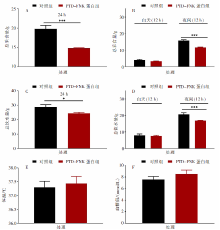
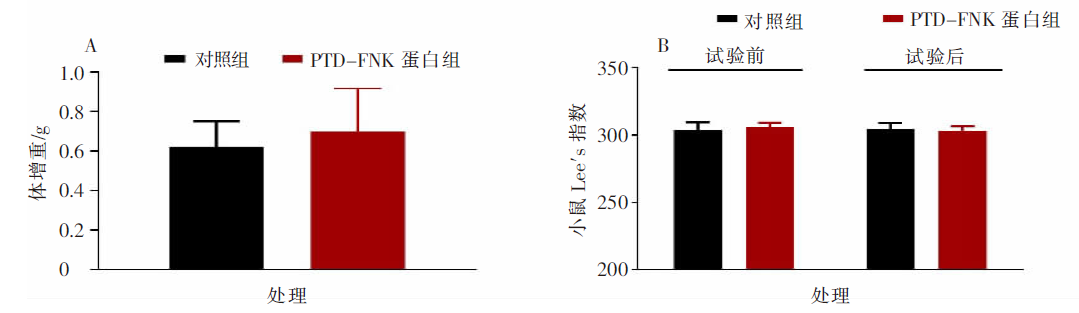
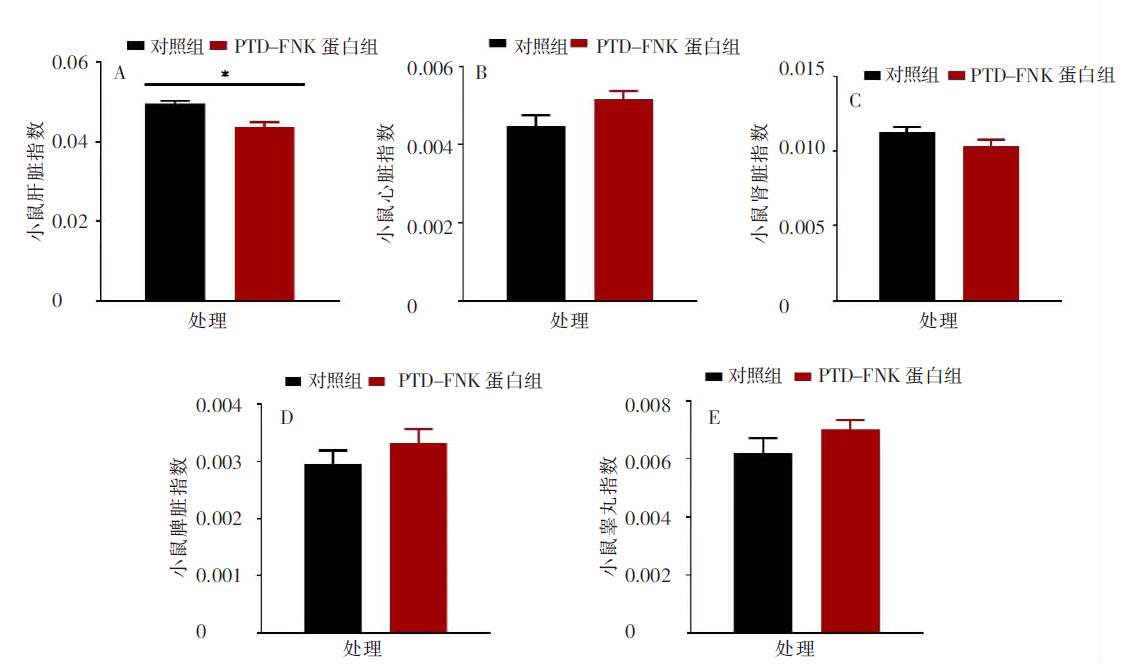
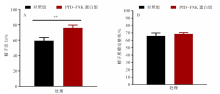
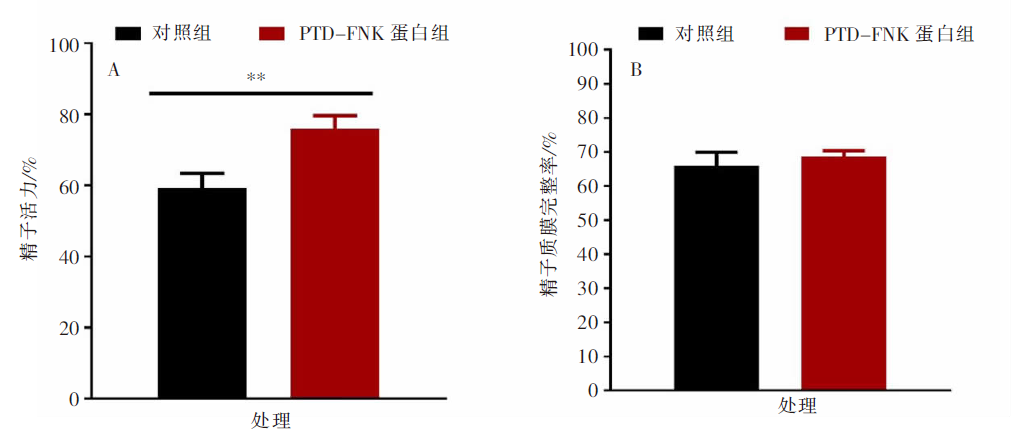
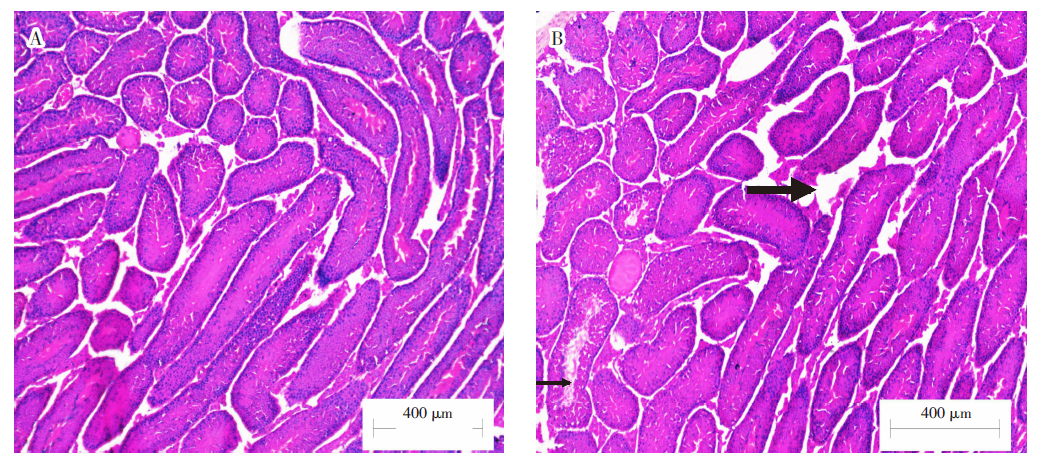
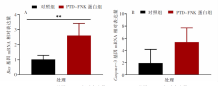
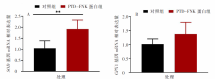
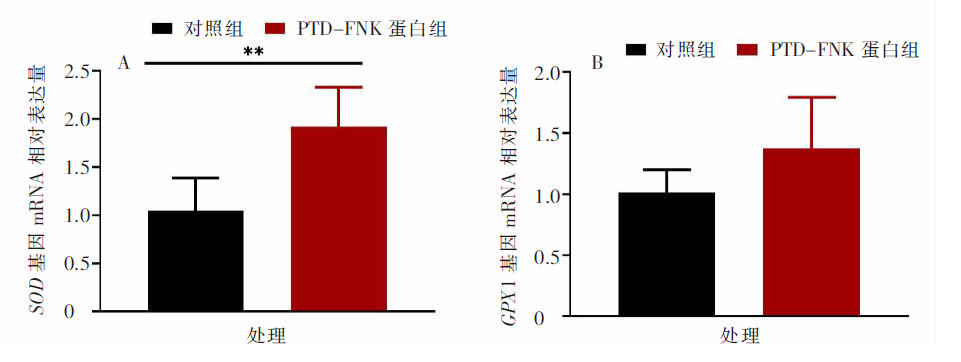
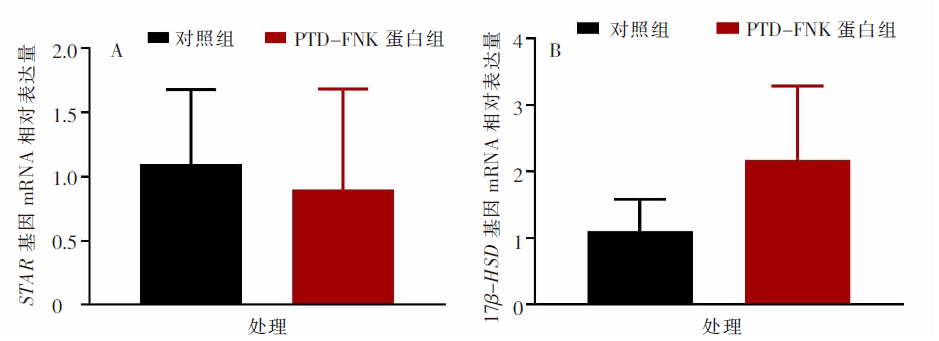
| [1] |
TARA S, MIYAMOTO M, ASOH S, et al. Transduction of the anti-apoptotic PTD-FNK protein improves the efficiency of transplantation of bone marrow mononuclear cells[J]. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 2007, 42(3):489-497.
doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.11.013
pmid: 17229437
|
| [2] |
NAKACHI N, ASOH S, WATANABE N, et al. Transduction of anti-cell death protein FNK suppresses graft degeneration after autologous cylindrical osteochondral transplantation[J]. The Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 2009, 57(3):197-206.
doi: 10.1369/jhc.2008.952754
|
| [3] |
NAKASHIMA-KAMIMURA N, NISHIMAKI K, MORI T, et al. Prevention of chemotherapy-induced alopecia by the anti-death FNK protein[J]. Life Sciences, 2008, 82(3/4):218-225.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.11.011
|
| [4] |
SUDO K, ASOH S, OHSAWA I, et al. The anti-cell death FNK protein protects cells from death induced by freezing and thawing[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2005, 330(3):850-856.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.059
pmid: 15809074
|
| [5] |
KATSURA K I, TAKAHASHI K, ASOH S, et al. Combination therapy with transductive anti‐death FNK protein and FK506 ameliorates brain damage with focal transient ischemia in rat[J]. Journal of Neurochemistry, 2008, 106(1):258-270.
doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05360.x
|
| [6] |
ARAKAWA M, YASUTAKE M, MIYAMOTO M, et al. Transduction of anti-cell death protein FNK protects isolated rat hearts from myocardial infarction induced by ischemia/reperfusion[J]. Life Sciences, 2007, 80(22):2076-2084.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.03.012
pmid: 17467744
|
| [7] |
李文霞, 曾本华, 袁静, 等. GF昆明小鼠主要重量系数及血液生理指标的测定[J]. 中国微生态学杂志, 2011, 23(9):780-783.
|
| [8] |
LI C L, ZHAO K, ZHANG H P, et al. Lead exposure reduces sperm quality and DNA integrity in mice[J]. Environmental Toxicology, 2018, 33(5):594-602.
doi: 10.1002/tox.22545
pmid: 29446210
|
| [9] |
POURENTEZARI M, TALEBI A R, MANGOLI E, et al. Additional deleterious effects of alcohol consumption on sperm parameters and DNA integrity in diabetic mice[J]. Andrologia, 2016, 48(5):564-569.
doi: 10.1111/and.12481
pmid: 26358836
|
| [10] |
SM S, BASHA P M. Fluoride exposure aggravates the testicular damage and sperm quality in diabetic mice: Protective role of ginseng and banaba[J]. Biological Trace Element Research, 2017, 177(2):331-344.
doi: 10.1007/s12011-016-0893-y
pmid: 27854046
|
| [11] |
OMMATI M M, HEIDARI R, JAMSHIDZADEH A, et al. Dual effects of sulfasalazine on rat sperm characteristics, spermatogenesis, and steroidogenesis in two experimental models[J]. Toxicology Letters, 2018, 284:46-55.
doi: S0378-4274(17)31495-9
pmid: 29197623
|
| [12] |
DOLATI P, ZAMIRI M J, AKHLAGHI A, et al. Reproductive and embryological toxicity of lead acetate in male mice and their offspring and mitigation effects of quercetin[J]. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 2021, 67:126793.
doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2021.126793
|
| [13] |
王艳梅. X射线电离辐射对成年小鼠睾丸组织的损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(20):3829-3832.
|
| [14] |
HU S J, REN G, LIU J L, et al. MicroRNA expression and regulation in mouse uterus during embryo implantation[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2008, 283(34):23473-23484.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800406200
|
| [15] |
NEMATOLLAHI S, MEHDIZADEH M, HOSSEINI S, et al. DNA integrity and methylation changes of mouse spermatozoa following prolonged incubation[J]. Andrologia, 2019, 51(6):e13276.
doi: 10.1111/and.2019.51.issue-6
|
| [16] |
李丹丹, 刘蛟, 王英群, 等. PTD-FNK蛋白对猪精子的冷冻保护作用及其机制[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(11):217-221.
|
| [17] |
CHEN H, ZHANG L, JIN Z, et al. Anti-apoptotic PTD-FNK protein suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats[J]. Experimental and Molecular Pathology, 2007, 83(3):377-384.
doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2007.08.016
pmid: 17959170
|
| [18] |
太田成男. 細胞死抑制活性強化因子を用いた蛋白質治療法の開発[J]. Journal of Nippon Medical School, 2003, 70(5):442-446.
doi: 10.1272/jnms.70.442
|
| [19] |
王英群, 石博妹, 李珣, 等. Bcl-xL及PTD-FNK蛋白的细胞保护作用研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2017, 44(7):1967-1974.
|
| [20] |
WU G, TU Z, YANG F, et al. Evaluating the inhibitory priority of Bcl-xL to Bad, tBid and Bax by using live-cell imaging assay[J]. Cytometry Part A, 2021, 99(11):1091-1101.
doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.24351
pmid: 33843148
|
| [21] |
陈竑, 宋钦华, 李红珊. 空腹血糖调节受损伴脂肪肝及其相关因素分析[J]. 广东医学, 2008, 29(7):1204-1205.
|
| [22] |
KE F, LANCASTER G I, GRABOW S, et al. Combined reduction in the expression of MCL-1 and BCL-2 reduces organismal size in mice[J]. Cell Death and Disease, 2020, 11(3):185.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2376-5
pmid: 32170090
|
| [23] |
MISHRA D P, PAL R, SHAHA C. Changes in cytosolic Ca2+ levels regulate Bcl-xS and Bcl-xL expression in spermatogenic cells during apoptotic death[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2006, 281(4):2133-2143.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508648200
|
| [24] |
CUTTLE L, ZHANG X J, ENDRE Z H, et al. Bcl-X(L) translocation in renal tubular epithelial cells in vitro protects distal cells from oxidative stress[J]. Kidney International, 2001, 59(5):1779-1788.
doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.0590051779.x
|
| [25] |
SHIMOKAWA K, OSHIRO R, YAMANAKA K, et al. Improvement of the post-thaw qualities of Okinawan native Agu pig sperm frozen in an extender supplemented with antiapoptotic PTD-FNK protein[J]. Theriogenology, 2012, 78(7):1446-1455.
doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2012.06.005
pmid: 22925637
|
| [26] |
刘蛟, 许春荣, 覃志贵, 等. PTD-FNK蛋白对水牛精子的冷冻保护作用[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2020, 50(3):396-402.
|
| [27] |
CUI N, LI S X, ZHAO X L, et al. Expression of Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 in nerve tissues of rats chronically exposed to 2,5-hexanedione[J]. Neurochemical Research, 2007, 32(9):1566-1572.
pmid: 17492505
|
| [28] |
WENNERSTEN A, HOLMIN S, MATHIESEN T. Characterization of Bax and Bcl-2 in apoptosis after experimental traumatic brain injury in the rat[J]. Acta Neuropathologica, 2003, 105(3):281-288.
pmid: 12557016
|
| [29] |
OLTVAI Z N, MILLIMAN C L, KORSMEYER S J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death[J]. Cell, 1993, 74(4):609-619.
doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90509-O
|
| [30] |
张仲迎, 高歌, 李莹, 等. 同型半胱氨酸致心血管疾病氧化应激机制的研究进展[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2019, 11(10):1270-1273.
|
| [31] |
ZOROV D B, FILBURN C R, KLOTZ L O, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced ROS release: A new phenomenon accompanying induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition in cardiac myocytes[J]. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 2000, 192(7):1001-1014.
doi: 10.1084/jem.192.7.1001
|
| [32] |
袁杨斌, 刘强, 陈瑞, 等. 辣椒碱对樱桃谷肉鸭生长性能、肉品质和抗氧化功能的影响[J]. 中国家禽, 2021, 43(7):69-75.
|