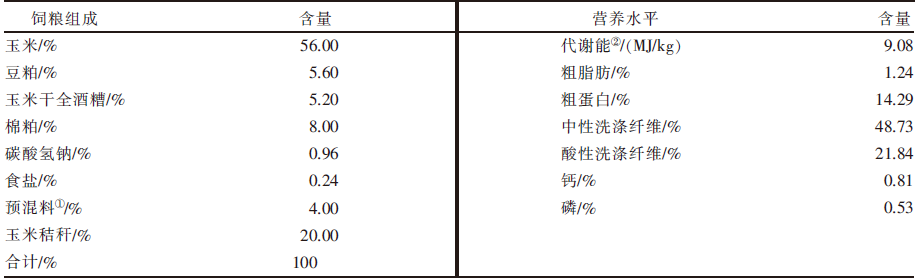
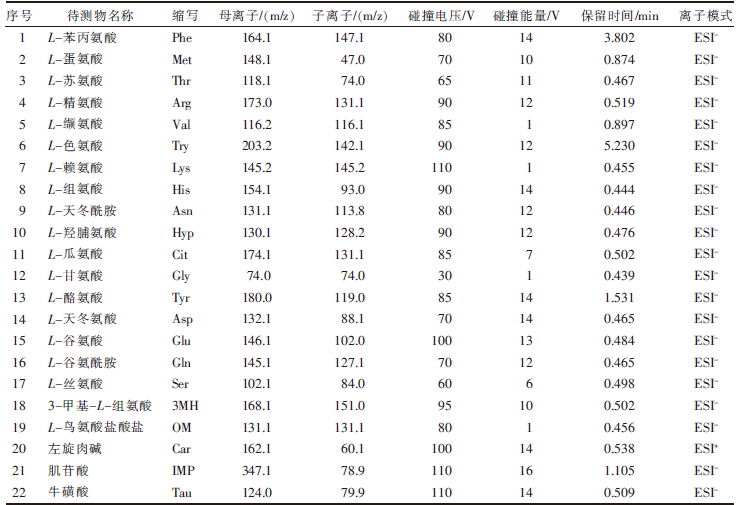
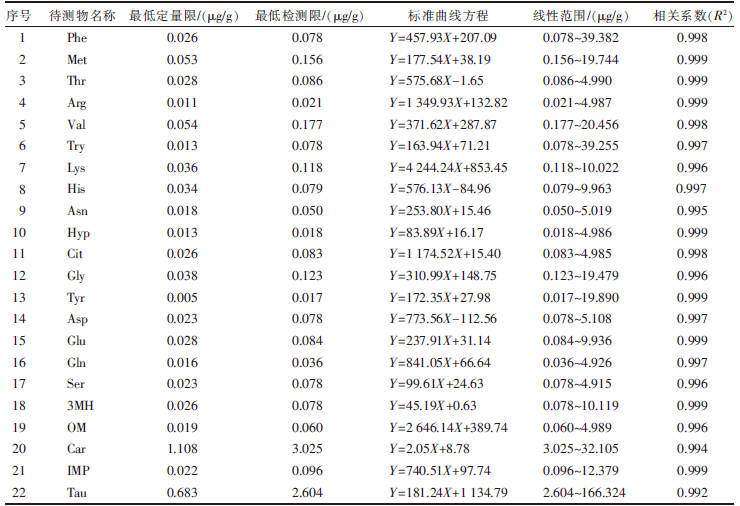
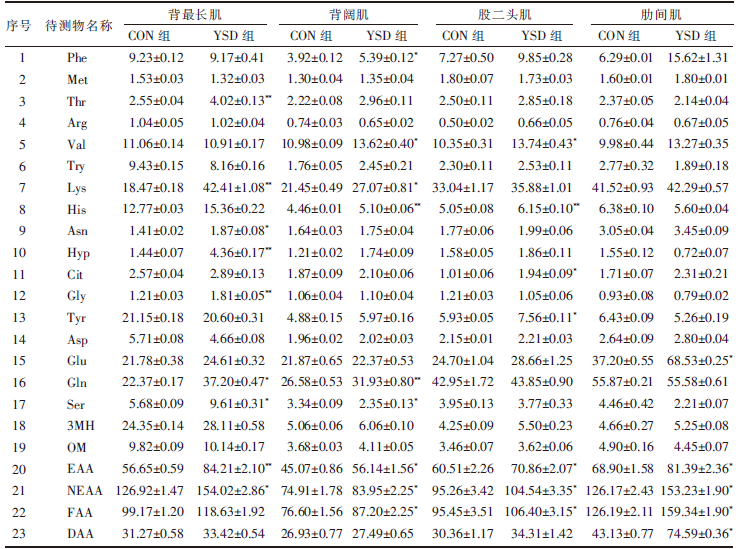
| [1] |
刁其玉, 马涛. 我国新版《肉羊营养需要量》概要[J]. 饲料工业, 2022, 43(11):1-7.
|
| [2] |
中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴2021[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022.
|
| [3] |
陈秋菊, 王韵斐, 王文义, 等. 复合益生菌培养物对肉羊生长性能、屠宰性能和免疫功能的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2022(5):58-61.
|
| [4] |
MAVROMMATIS A, MITSIOPOULOU C, CHRISTODOULOU C, et al. Dietary supplementation of a live yeast product on dairy sheep milk performance, oxidative and immune status in peripartum period[J]. Journal of Fungi, 2020, 6(4):334.
doi: 10.3390/jof6040334
|
| [5] |
DETERS E L, STOKES R S, GENTHER-SCHROEDER O N, et al. Effects of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product in receiving diets of newly weaned beef steers. Ⅱ. digestibility and response to a vaccination challenge[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2018, 96(9):3906-3915.
doi: 10.1093/jas/sky247
|
| [6] |
TITI H H, ABDULLAH A Y, LUBBADEH W F, et al. Growth and carcass characteristics of male dairy calves on a yeast culture-supplemented diet[J]. South African Journal of Animal Science, 2008, 38(3):174-183.
|
| [7] |
SWYERS K L, WAGNER J J, DORTON K L, et al. Evaluation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product as an alternative to monensin on growth performance, cost of gain, and carcass characteristics of heavy-weight yearling beef steers[J]. Journal of Animal Science, 2014, 92(6):2538-2545.
doi: 10.2527/jas.2013-7559
|
| [8] |
闫佰鹏, 兰贵生, 李国彰, 等. 不同淀粉来源饲粮中添加酵母培养物对育肥湖羊生长性能、养分消化率及瘤胃发酵参数的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30(12):5145-5152.
|
| [9] |
李敬, 杨媛媛, 赵青余, 等. 肉风味前体物质与风味品质的关系研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2019, 55(11):1-7.
|
| [10] |
田丰, 王利, 金海, 等. 饲喂水平对巴美肉羊生产性能、肉品质和肌肉氨基酸组成的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2021, 57(5):160-164.
|
| [11] |
CARRAPISO A I, VENTANAS J, GARCIA C. Characterization of the most odor-active compounds of Iberian ham headspace[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2002, 50(7):1996-2000.
pmid: 11902946
|
| [12] |
BARYŁKO-PIKIELNA N, KOSTYRA E. Snsory interaction of umami substances with model food matrices and its hedonic effect[J]. Food Quality and Preference, 2007, 18(5):751-758.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2007.01.002
|
| [13] |
聂芙蓉, 哈斯通拉嘎, 权凯. 不同肉用绵羊杂交羔羊肉中氨基酸及常规养分比较分析[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2016, 48(8):36-40.
|
| [14] |
CHIANG P D, YEN C T, MAU J L. Non-volatile taste components of various broth cubes[J]. Food Chemistry, 2007, 101(3):932-937.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.02.041
|
| [15] |
赵国宏, 王世国, 王芬, 等. 饲粮添加不同水平酵母培养物对育肥湖羊生长性能、屠宰性能、内脏器官发育及肉品质的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2020, 32(5):2273-2281.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.05.036
|
| [16] |
张爱忠, 卢德勋, 姜宁, 等. 酵母培养物对绒山羊机体抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2010, 22(3):781-786.
|
| [17] |
PRACHE S, SCHREURS N, GUILLIER L. Factors affecting sheep carcass and meat quality attributes[J]. Animal, 2022, 16(Suppl 1):100330.
doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2021.100330
|
| [18] |
FAN Y X, REN C F, MENG F X, et al. Effects of algae supplementation in high-energy dietary on fatty acid composition and the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism in Hu sheep managed under intensive finishing system[J]. Meat Science, 2019, 157:107872.
doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.06.008
|
| [19] |
陈雪, 梁克红, 朱宏, 等. 游离氨基酸检测方法及其应用[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2021, 12(18):7298-7304.
|
| [20] |
杨永慧, 杨发荣, 吴涛, 等. 全株青贮藜麦对小尾寒羊肌肉中氨基酸和脂肪酸的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2022, 39(10):2211-2221.
|
| [21] |
徐琪翔, 曹文豪, 罗双贵, 等. 复合植物提取物对湘东黑山羊胃肠道游离氨基酸含量及其转运载体相对表达量的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(10):5760-5770.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.10.035
|
| [22] |
WATKINS P J, FRANK D, SINGH T K, et al. Sheep meat flavor and the effect of different feeding systems: A review[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(15):3561-3579.
doi: 10.1021/jf303768e
|
| [23] |
尹杰, 韩慧, 刘泽民, 等. 功能性氨基酸调控猪氧化应激的研究进展[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2019, 49(3):193-201.
|
| [24] |
乔新月, 王梦竹, 贾军峰, 等. 功能性氨基酸对断奶仔猪肠道损伤修复机制的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2020, 51(7):1499-1505.
|
| [25] |
史岩峰. 谷氨酰胺对运动能力影响的研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2021, 12(8):3159-3163.
|
| [26] |
CARILLO M R, BERTAPELLE C, SCIALO F, et al. L-carnitine in Drosophila:A review[J]. Antioxidants, 2020, 9(12):1310.
doi: 10.3390/antiox9121310
|
| [27] |
LIU G W, DING Y Y, CHEN Y L, et al. Effect of energy intake and L-carnitine on fattening performance, carcass traits, meat quality, blood metabolites, and gene expression of lamb[J]. Small Ruminant Research, 2020, 183:106025.
doi: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2019.106025
|
| [28] |
杨东, 王文义, 马涛, 等. 甜菜碱和L-肉碱对蒙寒杂交羊生长性能、屠宰性能、器官发育及脂肪沉积的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30(12):5134-5144.
|
| [29] |
LIU Z H, WANG K, ZHANG Y R, et al. High prevalence and diversity characteristics of blaNDM, mcr, and blaESBLs harboring multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli from chicken, pig, and cattle in China[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2022, 11:755545.
|
| [30] |
罗玉龙, 刘畅, 李文博, 等. 两种饲养方式下苏尼特羊肉中鲜味物质含量及相关调控基因表达量[J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(13):8-13.
doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180629-518
|
| [31] |
周俊华, 梁琪妹, 梁方方, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定畜禽肉中肌苷酸研究[J]. 现代农业科技, 2014(19):294-295.
|