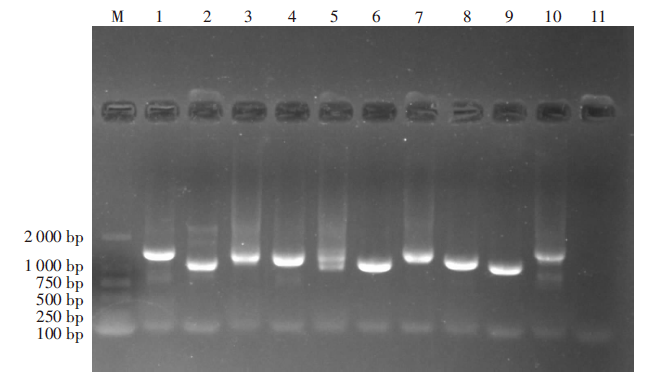
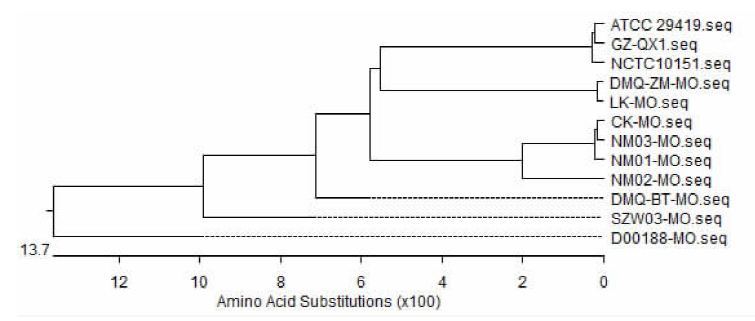
| [1] |
韩笑. 绵羊肺炎支原体HSP70基因遗传多样性及其在分子检测中的应用[D]. 成都: 西南民族大学, 2012.
|
| [2] |
ZHAO J Y, DU Y Z, SONG Y P, et al. Investigation of the prevalence of Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae in southern Xinjiang, China[J]. Journal of Veterinary Research, 2021, 65(2):155-160.
doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2021-0021
|
| [3] |
BESSER T E, LEVY J, ACKERMAN M, et al. A pilot study of the effects of Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae exposure on domestic lamb growth and performance[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(2):e0207420.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207420
|
| [4] |
JOHNSON T, JONES K, JACOBSON B T, et al. Experimental infection of specific-pathogen-free domestic lambs with Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae causes asymptomatic colonization of the upper airways that is resistant to antibiotic treatment[J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2022, 265:109334.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2022.109334
|
| [5] |
恽佳蕾, 何苗峰, 王少辉, 等. 某育肥羊场呼吸道疾病的诊断与病原学鉴定[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2022, 54(1):94-99.
|
| [6] |
王紫阳, 努尔比亚·艾克木, 屈勇刚, 等. 新疆某规模化羊场羊支原体肺炎的分子流行病学调查[J]. 现代畜牧兽医, 2022(5):58-62.
|
| [7] |
HSU T, ARTIUSHIN S, MINION F C. Cloning and functional analysis of the P97 swine cilium adhesin gene of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1997, 179(4):1317-1323.
doi: 10.1128/jb.179.4.1317-1323.1997
|
| [8] |
涂尾龙, 吴华莉, 黄济, 等. 猪肺炎支原体黏附因子P97蛋白研究进展[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(7):1545-1547,1552.
|
| [9] |
杨发龙, 张焕容, 汤承, 等. 绵羊肺炎支原体P113基因的序列分析及功能预测[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2013, 34(1):117-121.
|
| [10] |
杨鹏, 吴燕, 岳筠, 等. 绵羊肺炎支原体P113蛋白C末端基因真核表达载体的构建及其小鼠免疫应答[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2022, 42(3):496-501,521.
|
| [11] |
杨发龙, 张贤宇, 汤承, 等. 绵羊肺炎支原体P113蛋白C端重复区的表达及其免疫原性[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2013, 43(7):733-737.
|
| [12] |
倪珊珊, 薛冠华, 李少丽, 等. 肺炎支原体黏附细胞器的结构与功能[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2019, 35(9):831-836.
|
| [13] |
JIANG F, HE J Y, NAVARRO-ALVAREZ N, et al. Elongation factor tu and heat shock protein 70 are membrane-associated proteins from Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae capable of inducing strong immune response in mice[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(12): e0189562.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189562
|
| [14] |
ZHANG Y Y, MEI S F, ZHOU Y L, et al. TIPE2 negatively regulates Mycoplasma pneumonia-triggered immune response via MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7:13319.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13825-y
|
| [15] |
EINARSDOTTIR T, GUNNARSSON E, HJARTARDOTTIR S. Icelandic ovine Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae are variable bacteria that induce limited immune responses in vitro and in vivo[J]. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 2018, 67(10):1480-1490.
doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000818
|
| [16] |
LUO H X, WU X X, XU Z K, et al. NOD2/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase triggers Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae-induced macrophage autophagy[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2020, 202(20):e00689.
|
| [17] |
杨鹏, 吴燕, 岳筠, 等. 绵羊肺炎支原体P113蛋白和丝状支原体山羊亚种LppA蛋白共表达质粒对小鼠免疫应答的研究[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2022, 44(2):179-186.
|
| [18] |
李垚, 刀筱芳, 冯旭飞, 等. 绵羊肺炎支原体P113蛋白单克隆抗体的制备及其在免疫荧光检测中的应用研究[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2019, 49(4):410-417.
|
| [19] |
侯宏艳, 张丹俊, 赵瑞宏, 等. 绵羊肺炎支原体安徽株P113基因PCR检测与序列分析[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2019, 40(1):101-103.
|
| [20] |
林裕胜, 江锦秀, 张靖鹏, 等. 绵羊肺炎支原体TaqMan荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2018, 40(4):316-320.
|