北方农业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 72-79.doi: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2023.04.09
不同寄主对草地贪夜蛾生长发育和繁殖的影响
魏佩瑶1, 冯小军2, 谢飞舟2, 陈志杰1, 王天舒3, 赵世磊4, 洪波1
- 1.陕西省生物农业研究所,陕西 西安 710043
2.陕西省植物保护工作总站,陕西 西安 710003
3.西安市农产品质量安全检验监测中心,陕西 西安 710000
4.商洛市植保植检站,陕西 商洛 726000
Effects of different hosts on the growth,development and reproduction of Spodoptera frugiperda
WEI Peiyao1, FENG Xiaojun2, XIE Feizhou2, CHEN Zhijie1, WANG Tianshu3, ZHAO Shilei4, HONG Bo1
- 1. Bio-agriculture Institute of Shaanxi,Xi′an 710043,China
2. Plant Protection Station of Shaanxi,Xi′an 710003,China
3. Xi′an Agricultural Product Quality and Safety Inspection and Monitoring Center,Xi′an 710000,China
4. Shangluo Plant Protection and Inspection Station,Shangluo 726000,China
摘要:
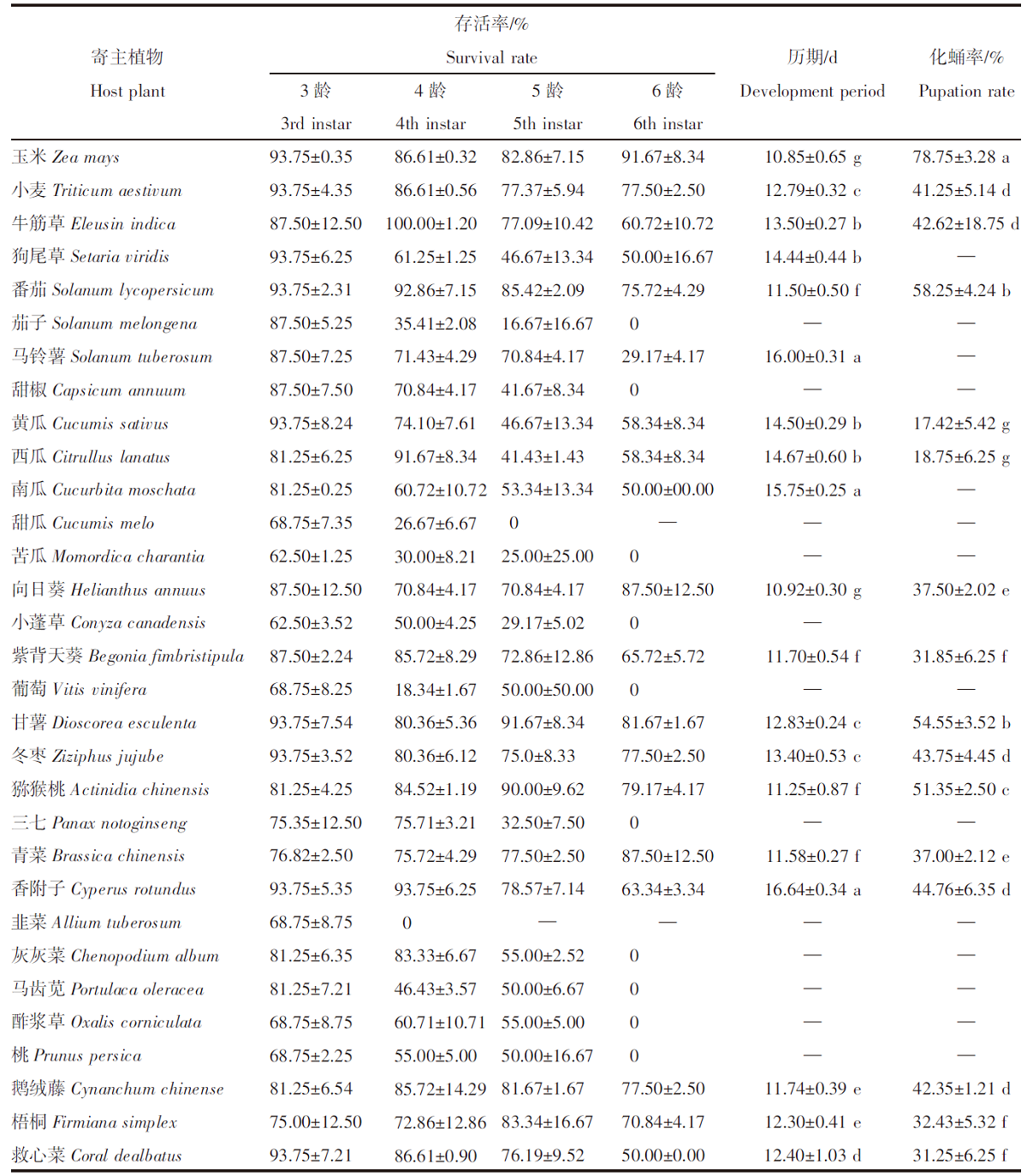
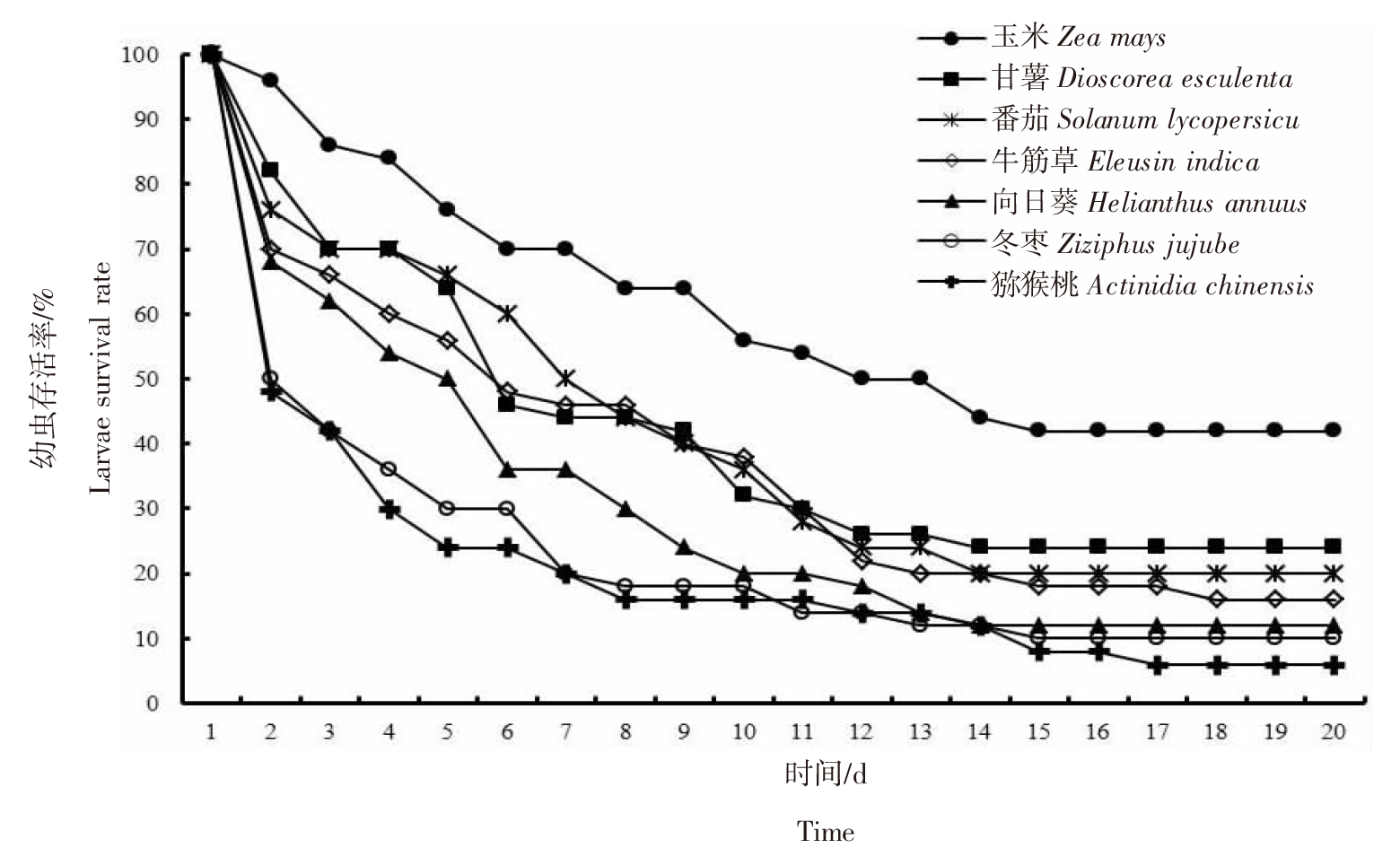
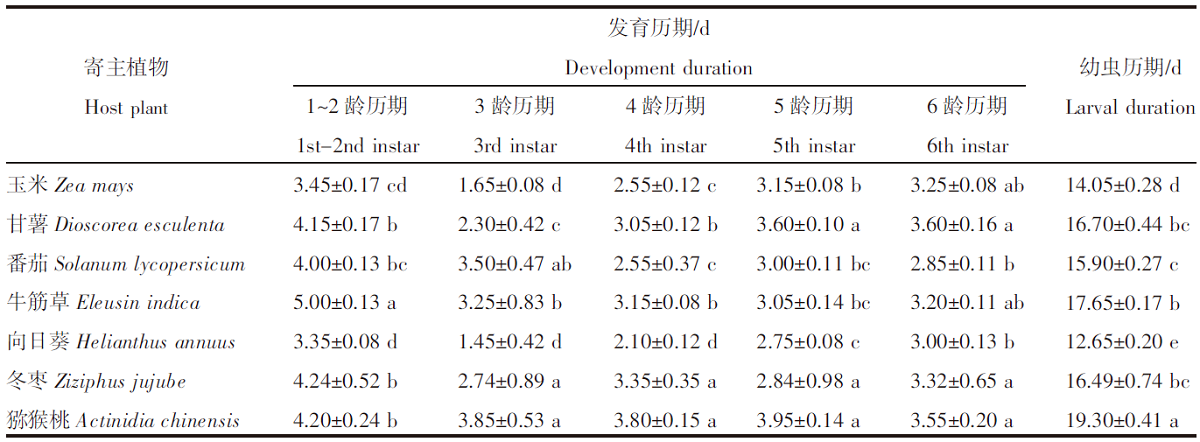
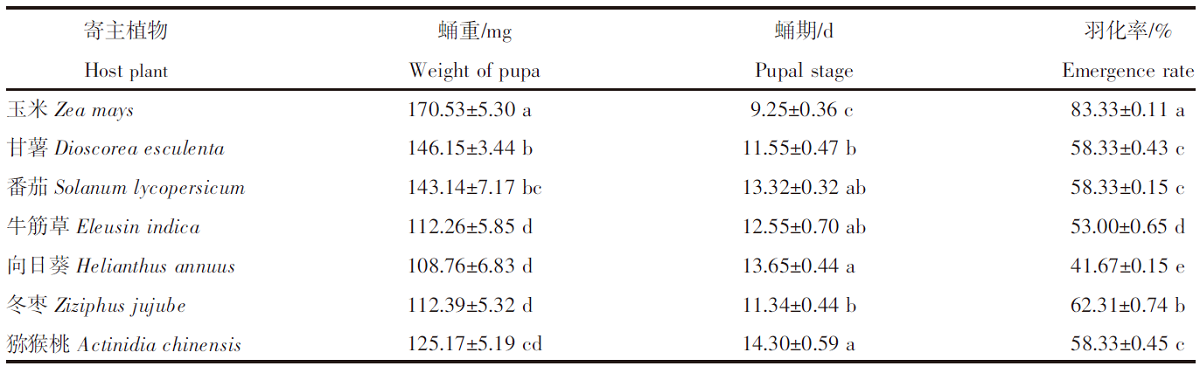
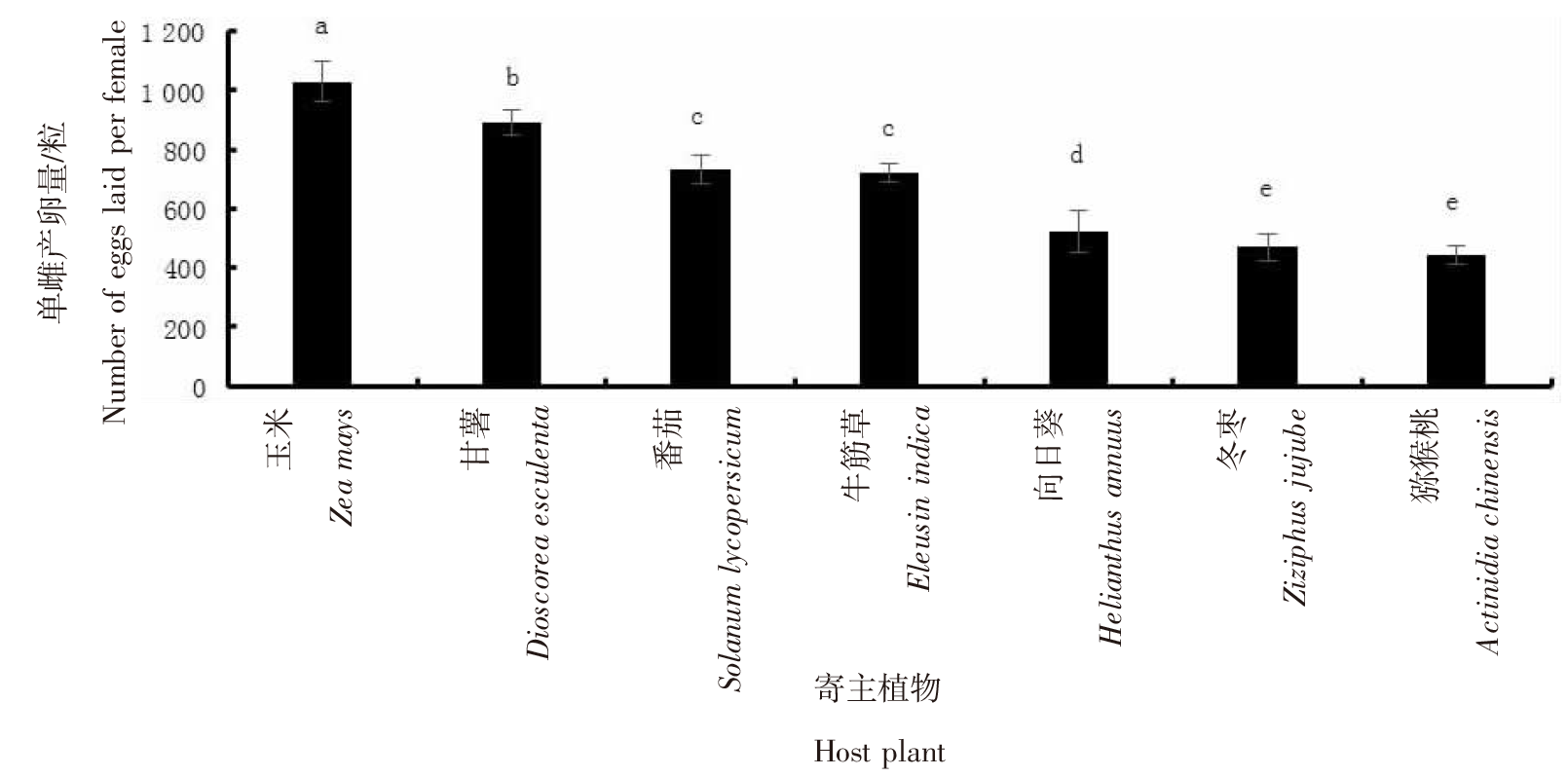
【目的】明确不同寄主对草地贪夜蛾(Spodoptera frugiperda)生长发育和繁殖的影响。【方法】采用室内饲养观察的方法比较分析草地贪夜蛾3龄幼虫取食玉米(Zea mays)、小麦(Triticum aestivum)、番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)等23种代表性作物,以及玉米田常见的牛筋草(Eleusin indica)、马齿苋(Portulaca oleracea)、香附子(Cyperus rotundus)等8种杂草后的生长发育及幼虫化蛹情况。选取其中适合度较高的7种植物作为供试寄主,比较草地贪夜蛾的生长、发育和繁殖情况。【结果】以小麦、甘薯(Dioscorea esculenta)和番茄等16种植物为食的3龄幼虫能够完成幼虫阶段的生长发育并成功化蛹。甘薯、番茄、牛筋草、向日葵(Helianthus annuus)、冬枣(Ziziphus jujube)和猕猴桃(Actinidia chinensis)是除玉米外取食生长适合度较高的寄主植物。其中,取食猕猴桃叶片的草地贪夜蛾幼虫历期最长,为19.30 d;取食向日葵叶片的草地贪夜蛾幼虫历期最短,为12.65 d。取食玉米叶片的幼虫,蛹重为170.53 mg,显著高于其他6种寄主植物(P<0.05),且蛹期最短(9.25 d)、羽化率最高(83.33%);取食甘薯叶片的草地贪夜蛾幼虫各项指标与取食玉米叶片的幼虫最接近,蛹重为146.15 mg、蛹期为11.55 d、羽化率为58.33%。取食玉米叶片的草地贪夜蛾单雌产卵量为1 030粒,显著高于其他6种寄主植物(P<0.05);取食甘薯叶片的草地贪夜蛾单雌产卵量次之,为892粒。【结论】草地贪夜蛾偏好选择玉米进行取食和产卵,但在甘薯、番茄、牛筋草、向日葵、冬枣和猕猴桃上可以实现种群繁衍,当其种群密度大时存在迁移扩散至其他作物的风险。
中图分类号:
- S433.4