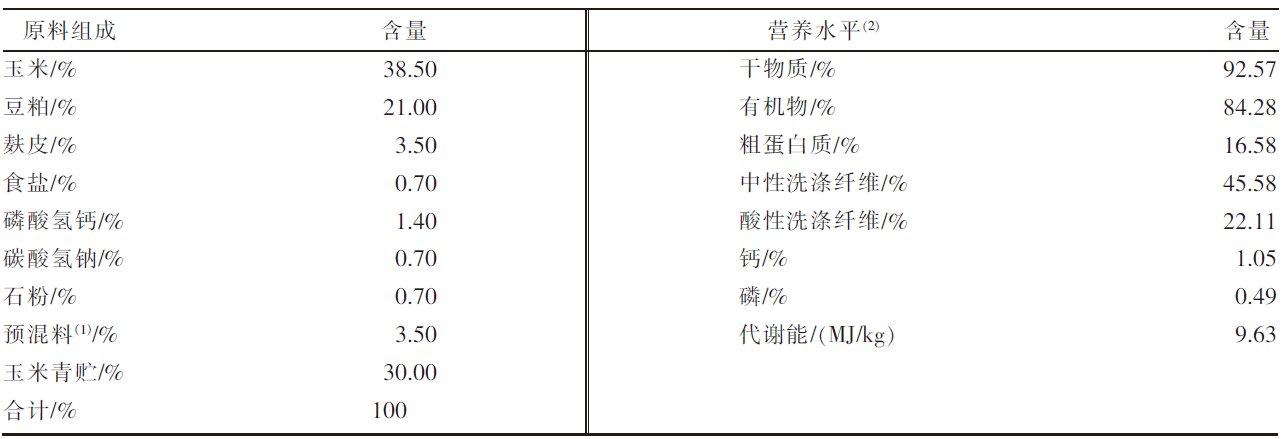
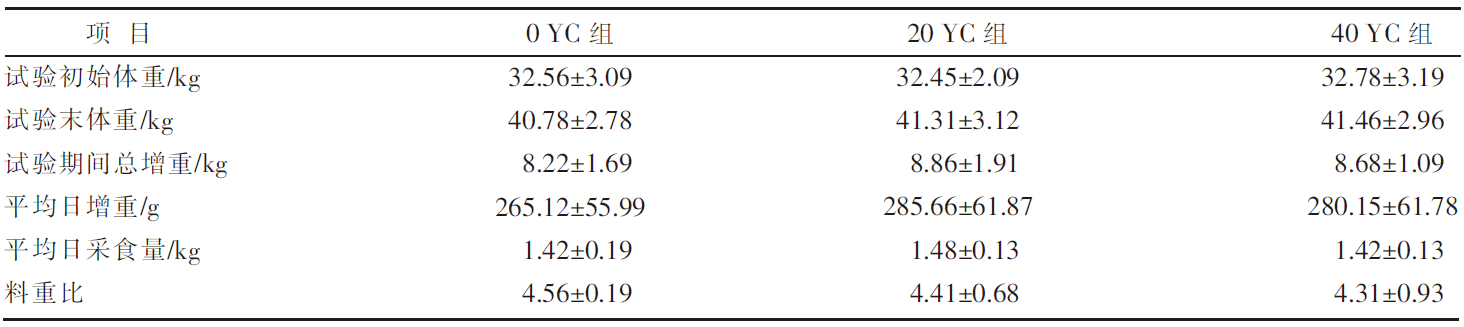
| [1] |
赵国宏, 王世琴, 刁其玉, 等. 酵母培养物在反刍动物高精料饲粮条件下的应用研究进展[J]. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(8):3473-3481.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2019.08.006
|
| [2] |
BRUNO R G S, RUTIGLIANO H M, CERRI R L, et al. Effect of feeding Saccharomyces cerevisiae on performance of dairy cows during summer heat stress[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2009, 150(3/4):175-186.
doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2008.09.001
|
| [3] |
DU D W, FENG L, CHEN P, et al. Effects of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cultures on performance and immune performance of dairy cows during heat stress[J]. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2022, 9:851184.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.851184
|
| [4] |
李海滨, 林英庭, 朱风华, 等. 酵母培养物对崂山奶山羊产奶性能、养分表观消化率、抗氧化能力及免疫功能的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34(7):4621-4629.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2022.07.050
|
| [5] |
BRUNO R G S, RUTIGLIANO H, CERRI R L, et al. Effect of feeding yeast culture on reproduction and lameness in dairy cows under heat stress[J]. Animal Reproduction Science, 2009, 113(1/4):11-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2008.06.007
|
| [6] |
ZHU W, ZHANG B X, YAO K Y, et al. Effects of supplemental levels of Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product on lactation performance in dairy cows under heat stress[J]. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2016, 29(6):801-806.
doi: 10.5713/ajas.15.0440
|
| [7] |
惠文. 复合酵母菌培养物对肉羊生长性能、免疫机能及抗氧化能力指标的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2020(13):60-63.
|
| [8] |
SHAN Q, MA F T, JIN Y H, et al. Chromium yeast alleviates heat stress by improving antioxidant and immune function in Holstein mid-lactation dairy cows[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2020, 269:114635.
doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2020.114635
|
| [9] |
MALEKKHAHI M, TAHMASBI A M, NASERIAN A A, et al. Effects of essential oils,yeast culture and malate on rumen fermentation,blood metabolites,growth performance and nutrient digestibility of Baluchi lambs fed high‐concentrate diets[J]. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2015, 99(2):221-229.
doi: 10.1111/jpn.12230
|
| [10] |
寇慧娟, 陈玉林, 刘敬敏, 等. 酵母培养物对羔羊生产性能、营养物质表观消化率及瘤胃发育的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(8):45-50.
|
| [11] |
陈作栋, 周珊, 赵向辉, 等. 酵母培养物对生长期锦江黄牛生产性能、抗氧化能力及免疫性能的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2017, 29(5):1767-1773.
|
| [12] |
POPPY G D, RABIEE A R, LEAN I J, et al. A meta-analysis of the effects of feeding yeast culture produced by anaerobic fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on milk production of lactating dairy cows[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2012, 95(10):6027-6041.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2012-5577
|
| [13] |
罗春发, 喻麟, 刘超, 等. 酵母培养物在动物生产中的应用研究进展[J]. 饲料博览, 2015(11):42-44.
|
| [14] |
ABOU ELENIN E I M, EL-GALIL E R A, ETMAN K E I, et al. Improvement of rumen fermentation and performance of growing lambs by adding natural microbial resources[J]. Asian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2016, 10(3):202-212.
doi: 10.3923/ajas.2016.202.212
|
| [15] |
CHAUCHEYRAS F, FONTY G, BERTIN G, et al. Effects of live Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells on zoospore germination,growth,and cellulolytic activity of the rumen anaerobic fungus,Neocallimastix frontalis MCH3[J]. Current Microbiology, 1995, 31(4):201-205.
doi: 10.1007/BF00298373
|
| [16] |
ALUGONGO G M, XIAO J X, WU Z H, et al. Utilization of yeast of Saccharomyces cerevisiae origin in artificially raised calves[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 2017, 8(1):34.
doi: 10.1186/s40104-017-0165-5
|
| [17] |
WU G Y. Principles of animal nutrition[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017.
|
| [18] |
田丰, 王利, 金海, 等. 饲喂水平对巴美肉羊生产性能、肉品质和肌肉氨基酸组成的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2021, 57(5):160-164.
|
| [19] |
狄方馨. 复合酵母菌固态制剂对波尔山羊生长性能、屠宰性能及经济效益的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2020(5):54-57.
|
| [20] |
TITI H H, ABDULLAH A Y, LUBBADEH W F, et al. Growth and carcass characteristics of male dairy calves on a yeast culture-supplemented diet[J]. South African Journal of Animal Science, 2008, 38(3):174-183.
|
| [21] |
赵艳兵, 任有蛇, 张春香, 等. 日粮中添加荞麦秸秆对绵羊屠宰性能、器官指数、肉品质及血液生化指标的影响[J]. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 37(12):872-878.
|
| [22] |
官丽辉, 刘海斌, 张立永, 等. 日粮不同能量水平对育成鸡体增质量、血液生化指标及内脏器官发育的影响[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2014, 34(2):350-356.
|