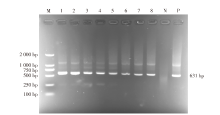
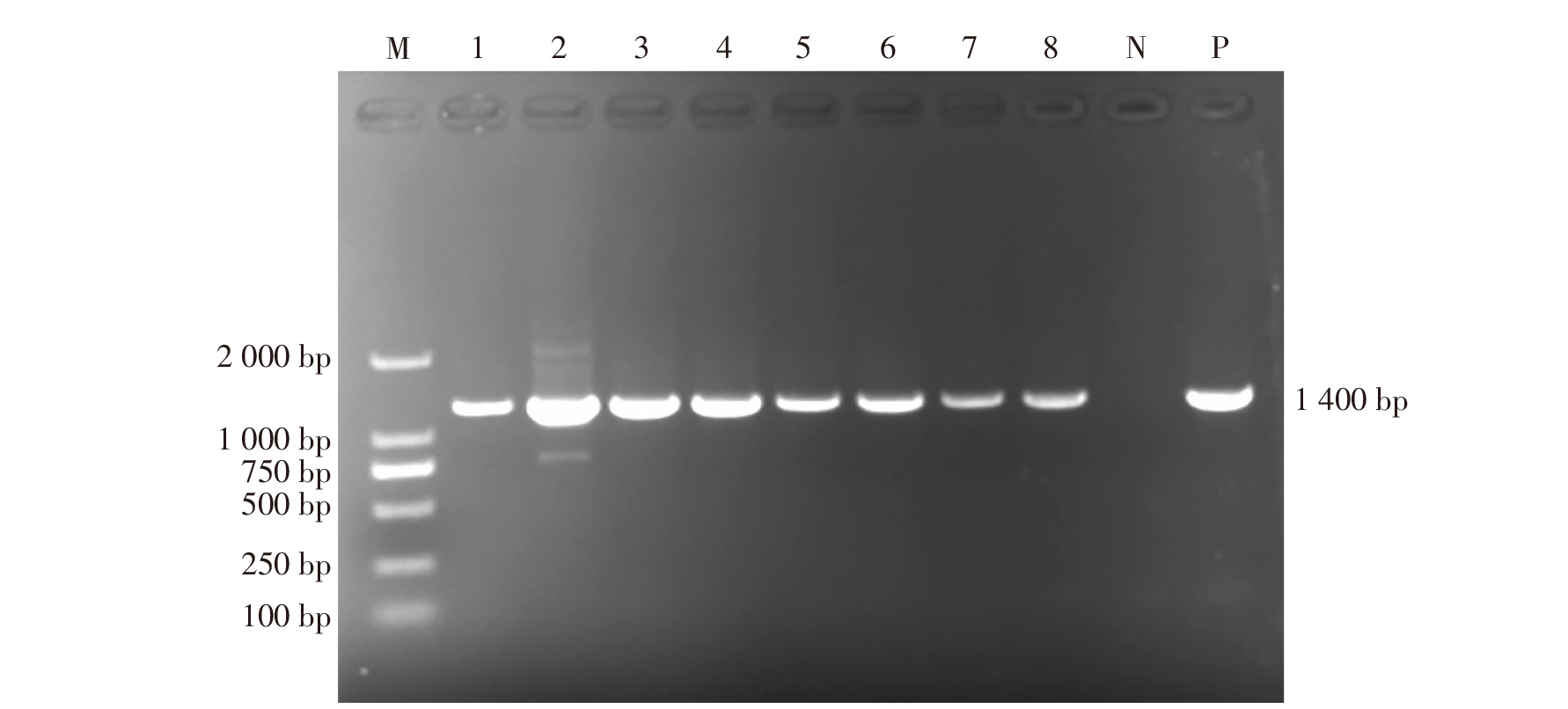
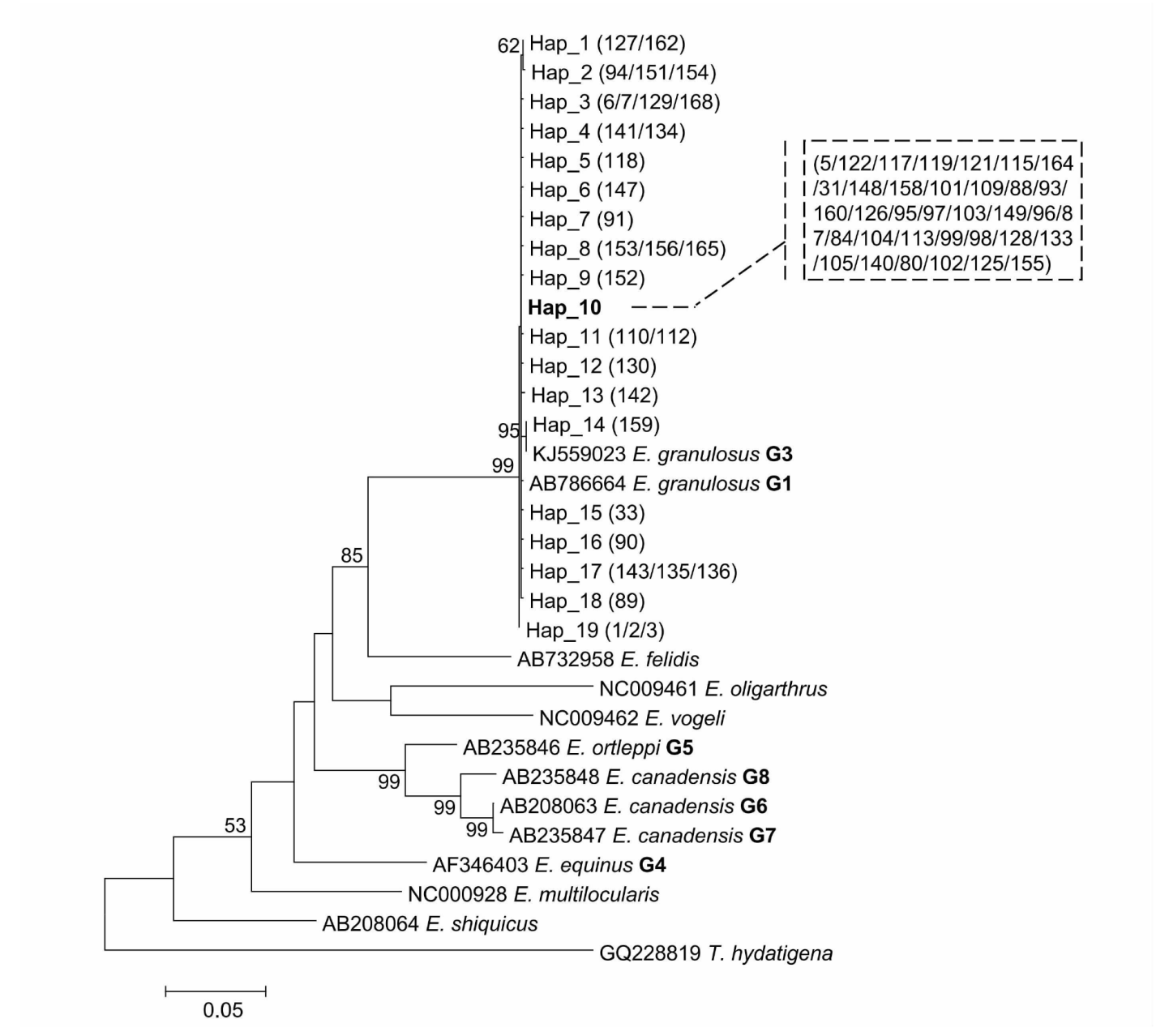
| [1] |
BRUNETTI E, KERN P, VUITTON D A. Expert consensus forthe diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans[J]. Acta tropica, 2010, 114(1):1-16.
doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2009.11.001
|
| [2] |
郭璐, 吴小霞, 段兰利, 等. 新疆部分地区牛、羊细粒棘球蚴感染情况调查及基因多态性分析[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2022, 40(5):603-609.
|
| [3] |
魏巍. 全国农牧系统包虫病防控[J]. 中国动物保健, 2017, 19(7):10-13.
|
| [4] |
吴星星, 蔡扩军, 王光雷, 等. 2010—2014年乌鲁木齐市羊屠宰场羊包虫病感染情况的调查[J]. 草食家畜, 2017(1):52-57.
|
| [5] |
尚婧晔, 张光葭, 何伟, 等. 细粒棘球蚴病病原分类学与分子流行病学研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018, 36(2):166-173.
|
| [6] |
魏玉环, 胡媛, 曹建平. 细粒棘球绦虫基因多态性的研究进展[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2019, 37(4):481-485.
|
| [7] |
玛依拉·艾尼瓦, 马力克, 王冰洁, 等. 新疆伊犁地区包虫病流行病学调查及重点县家畜感染包虫的基因型[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2019, 39(12):2356-2363.
|
| [8] |
GUO B, ZHANG Z, GUO Y, et al. High endemicity of alveolar echinococcosis in Yili Prefecture, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, the People′s Republic of China: Infection status in different ethnic communities and in small mammals[J]. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 2021, 15(1):e0008891.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008891
|
| [9] |
OHIOLEI J A, YAN H B, LI L, et al. Cystic echinococcosis in Nigeria: first insight into the genotypes of Echinococcus granulosus in animals[J]. Parasites and Vectors, 2019, 12(1): 392.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3644-z
|
| [10] |
MOHAGHEGH M A, YOUSOFI-DARANI H, JAFARIAN A H, et al. Correction to: Isolated human and livestock Echinococcus granulosus genotypes using real-time PCR of cox1 gene in northeast Iran[J]. Acta Parasitologica, 2019, 64(3):686.
doi: 10.2478/s11686-019-00133-w
|
| [11] |
GUO B, ZHANG Z, ZHENG X, et al. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto in Northern Xinjiang, China[J]. Korean Journal of Parasitology, 2019, 57(2):153-159.
doi: 10.3347/kjp.2019.57.2.153
|
| [12] |
陈晓英, 玉苏布江·赛提瓦尔, 史爱华, 等. 新疆克孜勒苏柯尔克孜自治州家犬棘球绦虫感染和家畜棘球蚴病流行病学调查[J]. 热带病与寄生虫学, 2016, 14(4):195-197.
|
| [13] |
GAO Y, WANG W, LYU C, et al. Meta-analysis of the prevalence of Echinococcus in sheep in China from 1983 to 2020[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2021, 11:711332.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.711332
|
| [14] |
MEHMOOD N, DESSÌ G, AHMED F, et al. Genetic diversity and trans-mission patterns of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto among domestic ungulates of Sardinia, Italy[J]. Parasitology Research, 2021, 120(7):2533-2542.
doi: 10.1007/s00436-021-07186-9
|
| [15] |
WU Y, LI L, ZHU G, et al. Mitochondrial genome data confirm that yaks can serve as the intermediate host of Echinococcus canadensis (G10) on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Parasites Vectors, 2018, 11(1):166.
doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2684-0
|
| [16] |
KINKAR L, LAURIMÄE T, ACOSTA-JAMETT G, et al. Global phylogeography and genetic diversity of the zoonotic tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto genotype G1[J]. International Journal for Parasitology, 2018, 48(9/10):729-742.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2018.03.006
|
| [17] |
热衣汗·玉素甫, 贾万忠, 闫鸿斌, 等. 新疆北疆部分地区牛羊包虫病流行病学调查与cox1和nad1基因分析[J]. 塔里木大学学报, 2020, 32(2):17-24.
|
| [18] |
薛新梅, 齐萌, 陶大勇, 等. 新疆和静县绵羊细粒棘球蚴流行株基因分型研究[J]. 中国奶牛, 2020(6):30-33.
|
| [19] |
VURAL G, BACA A U, GAUCI C G, et al. Variability in the Echinococcus granulosus Cytochrome C oxidase 1 mitochondrial gene sequence from livestock in Turkey and a re-appraisal of the G1-3 genotype cluster[J]. Veterinary Parasitology, 2008, 154(3/4):347-350.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.03.020
|
| [20] |
KINKAR L, LAURIMAE T, ACOSTA-JAMETTT G, et al. Distinguishing Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto genotypes G1 and G3 with confidence: A practical guide[J]. Infection Genetics and Evolution, 2018, 64:178-184.
doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.06.026
|