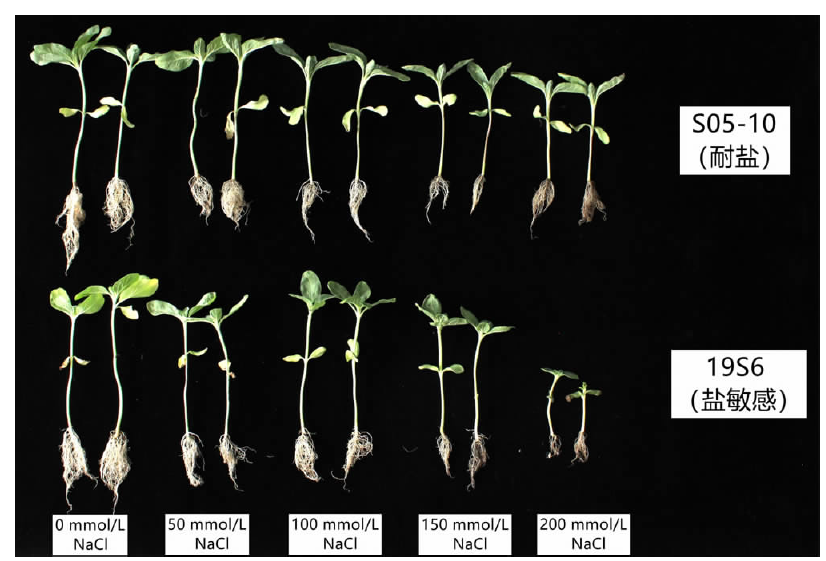
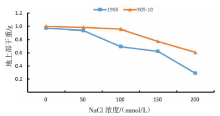
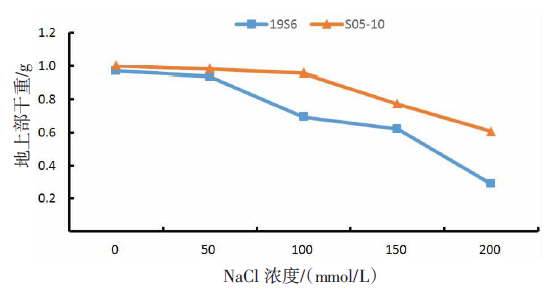
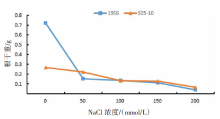
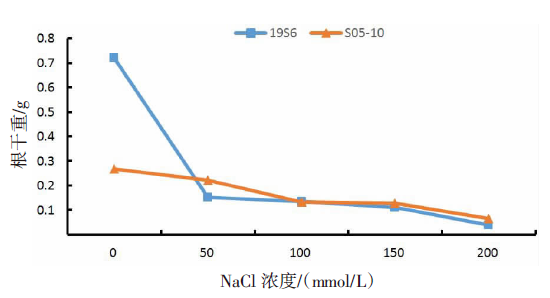
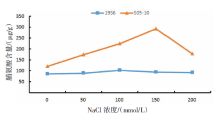
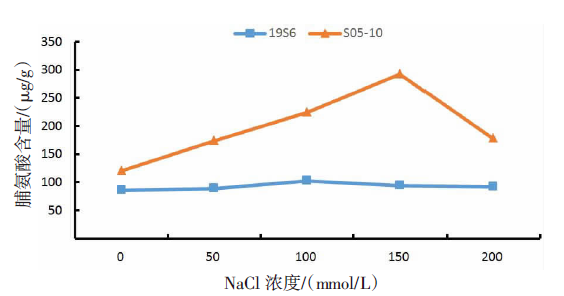
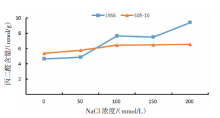
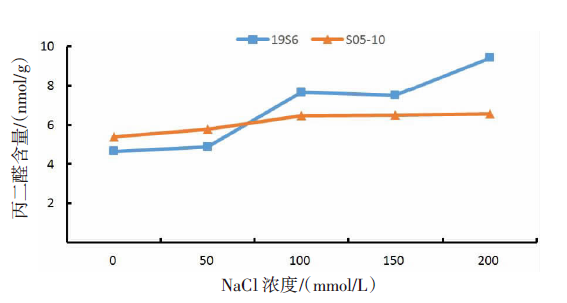
| [1] |
SHABALA S. Learning from halophytes:physiological basis and strategies to improve abiotic stress tolerance in crops[J]. Annals of Botany, 2013, 112(7):1209-1221.
doi: 10.1093/aob/mct205
|
| [2] |
HORVÁTH E, CSISZÁR J, GALLÉ Á, et al. Hardening with salicylic acid induces concentration-dependent changes in abscisic acid biosynthesis of tomato under salt stress[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2015, 183:54-63.
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2015.05.010
pmid: 26086888
|
| [3] |
SINGH V, SINGH A P, BHADORIA J, et al. Differential expression of salt-responsive genes to salinity stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive rice(Oryza sativa L.)at seedling stage[J]. Protoplasma, 2018, 255(6):1667-1681.
doi: 10.1007/s00709-018-1257-6
|
| [4] |
袁海, 何鹏飞, 武君洁, 等. 盐胁迫对耐盐和盐敏感玉米幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(19):86-89.
|
| [5] |
李焕春, 赵沛义, 吕艳霞, 等. 向日葵新品种对NaCl胁迫的响应及其耐盐阈值[J]. 土壤通报, 2018, 49(6):1452-1457.
|
| [6] |
杨国会, 石德成. NaCl胁迫对甘草叶片相对含水量及保护酶活性的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2009, 38(12):104-106.
|
| [7] |
赖弟利, 范昱, 朱红林, 等. 燕麦耐盐性的生理生化指标网络分析[J]. 作物杂志, 2020(2):147-155.
|
| [8] |
秦岭, 张艳亭, 陈二影, 等. 谷子萌发期耐盐种质筛选及其保护酶系统对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(22):4027-4040.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.22.008
|
| [9] |
汤章城. 现代植物生理学实验指南[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999:110-200.
|
| [10] |
张红, 王文浩, 刘文俊, 等. 2种向日葵杂交种的抗盐碱性鉴定[J]. 种子, 2020, 39(1):93-96.
|
| [11] |
李廷化, 王伦旺, 李翔, 等. 3个桂糖系列甘蔗新品种的种性和丰产性分析[J]. 广东农业科学, 2013, 40(15):21-23.
|
| [12] |
于志贤, 耿稞, 侯建华, 等. 盐胁迫对不同基因型向日葵种子萌发的影响[J]. 种子, 2013, 32(10):29-33.
|
| [13] |
MUELLER D M. Germination and root growth of 4 osmoconditioned cool-season grasses[J]. Journal of Range Management, 1996, 49(2):117-120.
doi: 10.2307/4002679
|
| [14] |
王新伟. 不同盐浓度对马铃薯试管苗的胁迫效应[J]. 中国马铃薯, 1998, 12(4):203-207.
|
| [15] |
凌云鹤, 周瑶, 景兵, 等. 盐胁迫对向日葵幼苗生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(4):139-145.
|
| [16] |
许祥明, 叶和春, 李国凤. 植物抗盐机理的研究进展[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2000, 6(4):379-387.
|
| [17] |
郭蓓, 邱丽娟, 李向华. 植物盐诱导基因的研究进展[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 1999, 7(4):401-408.
|
| [18] |
肖雯, 贾恢先, 蒲陆梅. 几种盐生植物抗盐生理指标的研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2000, 20(5):818-825.
|
| [19] |
王伟, 于海峰, 张永虎, 等. 盐胁迫对向日葵幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2013, 28(1):176-180.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7091.2013.01.032
|
| [20] |
毛爽, 周万里, 杨帆, 等. 植物根系应答盐碱胁迫机理研究进展[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(10):1991-2000.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2021.10.23
|
| [21] |
张俊莲, 陈勇胜, 武季玲, 等. 向日葵对盐逆境伤害的生理反应及耐盐性研究[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2003, 25(1):47-51.
|
| [22] |
赵娜, 徐庆国, 苏鹏, 等. 10个冷季型草坪草品种在高温胁迫下的抗性[J]. 草业科学, 2019, 36(7):1743-1753.
|
| [23] |
杨立飞, 朱月林, 胡春梅, 等. NaCl胁迫对嫁接黄瓜膜脂过氧化、渗透调节物质含量及光合特性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2006, 26(6):1195-1200.
|
| [24] |
焦德志, 赵泽龙. 盐碱胁迫对植物形态和生理生化影响及植物响应的研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(20):1-4.
|