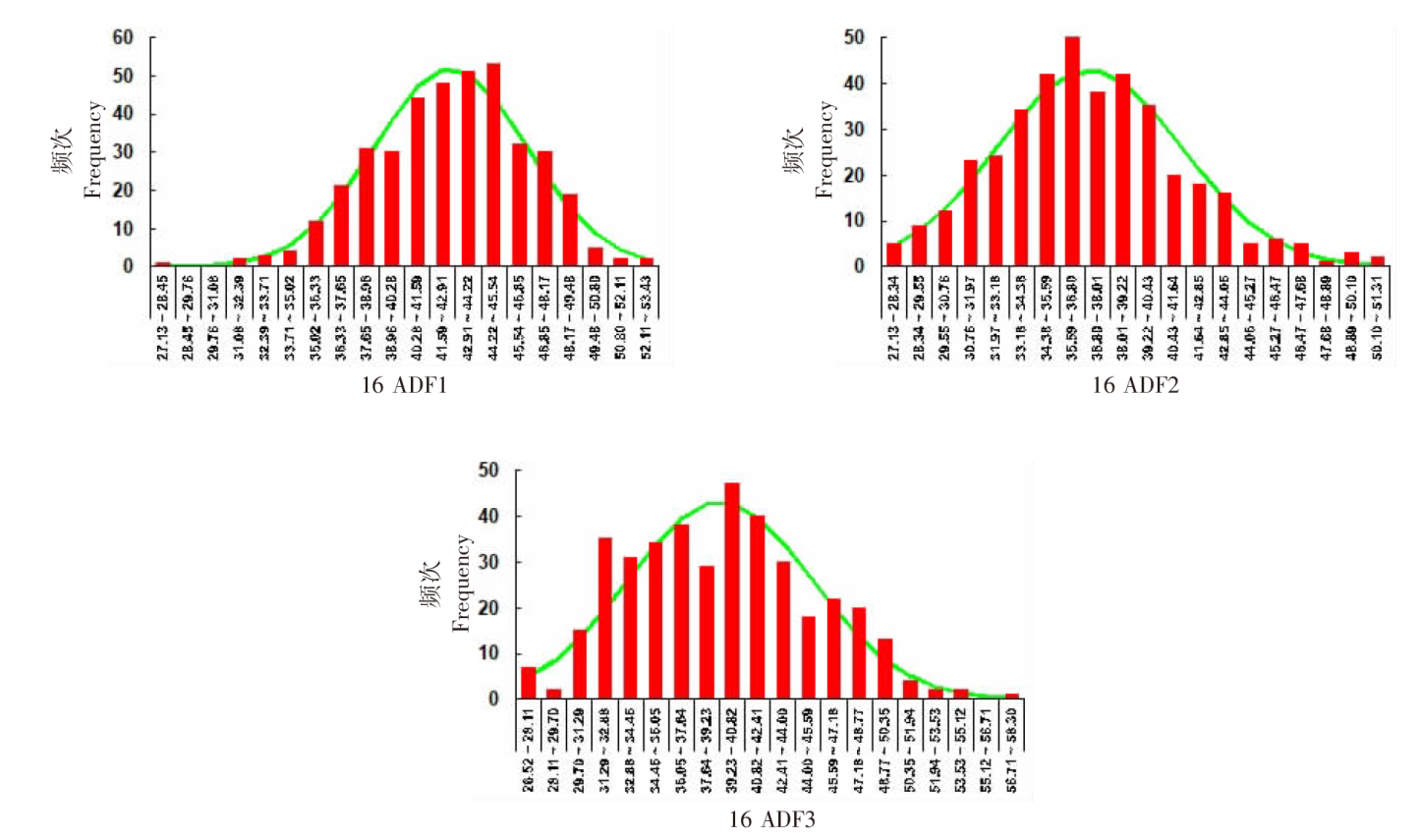
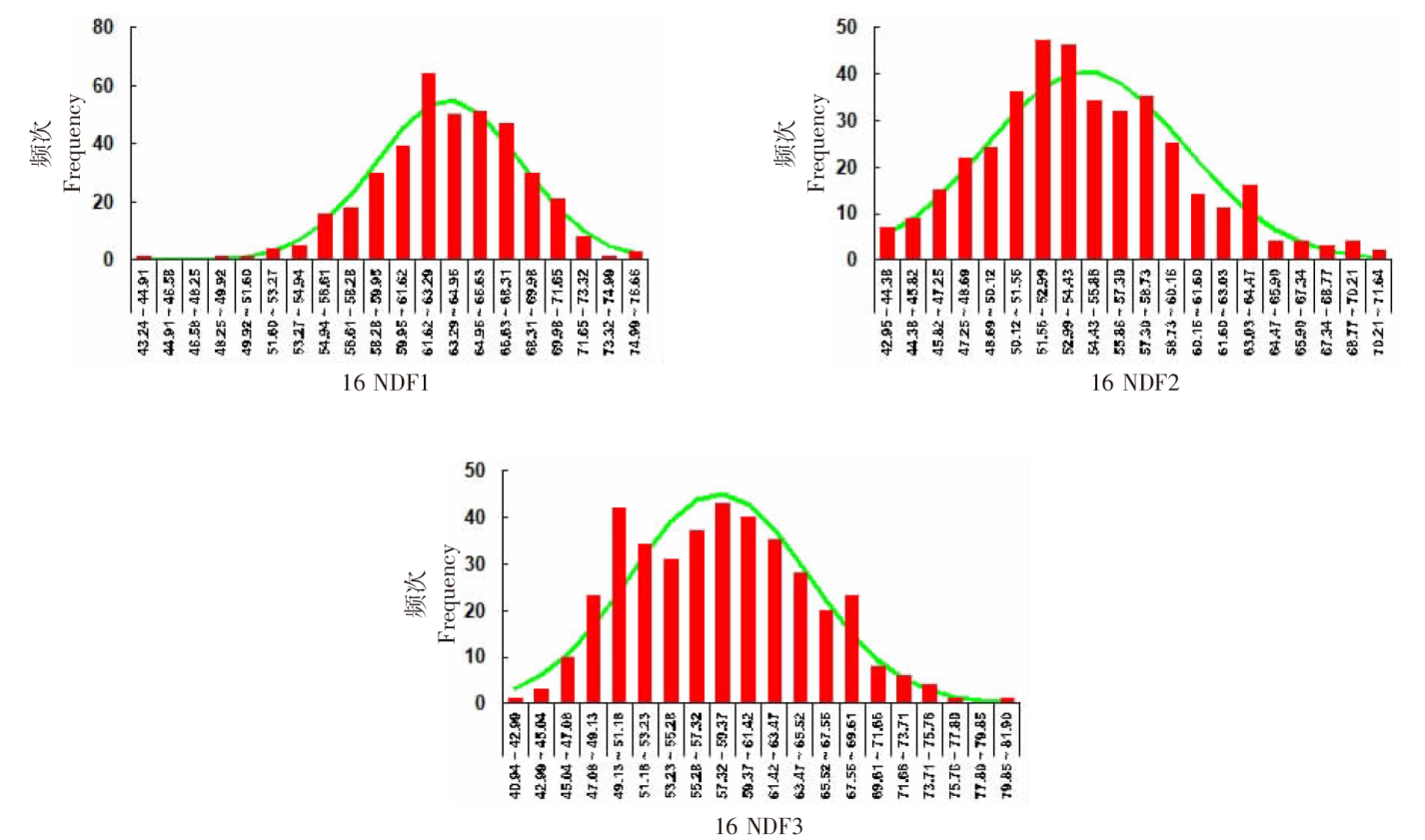
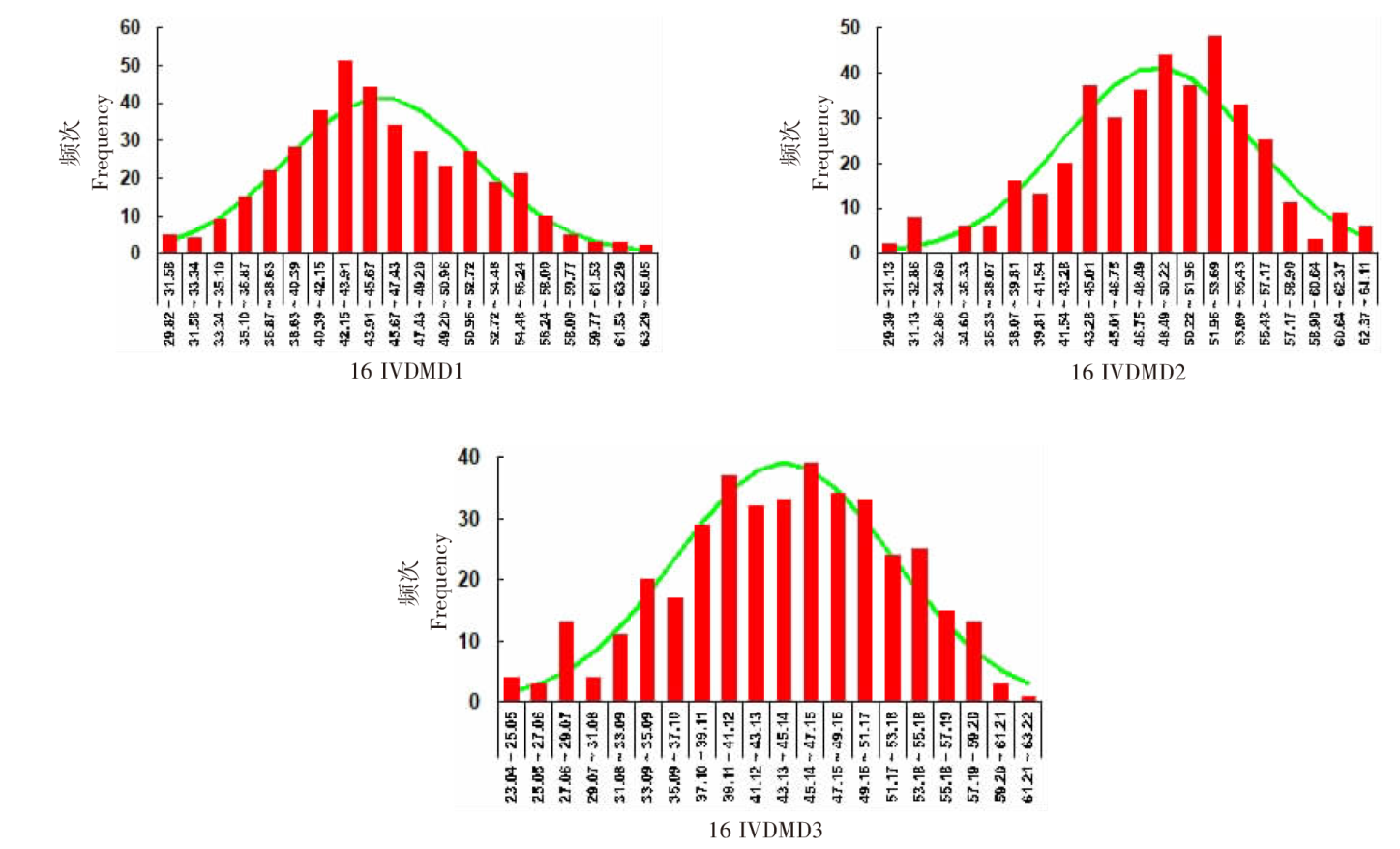
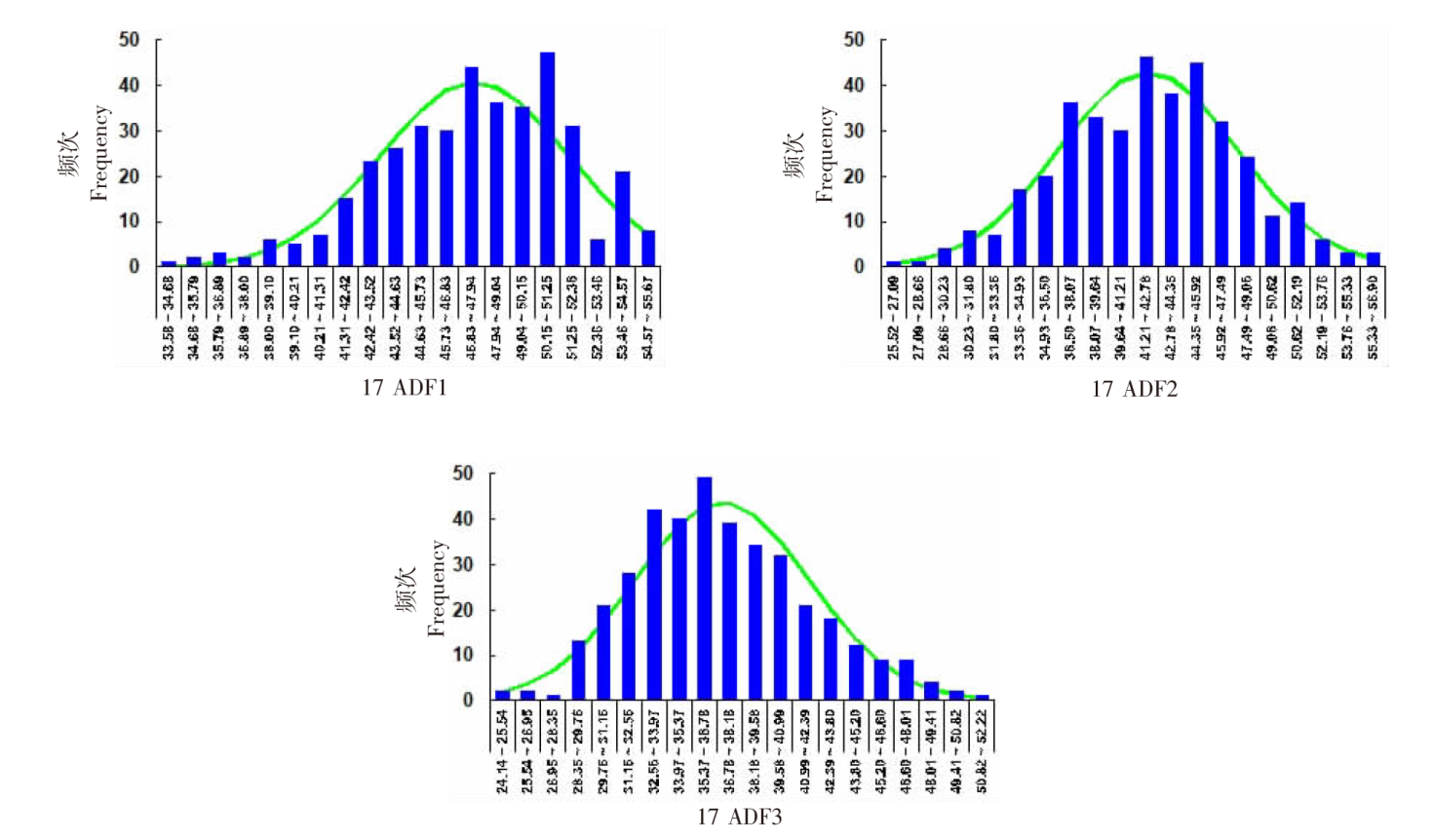
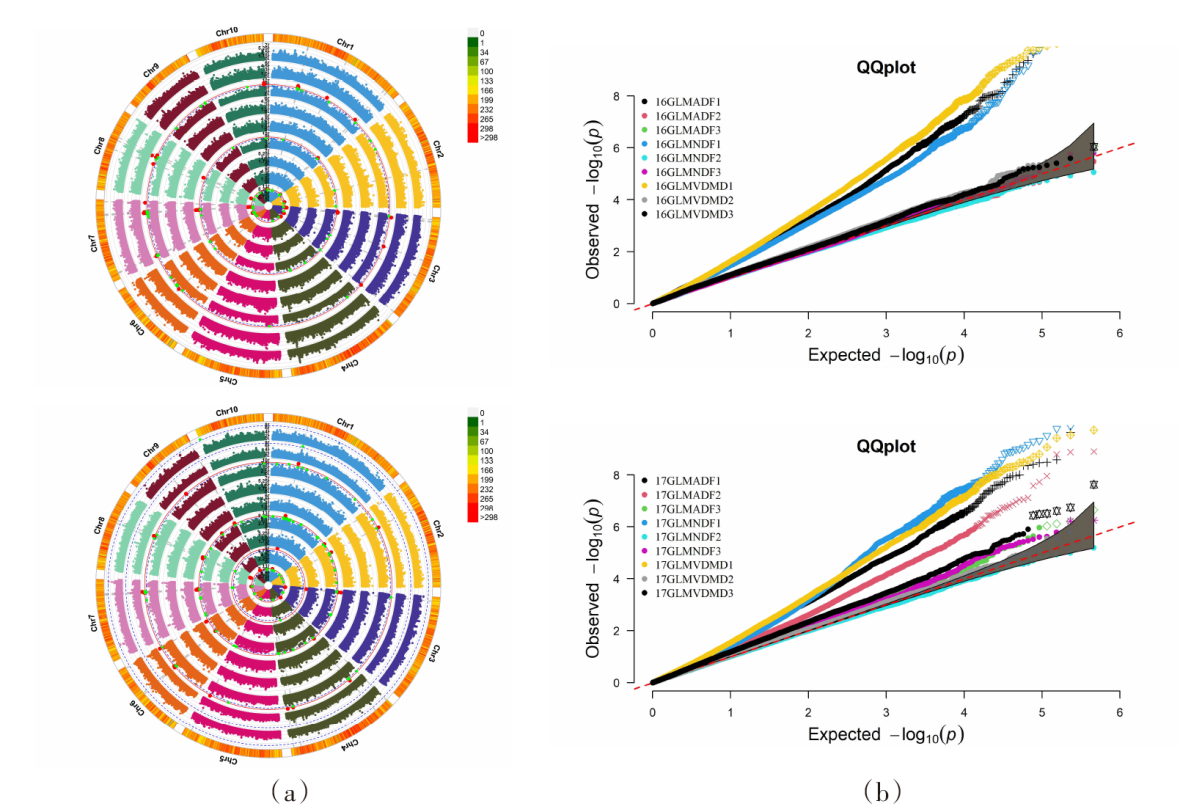
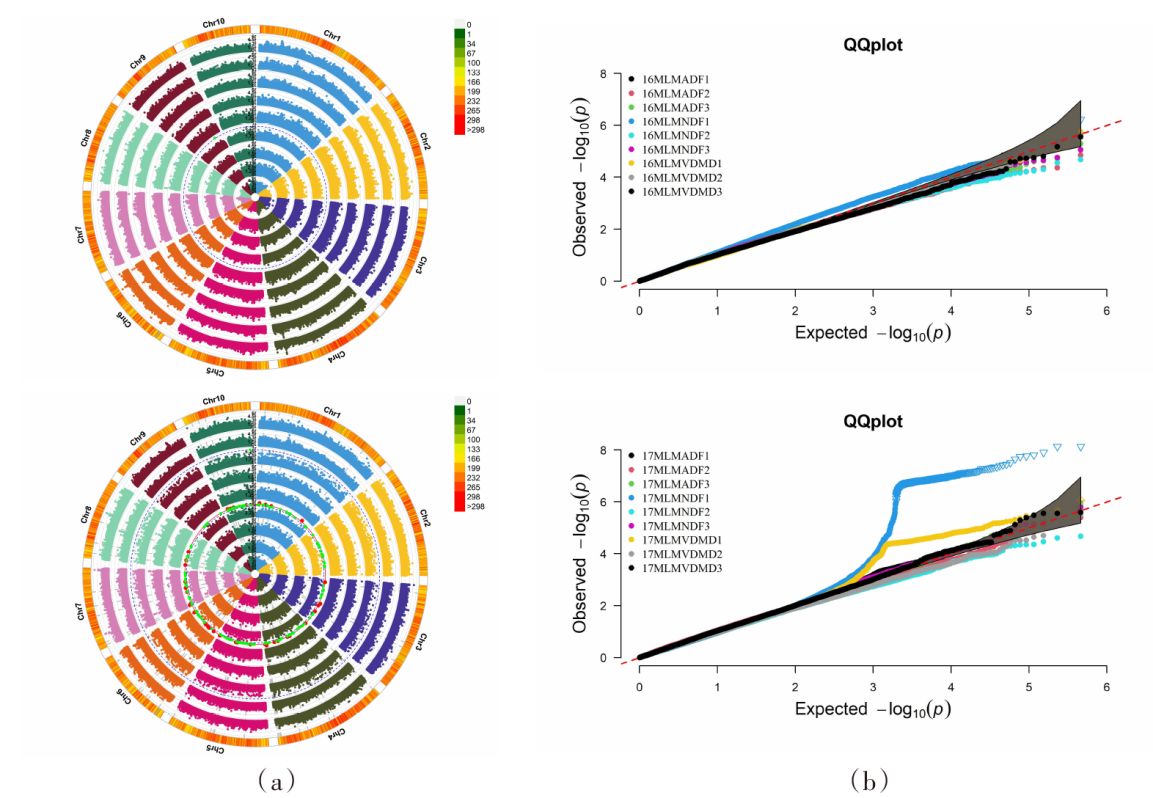
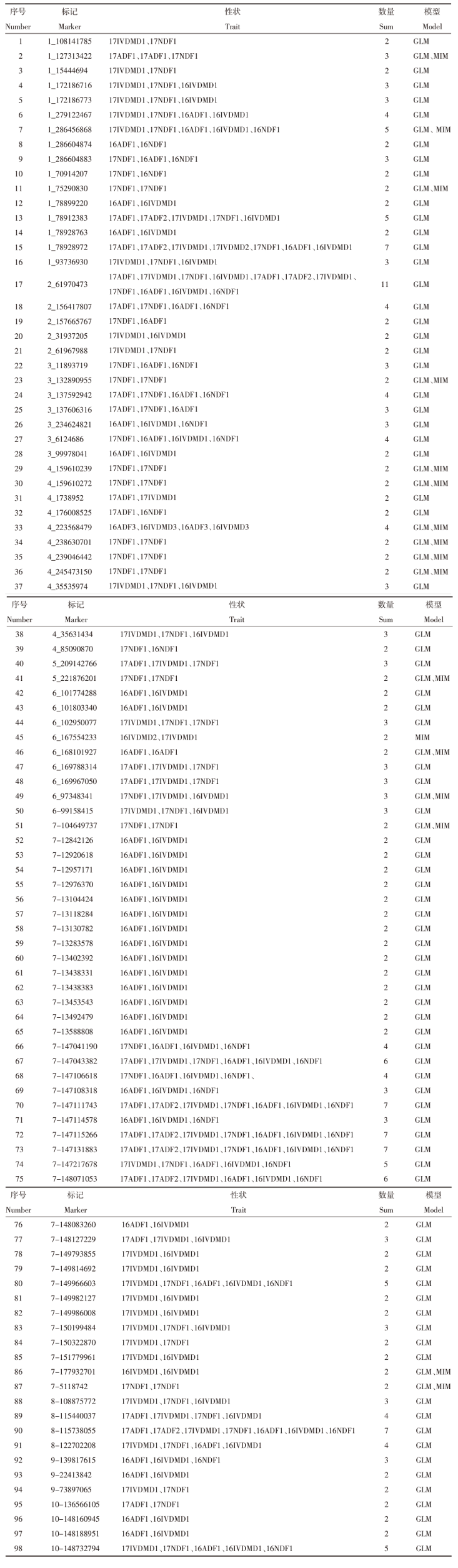
| [1] |
林淼, 张秋芝, 史利玉, 等. 玉米秸秆消化率全基因组关联分析[J]. 作物杂志, 2020(6):23-29.
|
| [2] |
LÜBBERSTEDT T, MELCHINGER A E, KLEIN D, et al. QTL mapping in testcrosses of European flint lines of maize:Ⅱ.Comparison of different testers for forage quality traits[J]. Crop Science, 1997, 37(6):1913-1922.
doi: 10.2135/cropsci1997.0011183X003700060041x
|
| [3] |
MÉCHIN V, ARGILLIER O, HÉBERT Y, et al. Genetic analysis and QTL mapping of cell wall digestibility and lignification in silage maize[J]. Crop Science, 2001, 41(3):690-697.
doi: 10.2135/cropsci2001.413690x
|
| [4] |
CARDINAL A, LEE M, MOORE K. Genetic mapping and analysis of quantitative trait loci affecting fiber and lignin content in maize[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2003, 106(5):866-874.
doi: 10.1007/s00122-002-1136-5
pmid: 12647061
|
| [5] |
BARRIÈRE Y, MÉCHIN V, DENOUE D, et al. QTL for yield,earliness,and cell wall quality traits in topcross experiments of the F838×F286 early maize RIL progeny[J]. Crop Science, 2010, 50(5):1761-1772.
doi: 10.2135/cropsci2009.11.0671
|
| [6] |
BARRIÈRE Y, RIBOULET C, MÉCHIN V, et al. Genetics and genomics of lignification in grass cell walls based on maize as model species[J]. Genes,Genomes and Genomics, 2007, 1(2):133-156.
|
| [7] |
BARRIÈRE Y, MÉCHIN V, LEFEVRE B, et al. QTLs for agronomic and cell wall traits in a maize RIL progeny derived from a cross between an old Minnesota13 line and a modern Iodent line[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2012, 125(3):531-549.
doi: 10.1007/s00122-012-1851-5
pmid: 22437492
|
| [8] |
WANG H W, LI K, HU X J, et al. Genome-wide association analysis of forage quality in maize mature stalk[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2016, 16(1):1-12.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0700-5
|
| [9] |
李灿. 玉米主要营养品质性状的全基因组关联分析[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2018.
|
| [10] |
李坤. 玉米茎秆细胞壁组分及消化品质性状的全基因组关联分析[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2017.
|
| [11] |
林淼, 张秋芝, 史利玉, 等. 青贮玉米中性洗涤纤维含量全基因组关联分析[J]. 玉米科学, 2021, 29(2):8-15.
|
| [12] |
WANG M, YAN J B, ZHAO J R, et al. Genome-wide association study(GWAS) of resistance to head smut in maize[J]. Plant Science, 2012, 196:125-131.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.08.004
|
| [13] |
BRADBURY P J, ZHANG Z W, KROON D E, et al. TASSEL:Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples[J]. Bioinformatics, 2007, 23(19):2633-2635.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
|
| [14] |
BASHLINE L, LEI L, LI S D, et al. Cell wall,cytoskeleton,and cell expansion in higher plants[J]. Molecular Plant, 2014, 7(4):586-600.
doi: 10.1093/mp/ssu018
|
| [15] |
关红辉, 刘文斯, 郭晋杰, 等. 不同杂种优势群玉米茎秆纤维品质及配合力分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2018, 19(5):925-936.
|
| [16] |
谢刘勇. 玉米茎秆强度相关性状全基因组关联分析与重要基因挖掘[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2021.
|
| [17] |
刘小刚. 玉米产量相关性状的全基因组选择[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2018.
|
| [18] |
马飞前, 刘小刚, 王红武, 等. 玉米茎秆纤维品质性状及其相关分析[J]. 作物杂志, 2014(4):44-48.
|
| [19] |
闫贵龙, 曹春梅, 鲁琳, 等. 玉米秸秆不同部位主要化学成分和活体外消化率比较[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2006, 11(3):70-74.
|
| [20] |
WAITITU K J. 不同玉米自交系响应非生物胁迫的转录组分析[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021.
|
| [21] |
林静, 林建新, 张扬, 等. 利用转录组解析鲜食玉米闽甜6855的耐寒机制[J]. 华北农学报, 2022, 37(5):1-8.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20193005
|
| [22] |
郭栋, 杜媚, 周宝元, 等. 玉米CCT基因家族的鉴定与生物信息学分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2019, 20(4):1001-1010.
|
| [23] |
杜雪梅. 结合多组学探索玉米愈伤发生和花期转换的分子机理[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020.
|
| [24] |
郭向阳. 基于关联分析和连锁分析策略挖掘玉米氮响应的株型性状关键位点[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2020.
|
| [25] |
孟爱菊. 玉米耐低温萌发相关性状全基因组关联分析及候选基因功能研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2022.
|
| [26] |
李春艳. 玉米ZF-HD转录因子家族耐盐、抗旱相关基因的鉴定及特性分析[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2018.
|
| [27] |
刘过. 玉米抗旱生理生化特性及差异表达基因分析[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2020.
|