北方农业学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 23-30.doi: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2023.05.02
玉米矮秆基因及调控机理的研究进展
唐兰, 吴元奇
- 四川农业大学 玉米研究所,四川 成都 611134
-
收稿日期:2023-09-13出版日期:2023-10-20发布日期:2024-01-04 -
通讯作者:吴元奇(1968—),男,副教授,博士,主要从事玉米遗传育种、数量遗传方面的研究工作。 -
作者简介:唐 兰(1998—),女,硕士,主要从事玉米遗传育种方面的研究工作。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目(2016YFD0300309)
Research progress of maize dwarf genes and their regulatory mechanisms
TANG Lan, WU Yuanqi
- Maize Research Institute,Sichuan Agricultural University,Chengdu 611134,China
-
Received:2023-09-13Online:2023-10-20Published:2024-01-04
摘要:
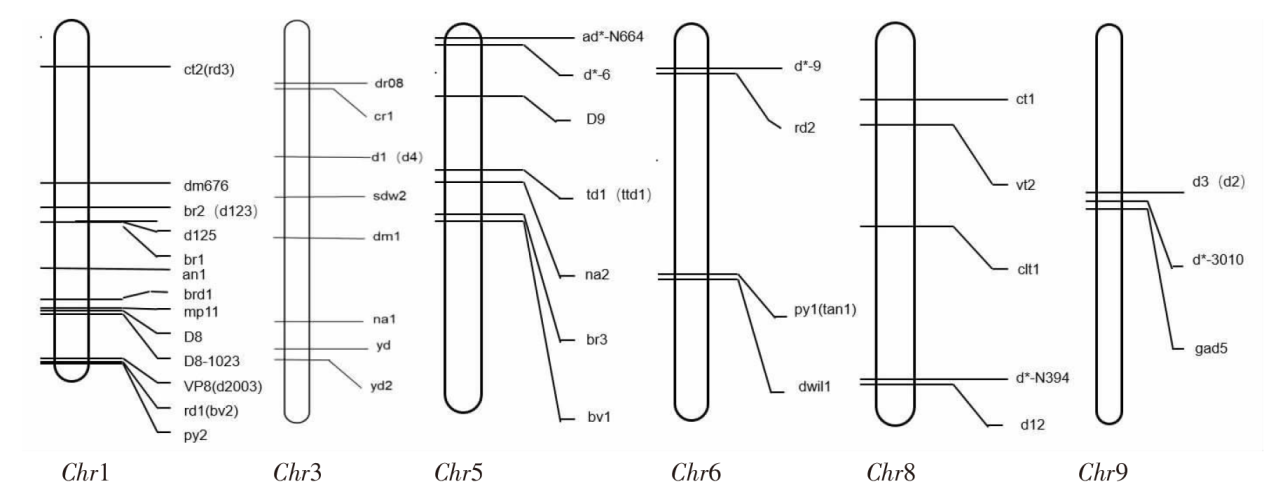
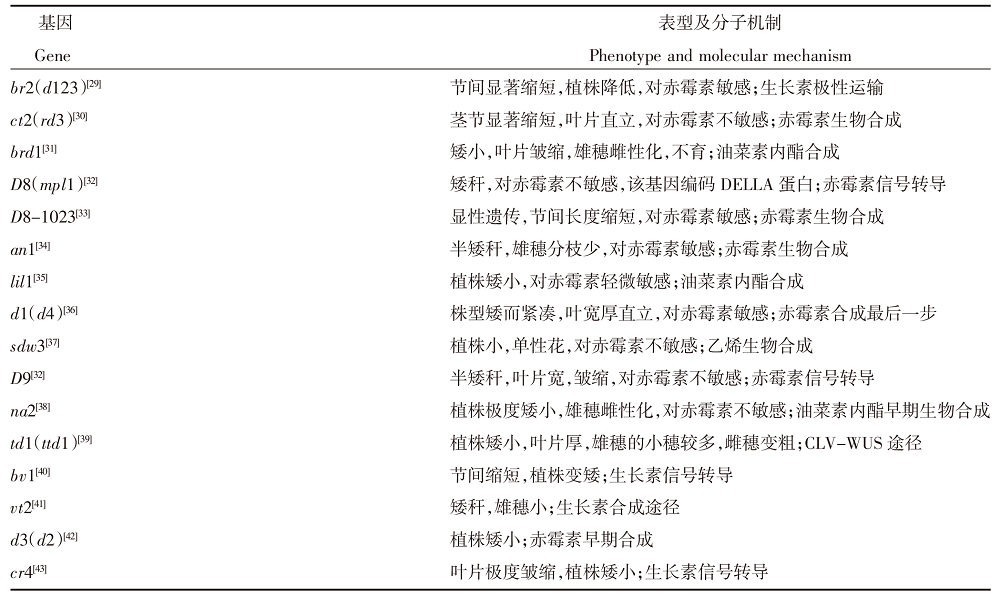
株高是玉米理想株型的重要指标,与产量密切相关,影响着植物光合利用率、抗倒伏性、收获指数等。植物激素通过影响细胞的分裂和伸长来改变玉米的节间长度和数目,从而调节玉米高度达到矮化的效果。文章综述了近年来控制玉米株高的QTL/基因定位和克隆的研究进展以及激素(GA3、IAA、BR)调控下矮化突变体的形成,以期为玉米育种生产和应用提供参考。
中图分类号:
- S513
引用本文
唐兰, 吴元奇. 玉米矮秆基因及调控机理的研究进展[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(5): 23-30.
TANG Lan, WU Yuanqi. Research progress of maize dwarf genes and their regulatory mechanisms[J]. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 2023, 51(5): 23-30.
| [1] |
QIN X L, FENG F, LI Y J, et al. Maize yield improvements in China:Past trends and future directions[J]. Plant Breeding, 2016, 135(2):166-176.
doi: 10.1111/pbr.2016.135.issue-2 |
| [2] | 周文期, 连晓荣, 刘忠祥, 等. 玉米株高和穗位高的调控机理研究[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(23):7965-7976. |
| [3] |
YIN X H, MCCLURE M A, JAJA N, et al. In-season prediction of corn yield using plant height under major production systems[J]. Agronomy Journal, 2011, 103(3):923-929.
doi: 10.2134/agronj2010.0450 |
| [4] | 史振声, 李海燕, 李凤海, 等. 玉米株高的年际间变化及其与产量的关系研究[J]. 玉米科学, 2013, 21(5):24-29. |
| [5] | 黄中文, 王伟, 徐新娟, 等. 大豆动态株高及其生长速率与产量的相关分析[J]. 河南科技学院学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(2):16-19. |
| [6] |
SASAKI A, ASHIKARI M, UEGUCHI-TANAKA M, et al. Green revolution:A mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6882):701-702.
doi: 10.1038/416701a |
| [7] |
董丽, 石海春, 赵长云, 等. 玉米矮秆突变体K718d的遗传鉴定[J]. 华北农学报, 2021, 36(6):71-77.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20192425 |
| [8] | 嵇怡, 缪旻珉, 陈学好. 植物矮生性状的分子遗传研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2006, 4(6):753-771. |
| [9] | 马尼奥·卡斯将罗. 适合高产的叶片直立的超矮秆玉米[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 1977(1):69-70. |
| [10] | 田齐建, 乔治军, 董存吉, 等. 玉米矮化育种研究进展及发展前景[J]. 山西农业科学, 2003, 31(2):23-26. |
| [11] | 杨永生. 南矮一号玉米试种表现及栽培要点[J]. 新疆农业科学, 1981, 18(3):11-12. |
| [12] | 何川, 郑祖平, 谢树果, 等. 隐性单基因br-2玉米矮生系的选育[J]. 中国农业科学, 2009, 42(8):2978-2981. |
| [13] | 李钟, 郑祖平, 张国清, 等. 矮生玉米自交系的选育和利用[J]. 玉米科学, 2006, 14(1):76-78. |
| [14] | 崔绍平. 玉米br-2矮生基因型杂交种矮单268的选育[J]. 中国种业, 2014(12):68-69. |
| [15] | 吴涛, 崔绍平. 矮单268玉米的选育概况及栽培技术[J]. 现代农村科技, 2016(7):17. |
| [16] | 姜惟廉, 郭日跻, 刘元芝, 等. 玉米优异核心种质资源多基因矮生系5003及其姊妹系5005创制[J]. 玉米科学, 2013, 21(5):1-5. |
| [17] |
邱正高, 杨华, 袁亮, 等. 一份新选玉米矮秆突变体的鉴定与遗传分析[J]. 华北农学报, 2015, 30(6):112-118.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2015.06.017 |
| [18] | GOODWIN A W, LINDSEY L E, HARRISON S K, et al. Estimating wheat yield with normalized difference vegetation index and fractional green canopy cover[J]. Crop,Forage & Turfgrass Management, 2018, 4(1):1-6. |
| [19] | 张君, 库丽霞, 张伟强, 等. 玉米穗上节间距的QTL定位[J]. 玉米科学, 2010, 18(4):45-48. |
| [20] |
CUI F, LI J, DING A M, et al. Conditional QTL mapping for plant height with respect to the length of the spike and internode in two mapping populations of wheat[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2011, 122(8):1517-1536.
doi: 10.1007/s00122-011-1551-6 pmid: 21359559 |
| [21] | 谷风娟. 玉米极低穗位材料EHel节间相关性状的表型鉴定与候选基因发掘[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2020. |
| [22] | 张贺通. 玉米株高基因ZmDLE1的精细定位[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2022. |
| [23] | 陆明洋, 陈春侠, 高岭巍, 等. 玉米矮秆主效 QTL qph1-4 的精细定位[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2012, 46(3):242-246. |
| [24] |
刘忠祥, 杨梅, 殷鹏程, 等. 玉米株高主效QTL qPH3.2精细定位及遗传效应分析[J]. 作物学报, 2018, 44(9):1357-1366.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2018.01357 |
| [25] | 尤诗婷, 邓策, 李会敏, 等. 玉米株高和穗位高的QTL定位[J]. 河南农业科学, 2019, 48(6):20-25. |
| [26] | 腾峰. 玉米株高主效QTL qPH3.1的克隆及其功能验证[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2013. |
| [27] | 杨梅. 玉米株高QTL qPH3.2和qPH3.3的精细定位[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2017. |
| [28] | 张梦迪, 张晓聪, 李新海, 等. 玉米株高主效QTL qPH2.4的定位分析[J]. 玉米科学, 2020, 28(2):61-68. |
| [29] | STEIN O L. Rates of leaf initiation in two mutants of Zea mays,dwarf-1 and brachytic-2[J]. American Journal of Botany, 1955, 42(10):885-892. |
| [30] |
BOMMERT P, JE B I, GOLDSHMIDT A, et al. The maize Gα gene COMPACT PLANT2 functions in CLAVATA signalling to control shoot meristem size[J]. Nature, 2013, 502(7472):555-558.
doi: 10.1038/nature12583 |
| [31] |
MAKAREVITCH I, THOMPSON A, MUEHLBAUER G J, et al. Brd1 gene in maize encodes a brassinosteroid C-6 oxidase[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(1):e30798.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030798 |
| [32] |
LAWIT S J, WYCH H M, XU D P, et al. Maize DELLA proteins dwarf plant8 and dwarf plant9 as modulators of plant development[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2010, 51(11):1854-1868.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcq153 pmid: 20937610 |
| [33] |
CASSANI E, BERTOLINI E, BADONE F C, et al. Characterization of the first dominant dwarf maize mutant carrying a single amino acid insertion in the VHYNP domain of the dwarf8 gene[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2009, 24(4):375-385.
doi: 10.1007/s11032-009-9298-3 |
| [34] | BENSEN R J, JOHAL G S, CRANE V C, et al. Cloning and characterization of the maize An1 gene[J]. The Plant Cell, 1995, 7(1):75-84. |
| [35] |
CASTORINA G, PERSICO M, ZILIO M, et al. The maize Lilliputian1(lil 1) gene,encoding a brassinosteroid cytochrome P450 C-6 oxidase,is involved in plant growth and drought response[J]. Annals of Botany, 2018, 122(2):227-238.
doi: 10.1093/aob/mcy047 |
| [36] |
CHEN Y, HOU M M, LIU L J, et al. The maize DWARF1 encodes a gibberellin 3-oxidase and is dual localized to the nucleus and cytosol[J]. Plant Physiology, 2014, 166(4):2028-2039.
doi: 10.1104/pp.114.247486 pmid: 25341533 |
| [37] |
LI H C, WANG L J, LIU M S, et al. Maize plant architecture is regulated by the ethylene biosynthetic gene ZmACS7[J]. Plant Physiology, 2020, 183(3):1184-1199.
doi: 10.1104/pp.19.01421 |
| [38] |
BEST N B, HARTWIG T, BUDKA J, et al. Nana plant2 encodes a maize ortholog of the Arabidopsis brassinosteroid biosynthesis gene DWARF1,identifying developmental interactions between brassinosteroids and gibberellins[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 171(4):2633-2647.
doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00399 |
| [39] |
BOMMERT P, LUNDE C N, NARDMANN J, et al. Thick tassel dwarf1 encodes a putative maize ortholog of the Arabidopsis CLAVATA1 leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase[J]. Development, 2005, 132(6):1235-1245.
doi: 10.1242/dev.01671 |
| [40] |
AVILA L M, CERRUDO D, SWANTON C, et al. Brevis plant1,a putative inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase,is required for internode elongation in maize[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(5):1577-1588.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv554 |
| [41] |
PHILLIPS K A, SKIRPAN A L, LIU X, et al. Vanishing tassel2 encodes a grass-specific tryptophan aminotransferase required for vegetative and reproductive development in maize[J]. The Plant Cell, 2011, 23(2):550-566.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.075267 pmid: 21335375 |
| [42] |
FUJIOKA S, YAMANE H, SPRAY C R, et al. Qualitative and quantitative analyses of gibberellins in vegetative shoots of normal,dwarf-1,dwarf-2,dwarf-3,and dwarf-5 seedlings of Zea mays L.[J]. Plant Physiology, 1988, 88(4):1367-1372.
doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1367 |
| [43] |
BECRAFT P W, STINARD P S, MCCARTY D R. CRINKLY4:A TNFR-like receptor kinase involved in maize epidermal differentiation[J]. Science, 1996, 273(5280):1406-1409.
doi: 10.1126/science.273.5280.1406 |
| [44] | 白丽君, 尹淑霞. 植物矮化突变体的来源及矮化机理研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2014(6):34-39. |
| [45] | YABUTA T, SUMIKI Y. On the crystal of gibberellin,a substance to promote plant growth[J]. Journal of the Agricultural Chemical Society of Japan, 1938, 14:1526. |
| [46] |
HELLIWELL C A, SULLIVAN J A, MOULD R M, et al. A plastid envelope location of Arabidopsis ent-kaurene oxidase links the plastid and endoplasmic reticulum steps of the gibberellin biosynthesis pathway[J]. The Plant Journal, 2001, 28(2):201-208.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2001.01150.x |
| [47] |
AACH H, BODE H K, ROBINSON D G, et al. Ent-Kaurene synthase is located in proplastids of meristematic shoot tissues[J]. Planta, 1997, 202(2):211-219.
doi: 10.1007/s004250050121 |
| [48] |
TENG F, ZHAI L H, LIU R X, et al. ZmGA3ox2,a candidate gene for a major QTL,qPH3.1,for plant height in maize[J]. The Plant Journal, 2013, 73(3):405-416.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2013.73.issue-3 |
| [49] |
SUN T P. Gibberellin-GID1-DELLA:A pivotal regulatory module for plant growth and development[J]. Plant Physiology, 2010, 154(2):567-570.
doi: 10.1104/pp.110.161554 |
| [50] |
YIN Y H, WANG Z Y, MORA-GARCIA S, et al. BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteroids to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation[J]. Cell, 2002, 109(2):181-191.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00721-3 pmid: 12007405 |
| [51] |
IKEDA A, UEGUCHI-TANAKA M, SONODA Y, et al. Slender rice,a constitutive gibberellin response mutant,is caused by a null mutation of the SLR1 gene,an ortholog of the height-regulating gene GAI/RGA/RHT/D8[J]. The Plant Cell, 2001, 13(5):999-1010.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.13.5.999 |
| [52] | 李辉, 左钦月, 涂升斌. 油菜素内酯生物合成和代谢研究进展[J]. 植物生理学报, 2015, 51(11):1787-1798. |
| [53] |
BAJGUZ A, TRETYN A. The chemical characteristic and distribution of brassinosteroids in plants[J]. Phytochemistry, 2003, 62(7):1027-1046.
doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(02)00656-8 pmid: 12591256 |
| [54] |
CASTORINA G, CONSONNI G. The role of brassinosteroids in controlling plant height in Poaceae:A genetic perspective[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(4):1191.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21041191 |
| [55] |
SALEHIN M, BAGCHI R, ESTELLE M. SCFTIR1/AFB-based auxin perception:Mechanism and role in plant growth and development[J]. The Plant Cell, 2015, 27(1):9-19.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.133744 |
| [56] |
MULTANI D S, BRIGGS S P, CHAMBERLIN M A, et al. Loss of an MDR transporter in compact stalks of maize Br2 and sorghum dw3 mutants[J]. Science, 2003, 302(5642):81-84.
doi: 10.1126/science.1086072 pmid: 14526073 |
| [57] | 夏慧. GA和其它植物激素的相互作用[J]. 生物技术世界, 2015, 12(8):227. |
| [58] |
LIN H, WANG R X, QIAN Q A, et al. DWARF27,an iron-containing protein required for the biosynthesis of strigolactones,regulates rice tiller bud outgrowth[J]. The Plant Cell, 2009, 21(5):1512-1525.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.065987 |
| [59] | 刘伯涵. 拟南芥转录因子GIS、GIS2和SPT调控生长发育分子作用机制的初步研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2016. |
| [60] | 叶梅荣, 朱昌华, 甘立军, 等. 激素间相互作用对植物茎伸长生长的调控综述[J]. 中国农学通报, 2007, 23(4):228-231. |
| [61] |
TAKAHASHI T, KAKEHI J I. Polyamines:Ubiquitous polycations with unique roles in growth and stress responses[J]. Annals of Botany, 2010, 105(1):1-6.
doi: 10.1093/aob/mcp259 |
| [1] | 韩超, 常春元, 张江鹏, 吴素芬, 李欣欣. 发酵菌糠和发酵玉米芯用于叶菜育苗基质的研究[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(6): 70-79. |
| [2] | 王光杰, 黄彬香, 宋尧, 闵矿楠, 李顺澳, 高日平, 赵熙玲, 王靖, 任永峰. 半干旱风沙区玉米关键需水期叶气温差变化特征及影响因素[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(6): 89-97. |
| [3] | 王帮太, 杨美丽, 郭华, 王静, 王志红, 鹿红卫, 程建梅, 秦贵文, 陈甲法. 玉米茎秆营养品质性状全基因组关联分析及候选基因筛选[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(5): 1-22. |
| [4] | 靖相柱, 孙霞, 郭业民, 赵文苹, 郭榛, 桑茂盛. 光谱成像技术在玉米种子质量检测方面的研究进展[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(5): 93-102. |
| [5] | 赵丽, 范铭元, 谢广明, 陆靖英, 张琪, 孙孝静, 郭虹霞, 邓妍, 王创云. 旱地不同春玉米品种光合特性、干物质积累及产量分析[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(4): 11-19. |
| [6] | 潘丽杰, 张宝林, 李瑞鑫, 牛潘婷, 郭建鹏, 斯琴高娃, 何美玲. 玉米不同叶位叶片叶绿素含量垂直分布研究进展[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(4): 28-37. |
| [7] | 张丽丽, 薛兵东, 樊叶, 莫姣娇, 赵新宇, 杨海龙, 付俊, 姜英, 齐华, 王璞. 辽东南地区酸性土壤连续施用调节剂对玉米生长发育及产量构成的影响[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(4): 38-47. |
| [8] | 何子涵, 吴星霖, 向志宇, 白光红, 王洋, 李松壕, 杜振华, 孜比尔尼沙·赛买提, 戴小华. 玉米须生物活性成分、功效与提取方法的研究进展[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(4): 96-104. |
| [9] | 程志鹏, 张成泽, 王富贵, 王振, 张悦忠, 闫立伟, 梁红伟, 杨志红, 高聚林, 王志刚. 耕作方式对内蒙古旱作区土壤水热及玉米产量的影响[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(2): 22-32. |
| [10] | 朱教宁, 高莉, 张静璇, 李永平, 汤昀, 史向远, 王秀红. 氨氮质量浓度对厌氧发酵产甲烷特性及产甲烷菌群落的影响[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(2): 91-100. |
| [11] | 张皓, 高聚林, 于晓芳, 马达灵, 胡树平. 秸秆深翻还田对盐碱化土壤玉米根系形态特征及产量的影响[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(1): 1-15. |
| [12] | 殷建军, 郭庆瑞, 郭凤琴, 张小娟, 王力. 宽窄行种植对青贮玉米光合特性、产量和品质的影响[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(1): 16-21. |
| [13] | 韩平安, 常悦, 唐宽刚, 李晓东, 王力伟, 梁亚晖, 杨静, 石海波, 吴新荣. 基于农杆菌介导法将CP4-EPSPS基因转入玉米自交系B73的研究[J]. 北方农业学报, 2023, 51(1): 31-37. |
| [14] | 柴文波, 李淑芬, 李洪涛, 许瀚元, 祝庆, 王军. 基于SSR分子标记技术的黄淮海玉米杂优模式分析[J]. 北方农业学报, 2022, 50(6): 17-24. |
| [15] | 邱贵兰, 李燕, 李红梅, 罗曦, 马孝玲, 何立群, 胡美琳, 赵后娟, 杜林, 吴元奇, 唐海涛. 玉米光周期途径相关基因的研究进展[J]. 北方农业学报, 2022, 50(5): 19-23. |
|
||