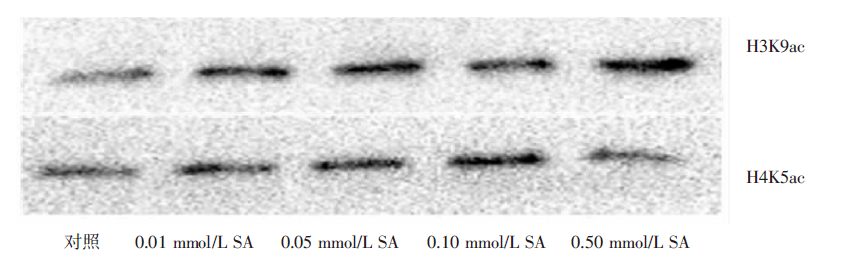
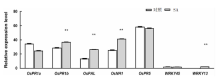
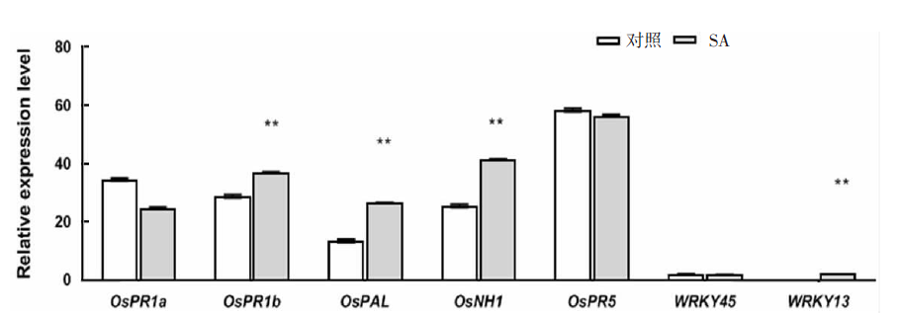
| [1] |
ZHU Y, CHEN H, FAN J, et al. Genetic diversity and disease control in rice[J]. Nature, 2000, 406(6797):718-722.
doi: 10.1038/35021046
|
| [2] |
AZIZI P, RAFII M Y, ABDULLAH S N A, et al. Toward understanding of rice innate immunity against Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2016, 36(1):165-174.
doi: 10.3109/07388551.2014.946883
|
| [3] |
TALBOT N J. On the trail of a cereal killer:Exploring the biology of Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2003, 57:177-202.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090957
|
| [4] |
PARKER D, BECKMANN M, ENOT D P, et al. Rice blast infection of Brachypodium distachyon as a model system to study dynamic host/pathogen interactions[J]. Nature Protocols, 2008, 3(3):435-445.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.499
|
| [5] |
胡朝芹, 刘剑宇, 王韵茜, 等. 粳稻子预44抗LP11稻瘟病菌基因Pizy6(t)的定位[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(1):61-69.
|
| [6] |
GUO J W, XIAO Q, LI Y R, et al. Studies on characterizations and avirulence genes of field Magnaporthe oryzae strains from Luoping of Yunnan Province,China[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 2021, 51(2):235-247.
|
| [7] |
张梦洋, 刘君, 王燕凌, 等. 外源水杨酸诱导黄瓜幼苗抗细菌性果斑病抗性浓度的筛选[J]. 新疆农业大学学报, 2015, 38(6):459-464.
|
| [8] |
蔡新忠, 郑重, 宋凤鸣. 水杨酸对水稻幼苗抗瘟性的诱导作用[J]. 植物病理学报, 1996, 26(1):7-12.
|
| [9] |
蔡新忠, 郑重. 水杨酸诱导水稻幼苗抗瘟性的生化机制[J]. 植物病理学报, 1997, 27(3):231-236.
|
| [10] |
王瑞霞, 王振中, 纪春艳, 等. 水杨酸诱导水稻抗菌物质对稻瘟病菌的抑制作用[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2011, 30(2):193-196.
|
| [11] |
赵宝海, 王世维, 郑文静, 等. 水杨酸诱导水稻抗氧化酶活性及抗瘟性的变化[J]. 西南农业学报, 2015, 28(1):127-130.
|
| [12] |
HU Y F, LU Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Histone acetylation dynamics integrates metabolic activity to regulate plant response to stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2019, 10:1236.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01236
pmid: 31636650
|
| [13] |
BERR A, SHAFIQ S, SHEN W H. Histone modifications in transcriptional activation during plant development[J]. BBA-Gene Regulatory Mechanisms, 2011, 1809(10):567-576.
|
| [14] |
CHEN Z J, TIAN L. Roles of dynamic and reversible histone acetylation in plant development and polyploidy[J]. BBA-Gene Structure and Expression, 2007, 1769(5/6):295-307.
|
| [15] |
FU W Q, WU K Q, DUAN J. Sequence and expression analysis of histone deacetylases in rice[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2007, 356(4):843-850.
pmid: 17399684
|
| [16] |
FANG H, LIU X, THORN G, et al. Expression analysis of histone acetyltransferases in rice under drought stress[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2014, 443(2):400-405.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.11.102
pmid: 24309107
|
| [17] |
LU Y, XU Q T, LIU Y, et al. Dynamics and functional interplay of histone lysine butyrylation,crotonylation,and acetylation in rice under starvation and submergence[J]. Genome Biology, 2018, 19(1):144.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1533-y
|
| [18] |
YIN J J, ZOU L J, ZHU X B, et al. Fighting the enemy:How rice survives the blast pathogen′s attack[J]. The Crop Journal, 2021, 9(3):543-552.
doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2021.03.009
|
| [19] |
燕高伟. 水稻病程相关蛋白质OsPR1A在白叶枯病抗性反应中的功能研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2020.
|
| [20] |
曾嘉丽, 欧阳林娟, 刘家林, 等. 水稻PAL基因的全基因组分析及胁迫表达研究[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2018, 37(9):3881-3888.
|
| [21] |
李娟, 罗雪梅, 韦海宏, 等. 过量表达OsNPR1基因稳定提高水稻对白叶枯病的抗性[J]. 广西农业生物科学, 2008, 27(4):335-342.
|
| [22] |
SHIMONO M, SUGANO S, NAKAYAMA A, et al. Rice WRKY45 plays a crucial role in benzothiadiazole-inducible blast resistance[J]. The Plant Cell, 2007, 19(6):2064-2076.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.046250
|
| [23] |
邱德运. 水稻WRKY转录因子OsWRKY13的功能鉴定和调控机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2007.
|