畜牧与饲料科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 112-116.doi: 10.12160/j.issn.1672-5190.2022.05.018
内蒙古某牲畜交易市场绵羊肠道蠕虫感染情况调查
张加宁,陈名利,邓金华,李凯,彭霞,信璐瑶,齐萌
- 塔里木大学动物科学与技术学院/新疆生产建设兵团塔里木动物疫病诊断与防控工程实验室,新疆 阿拉尔 843300
Investigation on Intestinal Helminth Infections in Sheep in a Livestock Trading Market in Inner Mongolia,China
ZHANG Jia-ning,CHEN Ming-li,DENG Jin-hua,LI Kai,PENG Xia,XIN Lu-yao,QI Meng
- College of Animal Science and Technology, Tarim University/Engineering Laboratory of Tarim Animal Diseases Diagnosis and Control,The Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps,Alar 843300,China
摘要:
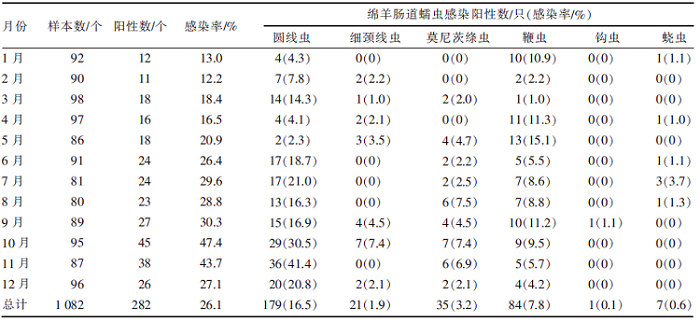
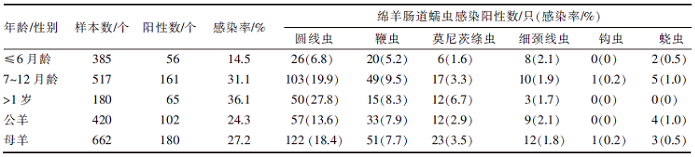
[目的]掌握内蒙古某大型牲畜交易市场绵羊肠道蠕虫的感染情况。[方法]2020年7月—2021年6月逐月收集该市场绵羊粪便样本12次,共1 082份,采用饱和蔗糖溶液漂浮法进行虫卵检查,对绵羊感染的肠道蠕虫卵进行形态学鉴定。采用统计学方法比较不同月份、年龄、性别绵羊肠道蠕虫感染率差异。[结果]282份粪便样本呈蠕虫卵阳性,感染率为26.1%(282/1 082)。鉴定出6种蠕虫,以圆线虫为主要感染虫种,感染率为16.5%(179/1 082);鞭虫、莫尼茨绦虫、细颈线虫、蛲虫和钩虫的感染率分别为7.8%(84/1 082)、3.2%(35/1 082)、1.9%(21/1 082)、0.6%(7/1 082)和0.1%(1/1 082)。10月和11月绵羊的肠道蠕虫感染率较高,分别为47.4%(45/95)和43.7%(38/87);1月和2月绵羊的肠道蠕虫感染率较低,分别为13.0%(12/92)和12.2%(11/90);不同采样月绵羊肠道蠕虫感染率统计学差异极显著(χ2=63.957,df=11,P<0.01)。≤6月龄、7~12月龄和>1岁的绵羊肠道蠕虫感染率分别为14.5%(56/385)、31.1%(161/517)和36.1%(65/180),不同年龄段绵羊肠道蠕虫的感染率统计学差异极显著(χ2=42.853,df=2,P<0.01)。公羊和母羊的肠道蠕虫感染率分别为24.3%(102/420)和27.2%(180/662),无统计学差异(P>0.05)。[结论]该牲畜交易市场绵羊肠道蠕虫感染与季节、年龄有关,应针对性确定防治方案。
中图分类号: