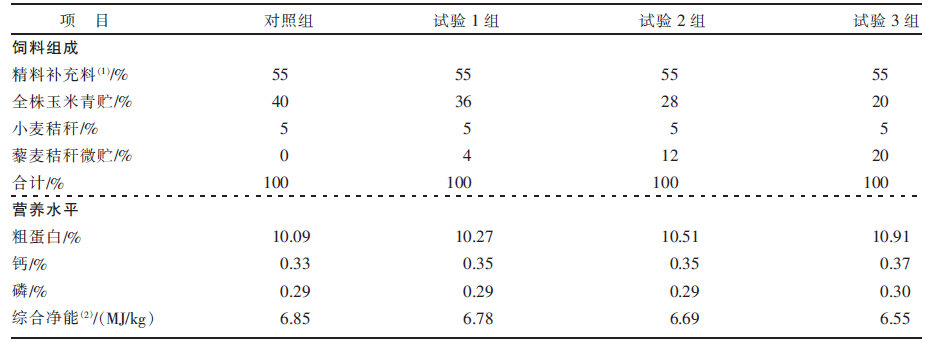
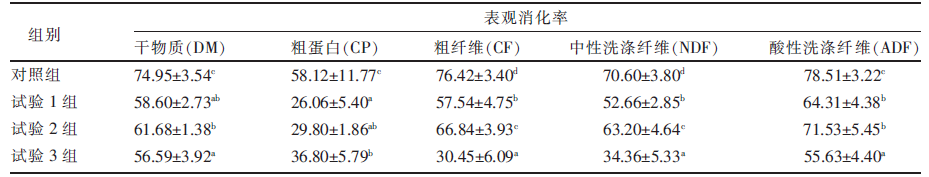
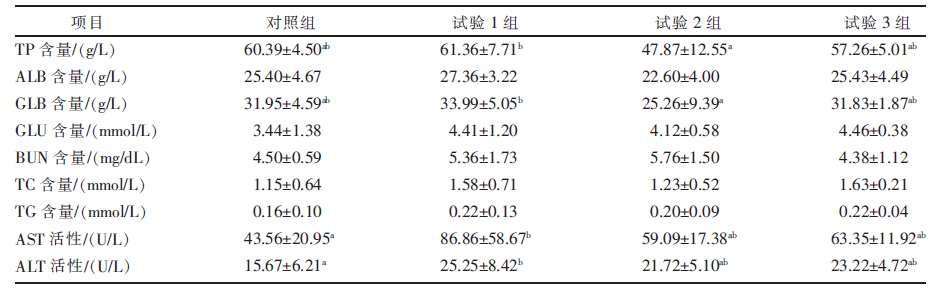
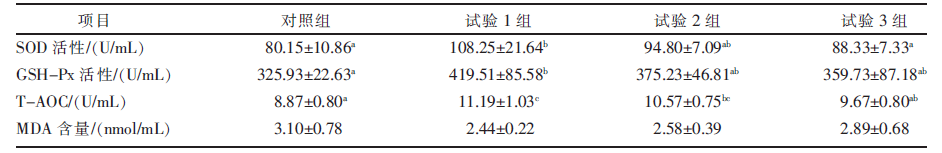
| [1] |
商海军, 蒋丽君, 江本利, 等. 藜麦秸秆蛋白的结构和功能性质[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2022, 43(17):49-56.
|
| [2] |
郝怀志, 董俊, 杨发荣. 日粮中添加藜麦秸秆对奶牛生产性能和血清生化指标的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2019(11):61-65.
|
| [3] |
任妍婧, 谢薇, 江帆, 等. 藜麦粉营养成分及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2019, 34(3):13-18.
|
| [4] |
刘雪, 宋菁景, 林小晖. 藜麦营养和生物活性成分研究进展[J]. 食品安全导刊, 2022(7):135-137.
|
| [5] |
郝怀志, 董俊, 何振富, 等. 藜麦茎秆对肉牛生产性能、养分表观消化率及血清生化指标的影响[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2017, 37(5):26-31.
|
| [6] |
LÓPEZ DE ROMAÑA G, GRAHAM G G, ROJAS M, et al. Digestibility and protein quality of quinua: Comparative study of quinua (Chenopodium quinoa) seed and flour in children[J]. Archivos Latinoamericanos De Nutricion, 1981, 31(3): 485-497.
|
| [7] |
刘敏国, 杨倩, 杨梅, 等. 藜麦的饲用潜力及适应性[J]. 草业科学, 2017, 34(6):1264-1271.
|
| [8] |
中华人民共和国农业农村部. 肉牛饲养标准:NY/T 815—2004[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2004.
|
| [9] |
李景伟. 木薯渣对肉牛生产性能、屠宰性能、胴体品质及血清生化指标的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2015:23.
|
| [10] |
张爱文, 杨永慧, 焦婷, 等. 青贮藜麦不同添加水平对小尾寒羊肉品质和血液生化指标的影响[J]. 中国牛业科学, 2022, 48(5):86-92.
|
| [11] |
杨永慧, 焦婷, 杨发荣, 等. 青贮藜麦对小尾寒羊生长性能、屠宰性能及血液生理指标的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2022(21):133-139.
|
| [12] |
唐振华, 周玲, 邹彩霞, 等. 青贮甘蔗尾、青贮玉米秸秆对生长水牛生长性能、消化代谢及血液生化指标的影响[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2016, 43(1):92-100.
doi: 10.16431/j.cnki.1671-7236.2016.01.014
|
| [13] |
张忠远, 徐宝成. 饲料中营养物质表观消化率的计算公式[J]. 饲料博览, 2004(4):48.
|
| [14] |
孙铎. 发酵玉米秸秆对肉牛生长性能、养分表观消化率及血液生化指标的影响[J]. 饲料研究, 2021, 44(1):10-13.
|
| [15] |
王波, 姜成钢, 纪守坤, 等. 日粮尿素水平对肉羊血液学、血清学指标和消化器官的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2014, 45(9):1449-1456.
|
| [16] |
高录贵, 王景, 仲华玲, 等. 竹酢粉对断奶湖羊生长性能、血液生理生化指标及血清抗氧化和免疫指标的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(9):5356-5362.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.09.054
|
| [17] |
次旦央吉, 李鑫, 孙光明, 等. 饲粮能量水平对育肥牦牛生长性能、血清生化指标及瘤胃发酵特征的影响[J]. 中国草食动物科学, 2022, 42(5):44-49.
|
| [18] |
王建东, 侯鹏霞, 马秀明, 等. 饲喂枸杞枝条颗粒饲料对肉牛增重和一些免疫指标的影响[J]. 动物医学进展, 2022, 43(2):95-98.
|
| [19] |
DONG S X, YANG X S, ZHAO L, et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. husks against foodborne pathogenic bacteria[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2020, 149:112350.
doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112350
|
| [20] |
李锋, 李永峰. 复合益生菌发酵玉米秸秆对肉牛生长性能、免疫功能及养分消化率的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2023(6):89-92.
|
| [21] |
张文火, 董国忠, 潘存霞. 紫苏籽提取物对肉牛生产性能和免疫性能的影响[C]// 2010植物提取物与营养及应用技术交流研讨会论文集. 乌鲁木齐: 国家饲料工程技术研究中心, 2010:121-123.
|