Journal of Northern Agriculture ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 51-61.doi: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2023.05.05
• Soil and fertilizer · Physiology and biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
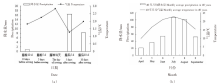
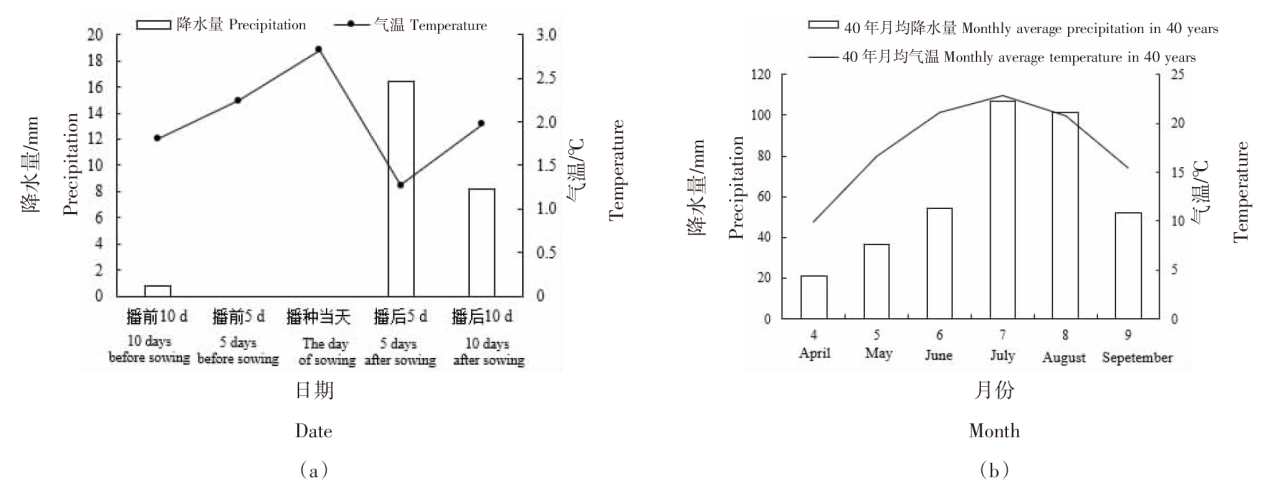
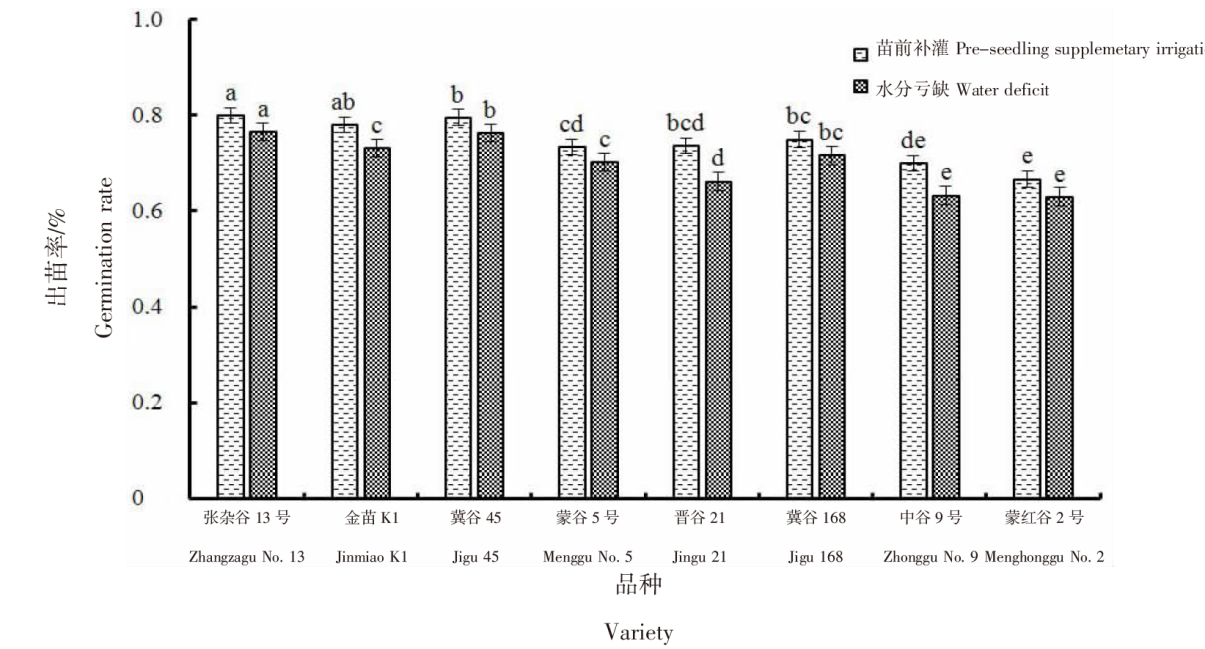
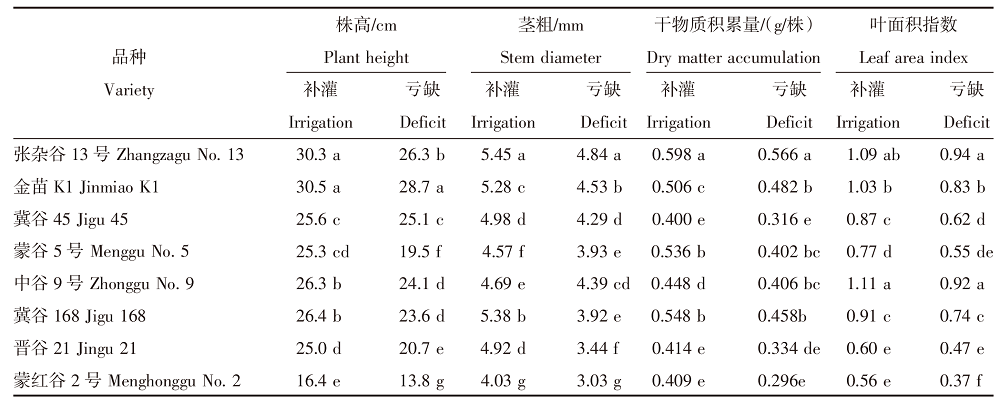
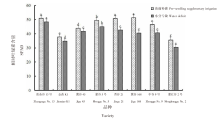
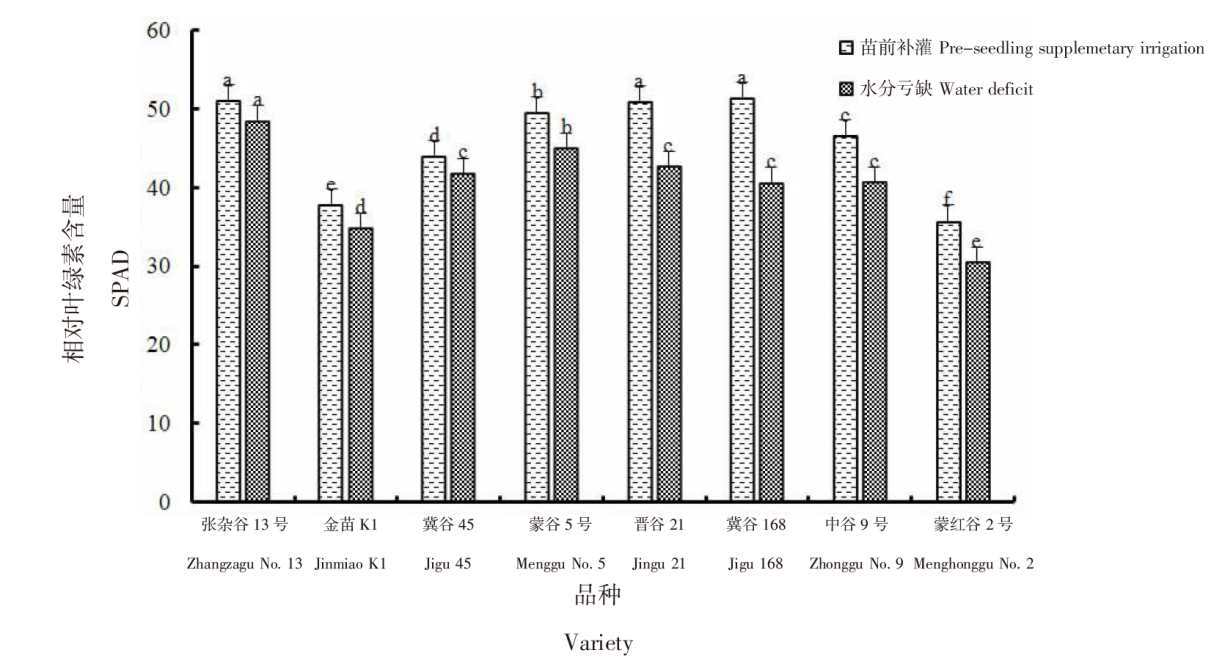
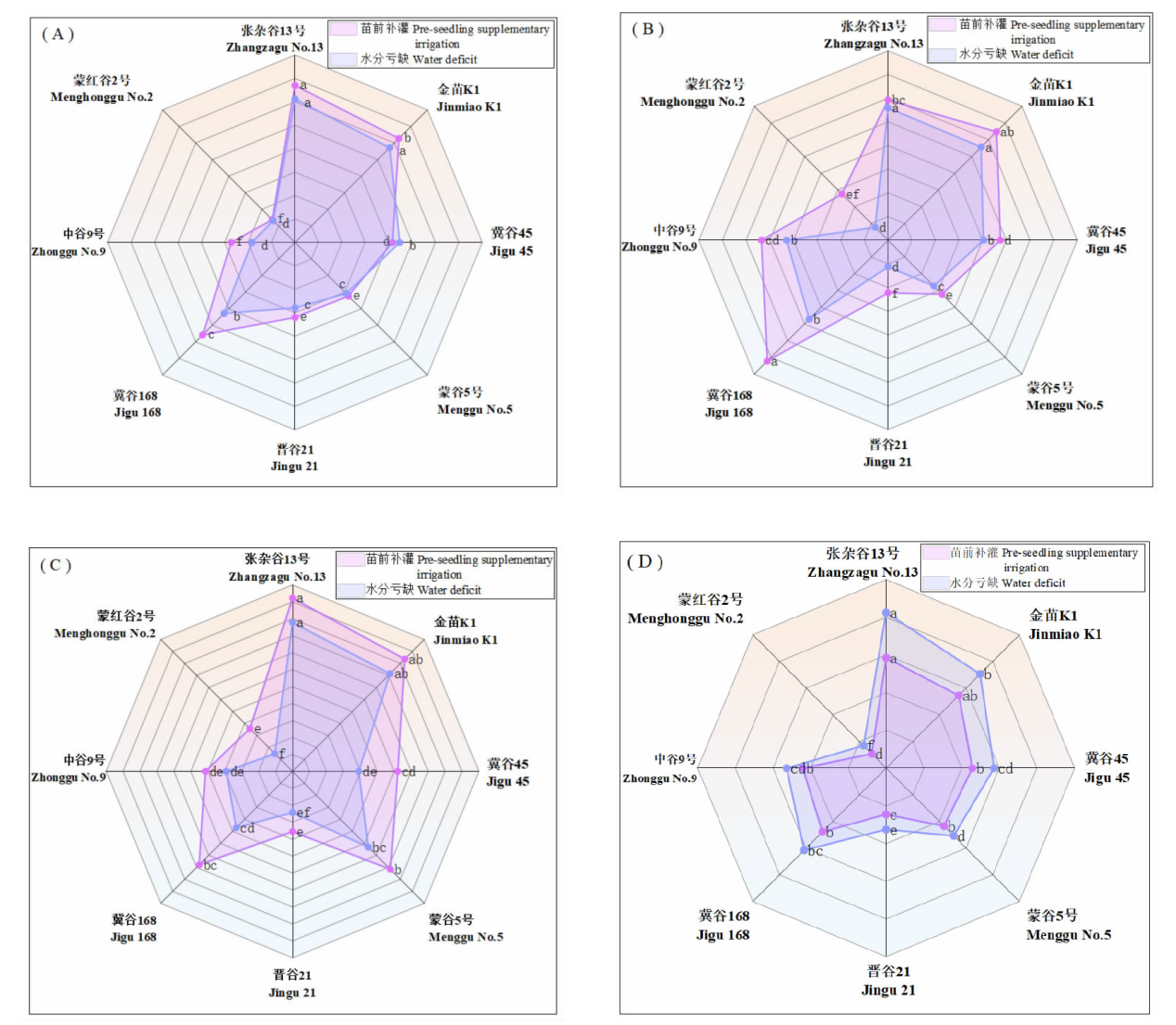
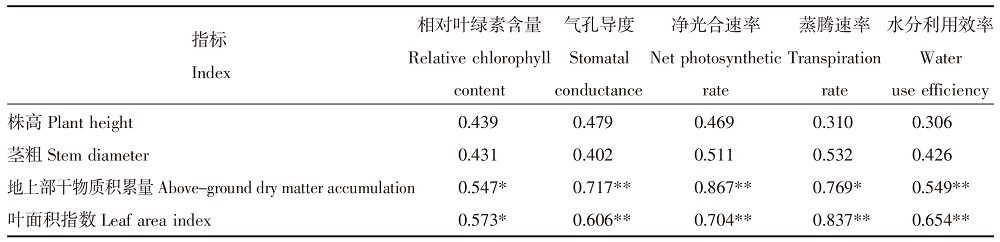
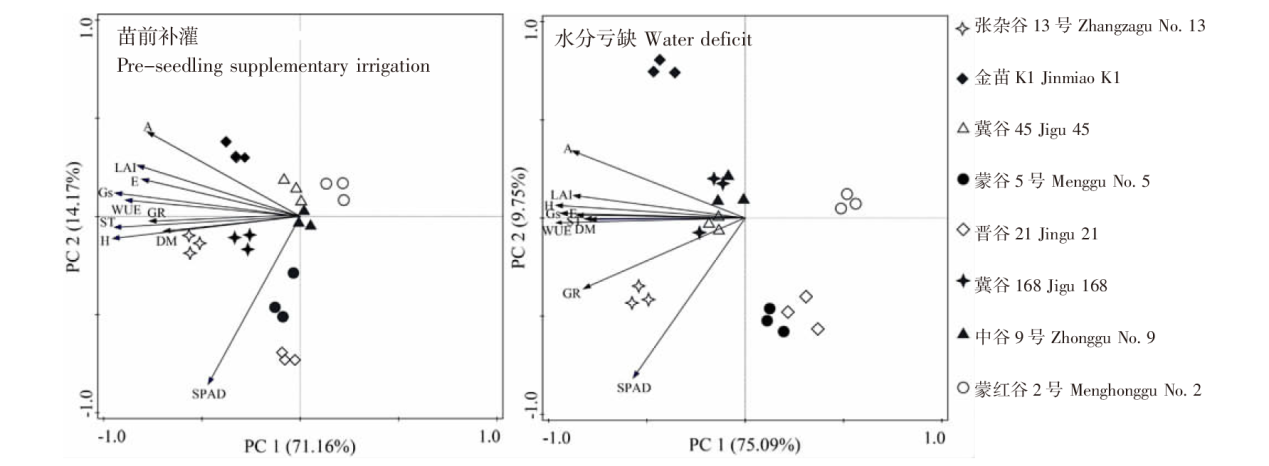
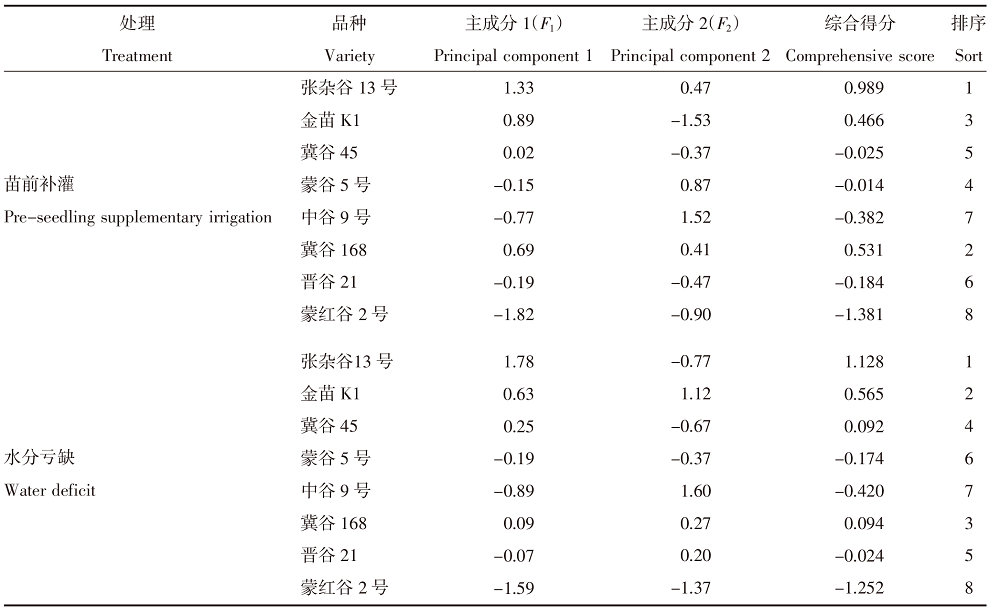
Effects of pre-seedling supplementary irrigation on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of millet in the dry farming area of the Loess Plateau in Inner Mongolia
WU Yao1,2, GAO Riping1,2, CAI Linlin1,2, HUANG Zhefan1,2, CHEN Xiao1,2, MEN Jingyu1,2, ZHAO Peiyi3, PAN Zhihua1,2
- 1. College of Resources and Environmental Sciences,China Agricultural University,Beijing 100091,China
2. China Meteorological Administration-China Agricultural University Jointly Laboratory of Agriculture Addressing Climate Change,Beijing 100193,China
3. Institute of Resources Environment and Sustainable Development,Inner Mongolia Academy of Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Sciences,Hohhot 010031,China
CLC Number:
- S515