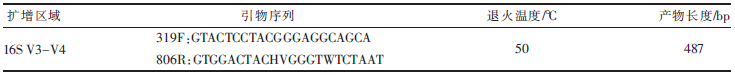
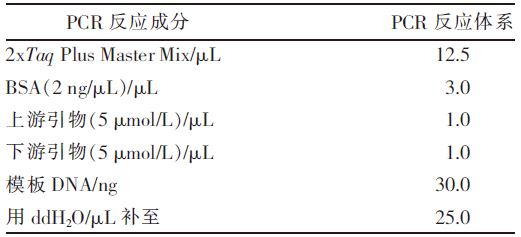
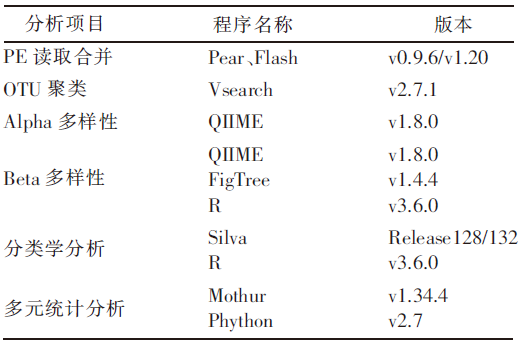
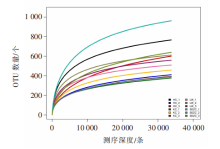
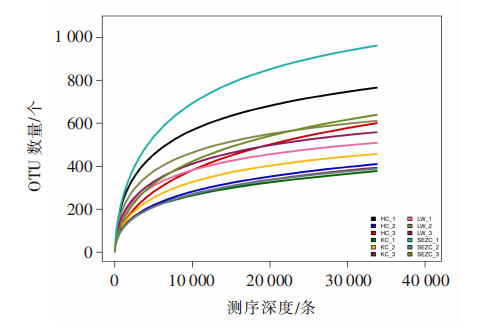
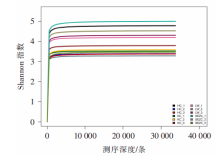
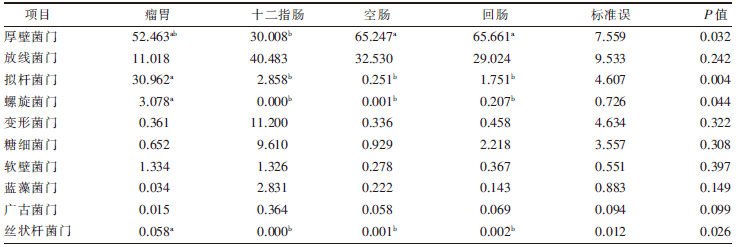
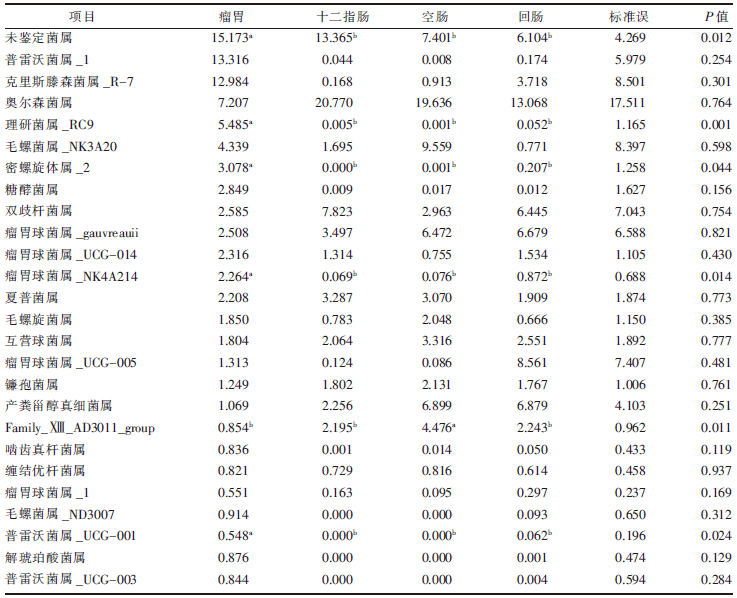
| [1] |
MACKIE R I, WHITE B A. Recent advances in rumen microbial ecology and metabolism: Potential impact on nutrient output[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 1990, 73(10):2971-2995.
pmid: 2178174
|
| [2] |
RUSSELL J B, RYCHLIK J L. Factors that alter rumen microbial ecology[J]. Science, 2001, 292(5519):1119-1122.
doi: 10.1126/science.1058830
pmid: 11352069
|
| [3] |
DODD D, SPITZER M H, VAN TREUREN W, et al. A gut bacterial pathway metabolizes aromatic amino acids into nine circulating metabolites[J]. Nature, 2017, 551(7682):648-652.
doi: 10.1038/nature24661
|
| [4] |
KADOKI M, PAT A, THAISS C C, et al. Organism-level analysis of vaccination reveals networks of protection across tissues[J]. Cell, 2017, 171(2):398-413.
doi: S0092-8674(17)30949-2
pmid: 28942919
|
| [5] |
BAUER P V, DUCA F A, WAISE T, et al. Metformin alters upper small intestinal microbiota that impact a glucose-SGLT1-sensing glucoregulatory pathway[J]. Cell Metabolism, 2018, 27(1):101-117.
doi: S1550-4131(17)30571-5
pmid: 29056513
|
| [6] |
LETTAT A, NOZIERE P, SILBERBERG M, et al. Rumen microbial and fermentation characteristics are affected differently by bacterial probiotic supplementation during induced lactic and subacute acidosis in sheep[J]. BMC Microbiology, 2012, 12(1):1-12.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-1
|
| [7] |
RIYANTI L, SURYAHADI, EVVYERNIE D. In vitro fermentation characteristics and rumen microbial population of diet supplemented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and rumen microbe probiotics[J]. Media Peternakan, 2016, 39(1):40-45.
doi: 10.5398/medpet
|
| [8] |
RAMIREZ-RESTREPO C A, TAN C, O′NEILL C J, et al. Methane production, fermentation characteristics, and microbial profiles in the rumen of tropical cattle fed tea seed saponin supplementation[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2016, 216:58-67.
doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.03.005
|
| [9] |
金磊, 周美丽, 王禄禄, 等. 不同能量代谢率的山羊瘤胃微生物结构与组成的差异性[J]. 微生物学通报, 2018, 45(1):91-101.
|
| [10] |
LIU X, FAN H, DING X, et al. Analysis of the gut microbiota by high-throughput sequencing of the V5-V6 regions of the 16S rRNA gene in donkey[J]. Current Microbiology, 2014, 68(5):657-662.
doi: 10.1007/s00284-014-0528-5
pmid: 24452427
|
| [11] |
DOUGAL K, HARRIS P A, EDWARDS A, et al. A comparison of the microbiome and the metabolome of different regions of the equine hindgut[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2012, 82(3):642-652.
doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2012.01441.x
pmid: 22757649
|
| [12] |
GU S, CHEN D, ZHANG J, et al. Bacterial community mapping of the mouse gastrointestinal tract[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(10):e74957.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074957
|
| [13] |
康润敏, 李瑶, 吕学斌, 等. 利用16S rDNA扩增子测序技术分析不同品种猪盲肠微生物菌落多样性[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2017, 44(11):3121-3129.
|
| [14] |
林奕岑, 徐帅, 倪学勤, 等. 利用Illumina MiSeq测序平台分析肉鸡盲肠微生物多样性[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2016, 21(12):65-73.
|
| [15] |
许宇静, 张煜坤, 沈雪梅, 等. 采用Illumina MiSeq 测序技术分析断奶幼兔盲肠微生物群落的多样性[J]. 动物营养学报, 2015, 27(9):2793-2802.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2015.09.017
|
| [16] |
SANDRI M, MANFRIN C, PALLAVICINI A, et al. Microbial biodiversity of the liquid fraction of rumen content from lactating cows[J]. Animal, 2014, 8(4):572-579.
doi: 10.1017/S1751731114000056
pmid: 24524278
|
| [17] |
李碧波. 绒山羊胃肠道微生物区系及其对日粮响应的研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2020.
|
| [18] |
QIN J, LI R, RAES J, et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7285):59-65.
doi: 10.1038/nature08821
|
| [19] |
SINGH K M, AHIR V B, TRIPATHI A K, et al. Metagenomic analysis of Surti buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) rumen: A preliminary study[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2012, 39(4):4841-4848.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-1278-0
pmid: 21947953
|
| [20] |
CHEN Y, PENNER G B, LI M, et al. Changes in bacterial diversity associated with epithelial tissue in the beef cow rumen during the transition to a high-grain diet[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(16):5770-5781.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00375-11
pmid: 21705529
|
| [21] |
EVANS N J, BROWN J M, MURRAY R D, et al. Characterization of novel bovine gastrointestinal tract Treponema isolates and comparison with bovine digital dermatitis Treponemes[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(1):138-147.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00993-10
|
| [22] |
TUMBAUGH P J, LEY R E, MAHOWALD M A, et al. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest[J]. Nature, 2006, 444(7122):1027-1031.
doi: 10.1038/nature05414
|
| [23] |
GUO X, XIA X, TANG R, et al. Real-time PCR quantification of the predominant bacterial divisions in the distal gut of Meishan and Landrace pigs[J]. Anaerobe, 2008, 14(4):224-228.
doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2008.04.001
pmid: 18524640
|
| [24] |
GANGARAPU V, YILDIZ K, INCE A T, et al. Role of gut microbiota: Obesity and NAFLD[J]. The Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology, 2014, 25(2):133-140.
|
| [25] |
MOUZAKI M, COMELLI E M, AREDT B M, et al. Intestinal microbiota in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 58(1):120-127.
doi: 10.1002/hep.26319
pmid: 23401313
|
| [26] |
王继文, 王立志, 闫天海, 等. 山羊瘤胃与粪便微生物多样性[J]. 动物营养学报, 2015, 27(8):2559-2571.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2015.08.030
|
| [27] |
JESUS-LABOY K M, GODOY-VITORINO F, PICENO Y M, et al. Comparison of the fecal microbiota in feral and domestic goats[J]. Genes, 2011, 3(1):1-18.
doi: 10.3390/genes3010001
|
| [28] |
丁赫, 刘旺景, 敖长金, 等. 饲粮中添加沙葱粉或复合益生菌制剂对杜寒杂交羊瘤胃发酵参数和瘤胃液菌群多样性的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2019, 33(1):324-333.
|
| [29] |
STEVENSON D M, WEIMERR P J. Dominance of Prevotella and low abundance of classical ruminal bacterial species in the bovine rumen revealed by relative quantification real-time PCR[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2007, 75(1):165-174.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-006-0802-y
|
| [30] |
DE OLIVEIRA M N V, JEWELL K A, FREITAS F S, et al. Characterizing the microbiota across the gastrointestinal tract of a Brazilian Nelore steer[J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2013, 164(3):307-314.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.02.013
|
| [31] |
BEKELE A Z, KOIKE S, KOBAYASHI Y. Genetic diversity and diet specificity of ruminal Prevotella revealed by 16S rRNA gene-based analysis[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2010, 305(1):49-57.
doi: 10.1111/fml.2010.305.issue-1
|
| [32] |
WISE M G, SIRAGUSA G R. Quantitative analysis of the intestinal bacterial community in one-to three-week-old commercially reared broiler chickens fed conventional or antibiotic-free vegetable-based diets[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2010, 102(4):1138-1149.
|
| [33] |
TOROK V A, ALLISON G E, PERCY N J, et al. Influence of antimicrobial feed additives on broiler commensal posthatch gut microbiota development and performance[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2011, 77(10):3380-3390.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.02300-10
pmid: 21441326
|
| [34] |
CHO S, CHO K, SHIN E, et al. 16S rDNA analysis of bacterial diversity in three fractions of cow rumen[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2006, 16(1):92-101.
|
| [35] |
FREY J C, PELL A N, BERTHIAUME R, et al. Comparative studies of microbial populations in the rumen, duodenum, ileum and faeces of lactating dairy cows[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2010, 108(6):1982-1993.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04602.x
pmid: 19863686
|
| [36] |
张红涛. 不同玉米青贮水平对荷斯坦后备牛瘤胃液微生物组及其代谢组的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017.
|
| [37] |
GIRIJA D, DEEPA K, XAVIER F, et al. Analysis of cow dung microbiota-A metagenomic approach[J]. Indian Journal of Biochemistry, 2013, 12(3):372-378.
|