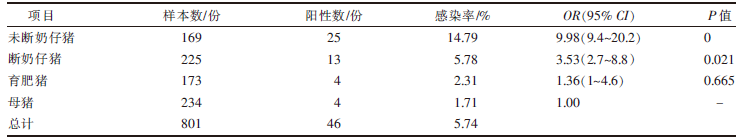
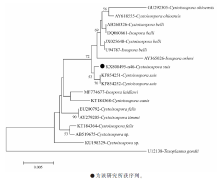
| [1] |
SHRESTHA A, ABD-ELFATTAH A, FREUDENSCHUSS B, et al. Cystoisospora suis - A model of mammalian cystoisosporosis[J]. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2015, 2:68.
|
| [2] |
王朋林, 陈凯丽, 郑玲, 等. 猪囊孢球虫和毕氏肠微孢子虫双重巢式PCR检测方法的建立[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2021, 41(3):500-504.
|
| [3] |
张伟. 猪球虫病的流行病学、临床症状、实验室检查及防治[J]. 现代畜牧科技, 2018(3):81.
|
| [4] |
DE ARAUJO H G, DA SILVA J T, SARMENTO W F, et al. Diversity of enteric coccidia in pigs from the paraíba semiarid region of northeastern Brazil[J]. Brazilian Journal of Veterinary Parasitology, 2020, 29(4):e009120.
|
| [5] |
PETTERSSON E, SJÖLUND M, DÓREA F C, et al. Gastrointestinal parasites in Swedish pigs: Prevalence and associated risk factors for infection in herds where animal welfare standards are improved[J]. Veterinary Parasitology, 2021, 295:109459.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2021.109459
pmid: 34029850
|
| [6] |
JOHNSON J, SAMARASINGHE B, BUDDLE R, et al. Molecular identification and prevalence of Isospora sp. in pigs in Western Australia using a PCR-RFLP assay[J]. Experimental Parasitology, 2008, 120(2):191-193.
doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2008.06.005
|
| [7] |
GONG Q L, ZHAO W X, WANG Y C, et al. Prevalence of coccidia in domestic pigs in China between 1980 and 2019:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Parasites and Vectors, 2021, 14(1):248.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04611-x
|
| [8] |
刘文婷, 王飞. 华北地区猪场仔猪等孢球虫病的流行病学调查[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2020(18):86-89,163.
|
| [9] |
姚雷. 猪等孢球虫部分生物学特性研究及巢式PCR方法建立[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2007.
|
| [10] |
RUTTKOWSKI B, JOACHIM A, DAUGSCHIES A. PCR-based differentiation of three porcine Eimeria species and Isospora suis[J]. Veterinary Parasitology, 2001, 95(1):17-23.
doi: 10.1016/S0304-4017(00)00408-8
|
| [11] |
盛祖勋, 汪凯, 汤川川, 等. 安徽省部分地区规模化猪场猪等孢球虫病流行病学调查[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2017, 39(8):678-681.
|
| [12] |
JOACHIM A, RUTTKOWSKI B, ZIMMERMANN M, et al. Detection of Isospora suis (biester and Murray 1934) in piglet faeces: Comparison of microscopy and PCR[J]. Journal of Veterinary Medicine B, Infectious Diseases and Veterinary Public Health, 2004, 51(3):140-142.
doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.2004.00736.x
|
| [13] |
戚南山, 康桦华, 林栩慧, 等. 猪等孢球虫研究进展[J]. 动物医学进展, 2019, 40(6):88-91.
|
| [14] |
SYMEONIDOU I, TASSIS P, GELASAKIS A Ι, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of intestinal parasite infections in Greek swine farrow-to-finish farms[J]. Pathogens, 2020, 9(7):556.
doi: 10.3390/pathogens9070556
|
| [15] |
KARAMON J, ZIOMKO I, CENCEK T. Prevalence of Isospora suis and Eimeria spp. in suckling piglets and sows in Poland[J]. Veterinary Parasitology, 2007, 147(1/2):171-175.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.03.029
|
| [16] |
黄仪娟. 广东猪等孢球虫感染情况调查及其部分生物学特性研究[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2016.
|
| [17] |
SCHUBNELL F, VON AH S, GRAAGE R, et al. Occurrence, clinical involvement and zoonotic potential of endoparasites infecting Swiss pigs[J]. Parasitology International, 2016, 65(6 Pt A):618-624.
doi: S1383-5769(16)30227-6
pmid: 27639842
|
| [18] |
刘锦, 梁全顺. 猪等孢球虫的分离、分子生物学初步鉴定及PCR诊断方法的建立[J]. 福建畜牧兽医, 2010, 32(4):11-13.
|
| [19] |
MATSUBAYASHI M, TAKAYAMA H, KUSUMOTO M, et al. First report of molecular identification of Cystoisospora suis in piglets with lethal diarrhea in Japan[J]. Acta Parasitologica, 2016, 61(2):406-411.
|
| [20] |
臧传佼. 猪等孢球虫的分离鉴定及其防治药物的效力试验[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2015.
|