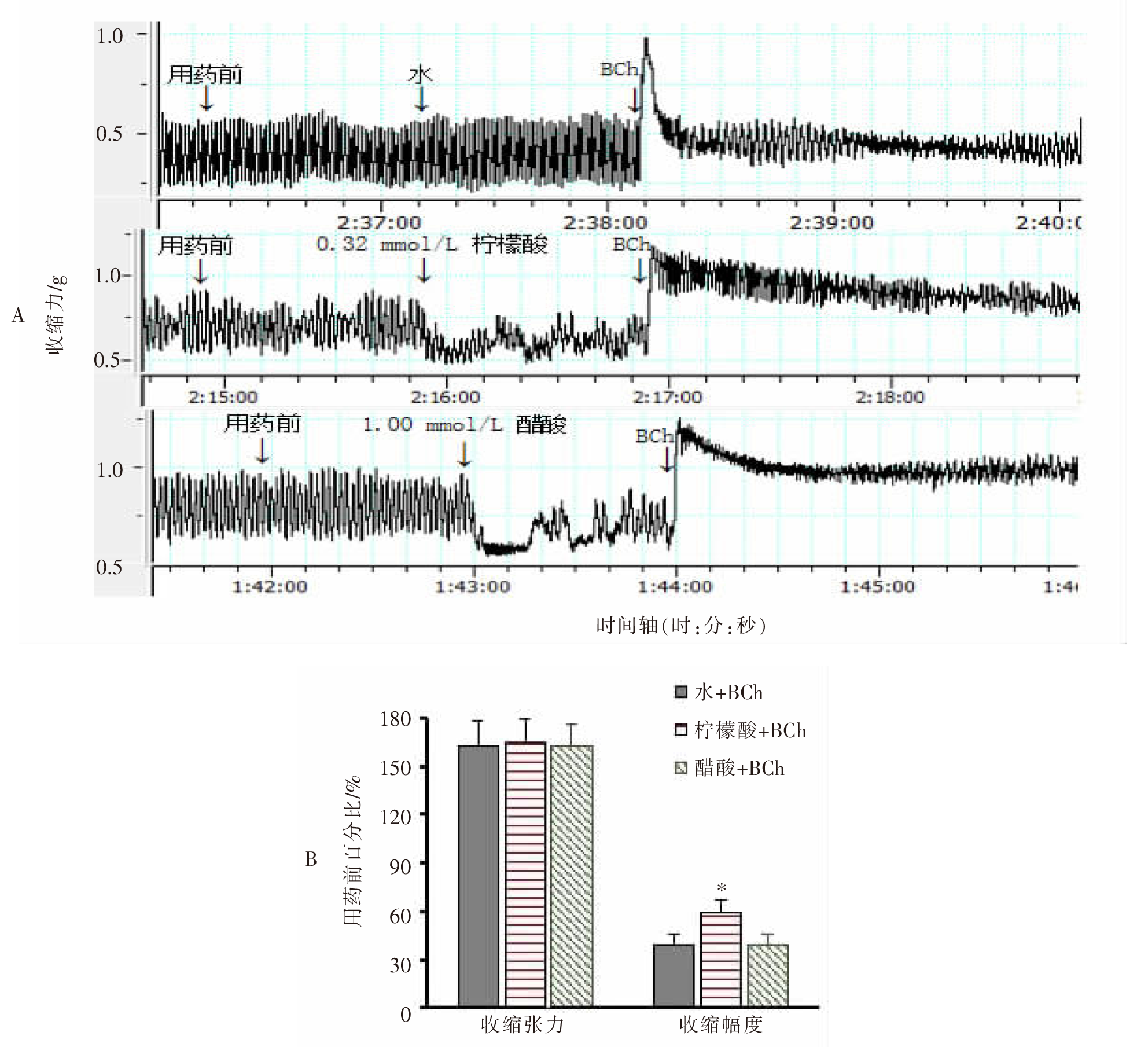
| [1] |
岳玉秀, 岳玉妍. 柠檬酸对肥育猪生长性能和抗氧化功能的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2022(18):55-58.
|
| [2] |
陈亚军, 周怿, 张强, 等. 肉桂酸柠檬酸复合物添加对产蛋鸡生产性能的影响[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2017, 38(7):47-50.
|
| [3] |
栾一丹, 李进展, 贠梦瑶, 等. 柠檬园里柠檬香,柠檬果实至尊王[J]. 大学化学, 2021, 36(10):85-92.
|
| [4] |
高玉录, 仝亚军, 杨兴旺, 等. 乙酸及ABA对田间高温胁迫下‘摩尔多瓦’葡萄叶片光抑制的影响[J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒, 2020(5):1-5.
|
| [5] |
黄伟, 陶诗琪. CH4和CO2偶联直接合成乙酸的研究进展[J]. 低碳化学与化工, 2023, 48(2):1-13.
|
| [6] |
王亚玲, 孔鹏辉, 袁冬冬, 等. 饲粮添加乙酸钠对奶山羊泌乳性能和瘤胃微生物区系的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2023, 35(1):428-438.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2023.01.042
|
| [7] |
黄兴海. 柠檬酸对草鱼生长性能的影响[J]. 黑龙江水产, 2023, 42(2):119-121.
|
| [8] |
夏飞, 张处处, 武子宁, 等. 柠檬酸对食用菌腐败菌的抑制作用及其作用机制[J]. 陕西科技大学学报, 2023, 41(2):40-45.
|
| [9] |
袁梦, 黄慧清, 陈澜, 等. 柠檬酸对机体生长及消化功能影响的研究[J]. 福建畜牧兽医, 2022, 44(4):21-25.
|
| [10] |
刘俊栋, 刘海霞, 赵佳, 等. 乙酸及其钠盐对奶牛离体真胃平滑肌收缩的影响[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2012, 48(1):25-26.
|
| [11] |
SHIMAMURA H, HIROTA M, MIYAZAWA M, et al. Contractile and extensile effects of red and white wine on rat and Mongolian gerbil gastrointestinal smooth muscle[J]. Journal of Oleo Science, 2010, 59(3):143-150.
pmid: 20124756
|
| [12] |
蔡鹏, 孙小燕, 阿迪莱·艾力, 等. 荨麻皮刺水提液对小鼠离体肠平滑肌运动的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(3):767-773.
doi: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.03.027
|
| [13] |
陈哲宇. 胃肠平滑肌运动的细胞信号转导机制[J]. 国外医学(消化系疾病分册), 2003(3):138-141.
|
| [14] |
RATZ P H, BERG K M, URBAN N H, et al. Regulation of smooth muscle calcium sensitivity: KCl as a calcium-sensitizing stimulus[J]. American Journal of Physiology Cell Physiology, 2005, 288(4):769-783.
|
| [15] |
周杰. 动物生理学[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2022.
|
| [16] |
田姣, 王宝西, 江逊. 胃肠道Cajal间质细胞与干细胞因子/c-kit信号系统的研究进展[J]. 临床儿科杂志, 2013, 31(4):385-388.
|
| [17] |
李亦汉, 王琳琳, 赵建新, 等. 两歧双歧杆菌CCFM1167通过提升肠道中乙酸水平以抑制炎症从而缓解便秘[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2023, 49(6):35-41.
|
| [18] |
曹山川, 杨跃奎, 刘静波. 有机酸对断奶仔猪生长性能和肠道健康的影响[J]. 饲料工业, 2015, 36(2):47-51.
|
| [19] |
梅俏, 许建明, 项立. 乙酸体外损伤大鼠结肠模型的建立及褪黑素的影响[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2006(1):117-120.
|
| [20] |
楼彩霞, 胡立春, 黎小平, 等. 乙酸诱导建立大鼠急性直肠黏膜损伤模型的形态学观察[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2015, 23(2):143-146,152.
|