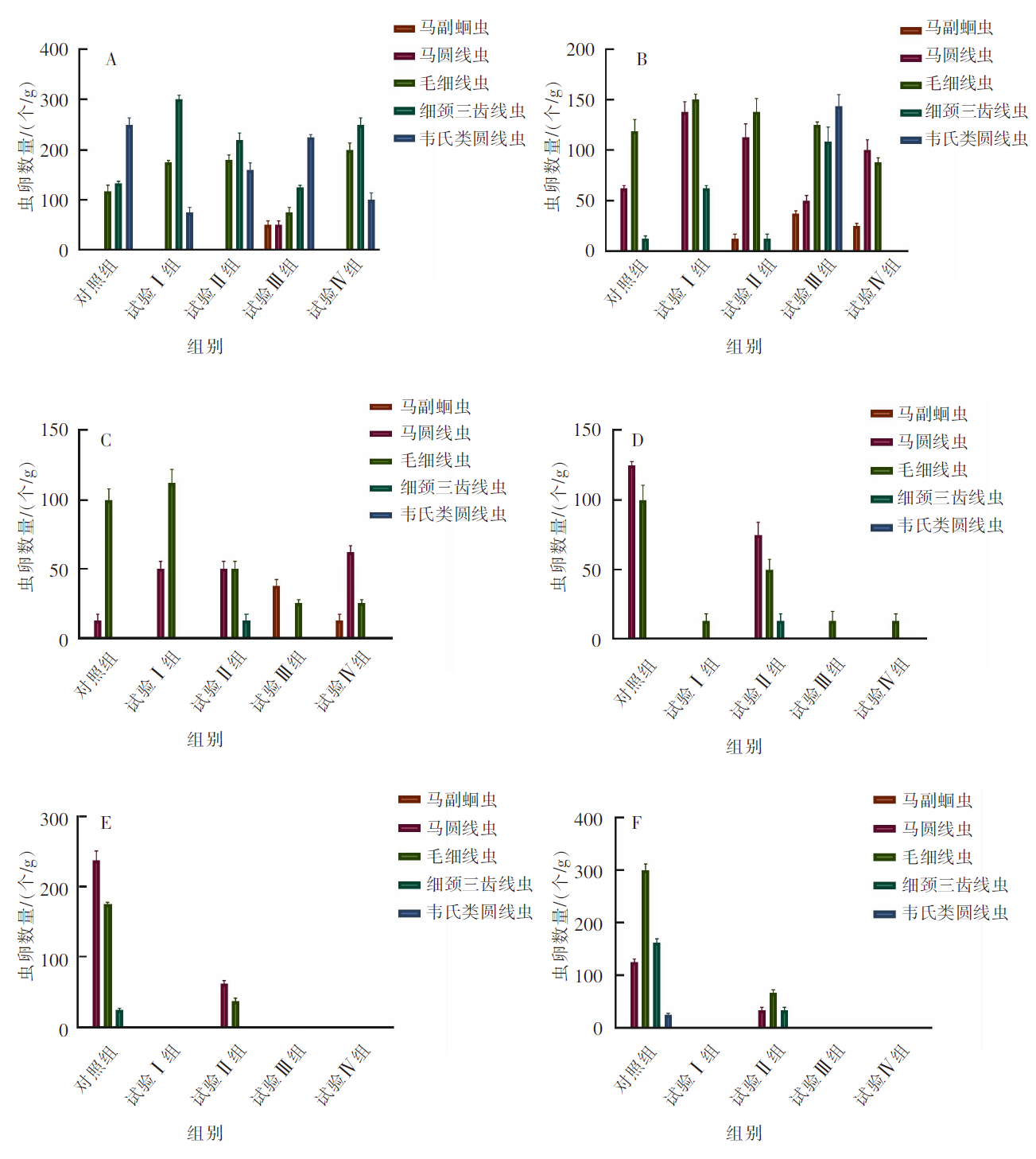
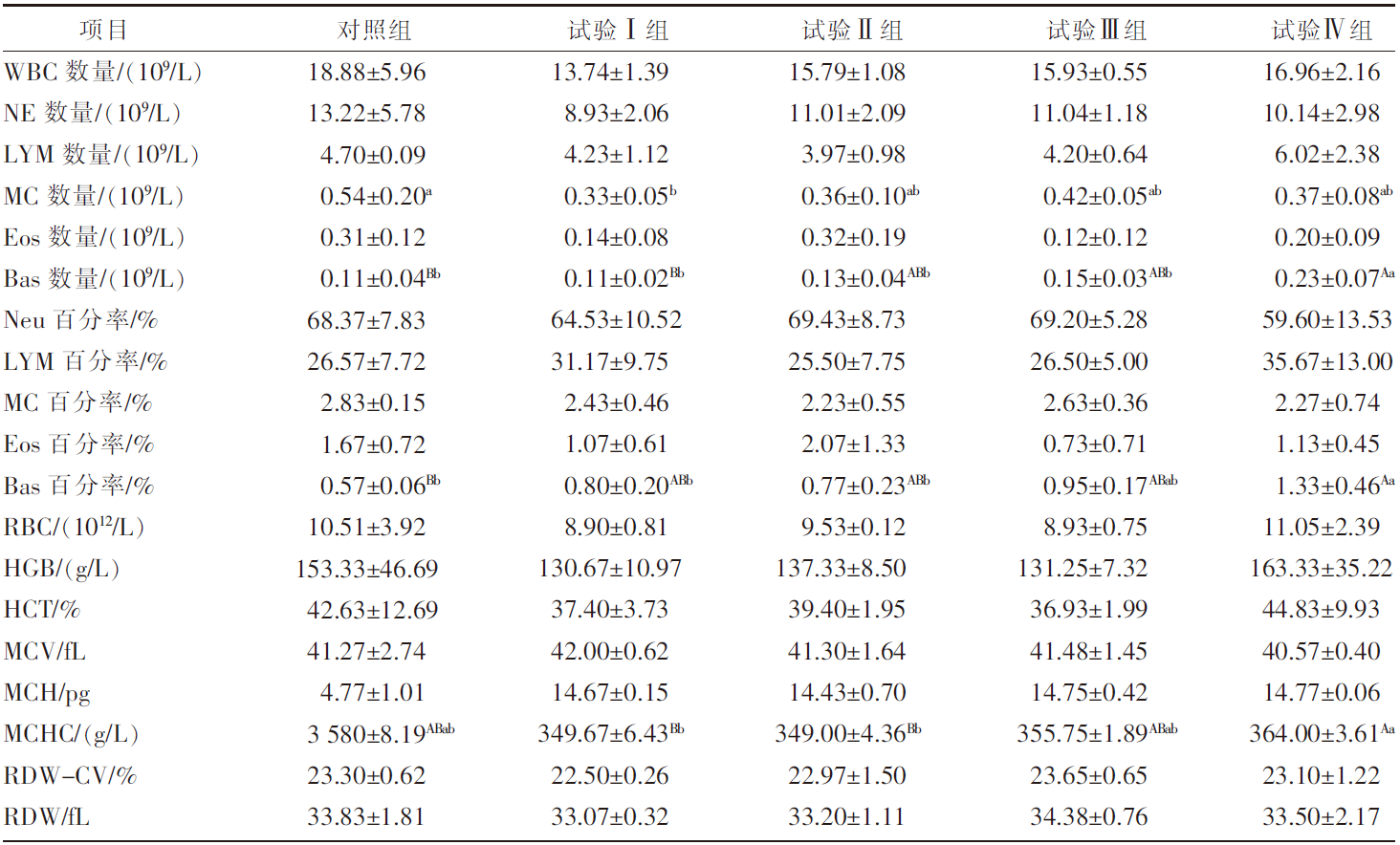
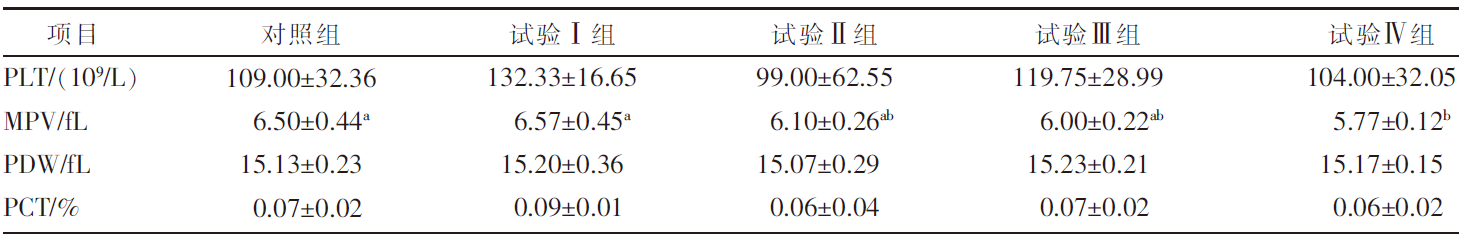
[目的]探究不同驱虫药驱虫前后伊犁马粪便中虫卵种类及数量的变化以及驱虫药对马匹血液生理指标的影响。[方法]选择平均体重(265.5±35.6)kg、出生日期相近的1岁伊犁马40匹,随机分为5组,每组8匹,分别为对照组、试验Ⅰ组、试验Ⅱ组、试验Ⅲ组和试验Ⅳ组。在相同的饲养管理和日粮营养水平条件下,试验Ⅰ组给予伊维菌素,试验Ⅱ组给予吡喹酮,试验Ⅲ组给予阿苯达唑,试验Ⅳ组给予伊维菌素和阿苯达唑的混合药剂驱虫,对照组不驱虫。在驱虫前及驱虫后1、2、3、7、14 d采集马匹粪便样本,进行虫卵鉴别与计数,计算寄生虫感染率;驱虫后14 d采集马匹血液样品,测定血液生理指标。[结果]①驱虫后14 d,除对照组粪便中虫卵种类和数量较多,试验Ⅱ组粪便中有少量虫卵外,其余试验组均未发现虫卵;与对照组相比,试验Ⅰ组、试验Ⅲ组、试验Ⅳ组马匹粪便中每克粪便虫卵数(eggs per gram,EPG)均降低了612.50个(P<0.01),试验Ⅱ组EPG降低了562.50个(P<0.01)。②试验Ⅰ组单核细胞数量极显著(P<0.01)低于对照组;试验Ⅳ组嗜碱性粒细胞数量极显著(P<0.01)高于对照组和试验Ⅰ组,显著(P<0.05)高于试验Ⅱ组和试验Ⅲ组;试验Ⅳ组嗜碱性粒细胞百分率(P<0.01)极显著高于对照组,显著(P<0.05)高于试验Ⅰ组和试验Ⅱ组;试验Ⅳ组平均红细胞血红蛋白浓度极显著(P<0.01)高于试验Ⅰ组和试验Ⅱ组。③对照组和试验Ⅰ组平均血小板体积均显著(P<0.05)高于试验Ⅳ组。[结论]4种驱虫药或其组合对伊犁马肠道寄生虫均有显著的驱虫效果,其中,阿苯达唑能够显著减少马匹粪便中EPG数量,有效防治寄生虫感染,并对马匹血液生理指标有积极影响。
中图分类号: