畜牧与饲料科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 109-115.doi: 10.12160/j.issn.1672-5190.2022.04.016
基于Pubmed数据库检索的人兽共患病及其病原微生物研究现状与趋势分析
陈莉,顾晓红,季文君,潘尔卓
- 苏州市药品检验检测研究中心,江苏 苏州 215104
Research Status and Trend of Zoonosis and Zoonotic Microorganisms Based on PubMed Database Retrieval
CHEN Li,GU Xiao-hong,JI Wen-jun,PAN Er-zhuo
- Suzhou Institute for Drug Control,Suzhou 215104,China
摘要:
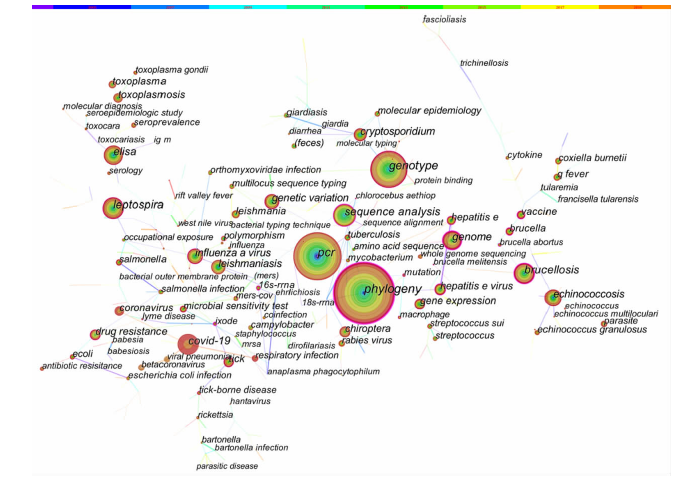
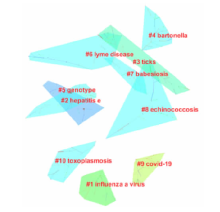
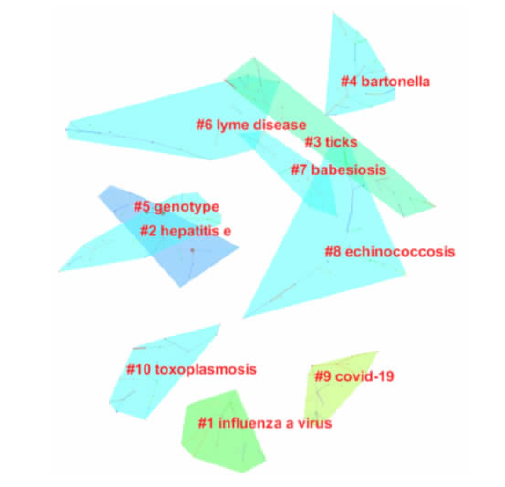
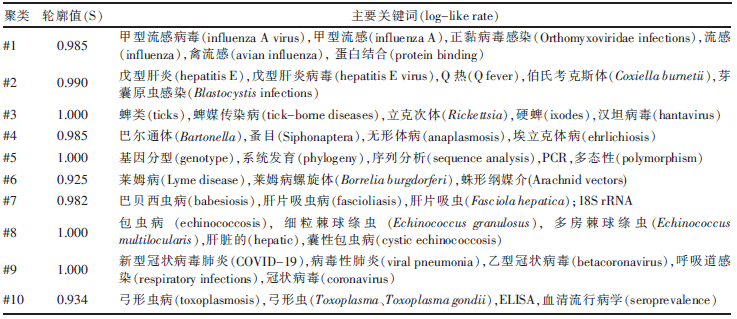
[目的]获得全球范围内人兽共患病及其病原微生物研究现状和热点变化趋势信息,为我国人兽共患病的防控提供参考。[方法]利用COOC 12.6和Citespace 5.8 R1软件对Pubmed数据库中的人兽共患病及其病原微生物相关的关键词进行了频次统计、共现分析、聚类分析、时间线分析和突现词分析。[结果]根据Pubmed数据库中 2001—2021年关键词频次统计和共现分析结果,国际关注度较高的人兽共患病及其病原微生物有以下3类:第1类为常见的人兽共患病病原,包括布鲁菌(Brucella)、戊型肝炎病毒(hepatitis E virus)、链球菌(Streptococcus)、大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)和沙门菌(Salmonella)等,需要持续关注;第2类为近些年在国际上被广泛关注的人兽共患病病原,如新型冠状病毒(SARS-CoV-2)和甲型流感病毒(influenza A virus)等,需要更为深入研究,以尽早控制这些病原的扩散;第3类为在国外特定地区曾大规模出现的人兽共患病,如Q热(Q fever)和中东呼吸综合征(middle east respiratory syndrome,MERS)等,应当重点关注其输入性风险,避免这些疾病在我国暴发。除疾病和病原微生物外,与检测和诊断相关的关键词,如系统发育(phylogeny)和聚合酶链式反应(PCR)等关键词的关注度也较高。聚类分析生成了10个聚类,蜱媒传染病大类提示蜱虫在人兽共患病传播中的作用。时间线和突现词分析结果显示,在病原微生物中,对甲型流感病毒以及新型冠状病毒等的关注度还在逐渐增加。同时,病原微生物检测技术正在从特定序列检测向全基因组学检测技术发展,这些领域极有可能是今后的研究方向和趋势。[结论]结果提示,人们对人兽共患病及其病原微生物研究的关注度越来越高,人兽共患病病原微生物检测技术正在发生更新和迭代。我国应重点关注甲型流感以及新型冠状病毒肺炎等疾病的防控,并适当关注蜱媒传染病。这些信息的获取可为我国的人兽共患病的防控提供参考。
中图分类号: