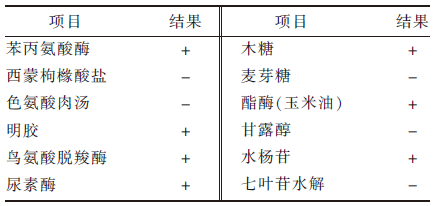
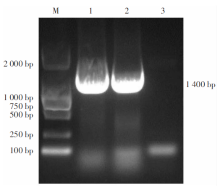
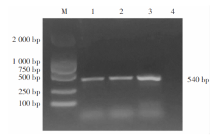
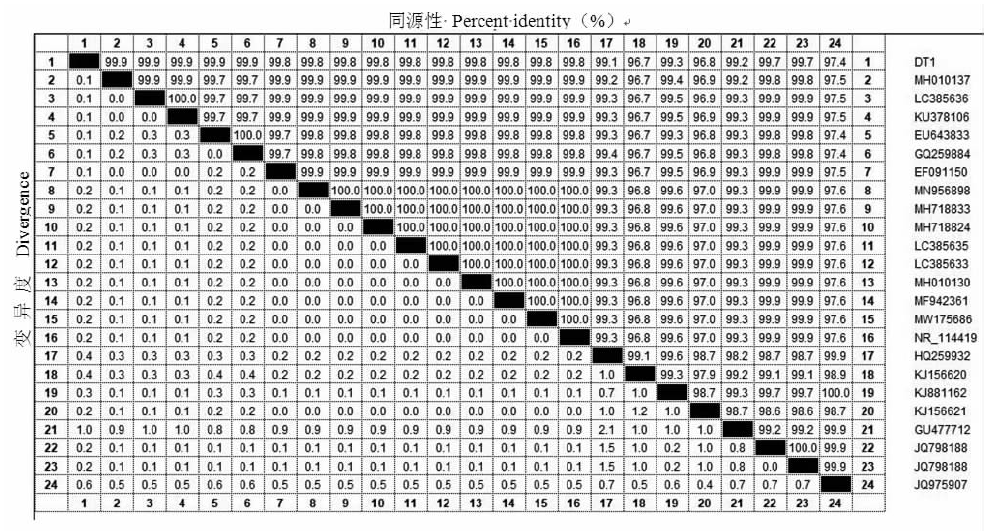
| [1] |
刘燕云, 柴家前. 奇异变形杆菌研究进展[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2017, 37(1):196-200.
|
| [2] |
MARQUES C, BELAS A, ABOIM C, et al. Clonal relatedness of Proteus mirabilis strains causing urinary tract infections in companion animals and humans[J]. Veterinary Microbiology, 2019, 228:77-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.10.015
|
| [3] |
ARGELICH R, IBANEZ-FLORES N, BARDAVIO J, et al. Orbital cellulitis and endogenous endophthalmitis secondary to Proteus mirabilis cholecystitis[J]. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease, 2009, 64 (4):442-444.
doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2009.04.014
|
| [4] |
CHEN C Y, CHEN Y H, LU P L, et al. Proteus mirabilis urinary tract infection and bacteremia:Risk factors,clinical presentation,and outcomes[J]. Journal of Microbiology,Immunology,and Infection, 2012, 45 (3):228-236.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2011.11.007
|
| [5] |
石晓路, 扈庆华, 林一曼, 等. 致腹泻奇异变形杆菌病原学及其分子特征研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2014, 35(6):724-728.
|
| [6] |
苏治国, 陈文芳. 泰州地区致仔猪腹泻奇异变形杆菌鉴定及其毒力基因与耐药性检测[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2019, 51(11):118-122.
|
| [7] |
王红均, 游慧慧, 李清丰, 等. 1株仔猪源腹泻奇异变形杆菌的分离鉴定及药敏试验[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2018(24):118-121.
|
| [8] |
王道宁, 孔令聪, 董文龙, 等. 犬源奇异变形杆菌的分离鉴定及生物学特性分析[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2020(1):72-76.
|
| [9] |
张萍, 程悦宁, 张海威, 等. 狐狸流产奇异变形杆菌的分离鉴定及特征分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2019, 46(11):3370-3377.
|
| [10] |
刘权, 刘雨, 李艳艳, 等. 食蟹猴奇异变形杆菌的分离鉴定及药敏试验[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2020, 30(6):88-92.
|
| [11] |
侯晓, 徐结, 张雪婧, 等. 甘肃某牦牛场奇异变形杆菌的分离鉴定及小鼠致病性试验[J]. 动物医学进展, 2019, 40(10):44-48.
|
| [12] |
谢秀兰, 黎帅, 马小明, 等. 羊奇异变形杆菌的分离鉴定及药敏试验[J]. 动物医学进展, 2017, 38(7):115-119.
|
| [13] |
周建波, 胡丽萍, 马宁宁, 等. 致羔羊腹泻奇异变形杆菌的分离鉴定及迁徙行为分析[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2017, 37(7):1274-1282.
|
| [14] |
李欣南, 韩镌竹, 宁宜宝. 鸡源奇异变形杆菌的分离鉴定及耐药性研究[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2015(11): 165-167.
|
| [15] |
徐睿, 李颜桃. 鸡源致病性奇异变形杆菌的分离鉴定与遗传进化分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2018, 45(9): 2550-2558.
|
| [16] |
庞洪泽, 张召兴, 张海龙, 等. 雏鸡源致病性奇异变形杆菌的鉴定与药敏试验[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2019, 55(12):96-98.
|
| [17] |
刘文强, 贾玉萍, 赵宏坤. 16S rRNA在细菌分类鉴定研究中的应用[J]. 动物医学进展, 2006(11):15-18.
|
| [18] |
蒋波, 范一灵, 房蕊, 等. 16S rRNA序列分析法与生化鉴定法对药品检验中细菌的鉴定比较[C]// 2016年中国药学大会暨第十六届中国药师周论文集. 北京: 中国药学会, 2016:729-736.
|
| [19] |
刘秘, 李万翔, 李世荣. 整合子与细菌耐药性的相关研究进展[J]. 中国微生态学杂志, 2020, 32(4):465-468.
|
| [20] |
张利锋, 李娟, 卢金星. 奇异变形杆菌耐药性研究进展[J]. 疾病监测, 2016, 31(5):427-432.
|