北方农业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 24-33.doi: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2022.05.04
老芒麦、加拿大披碱草及其杂交一代根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性
王伶瑞1, 红雨1,2, 李慧玲1, 李景环1
- 1.内蒙古师范大学 生命科学与技术学院,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010022
2.内蒙古自治区高等学校生物多样性保护与可持续利用重点实验室,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010022
Bacterial community structure and diversity in the rhizosphere soil of Elymus sibiricus Linn.,Elymus canadensis L. and the first hybrid generation
WANG Lingrui1, Hongyu 1,2, LI Huiling1, LI Jinghuan1
- 1. College of Life Science and Technology,Inner Mongolia Normal University,Hohhot 010022,China
2. Key Laboratory of Biodiversity Conservation and Sustainable Utilization for College and University of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region,Hohhot 010022,China
摘要:
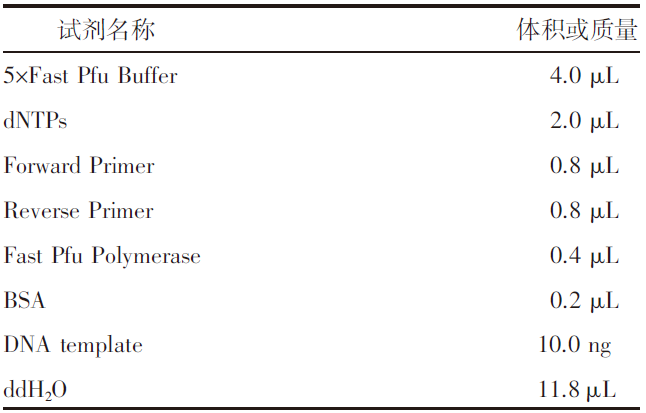
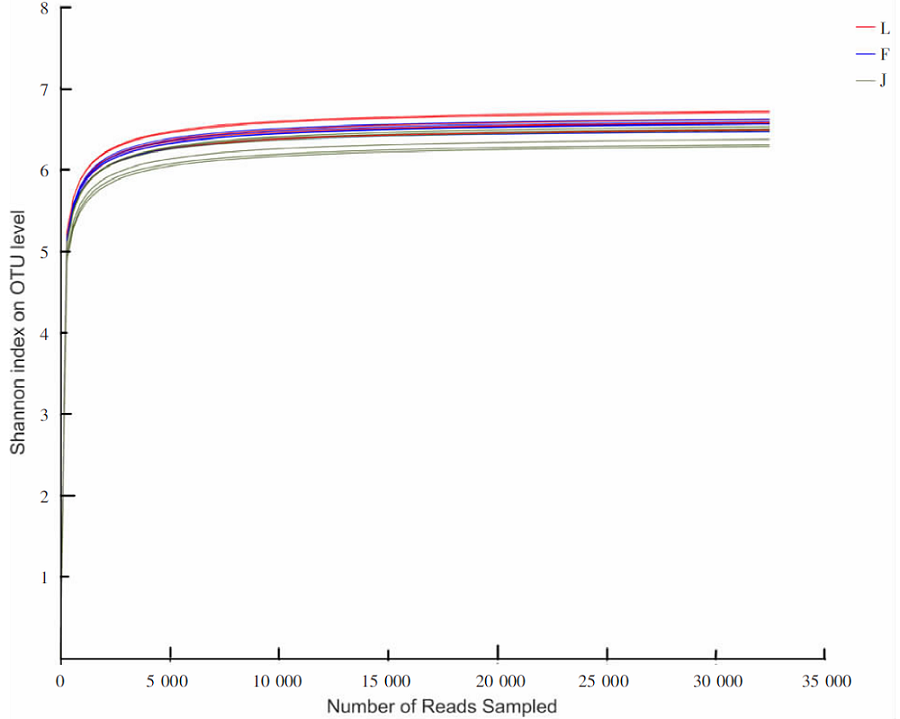
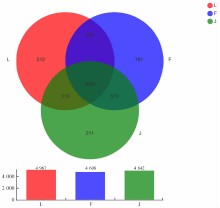
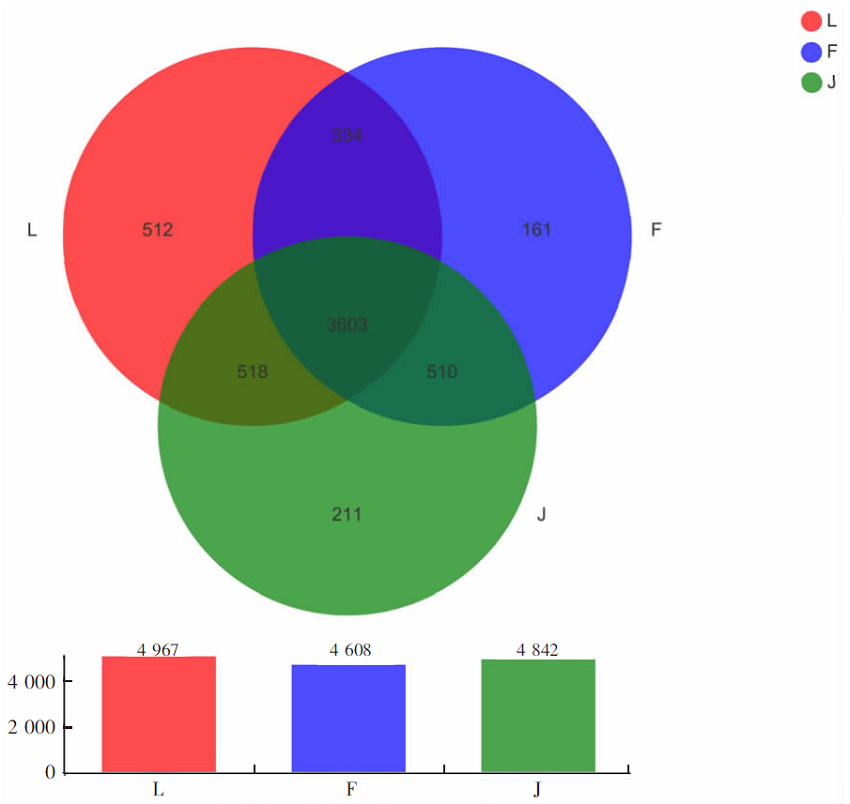
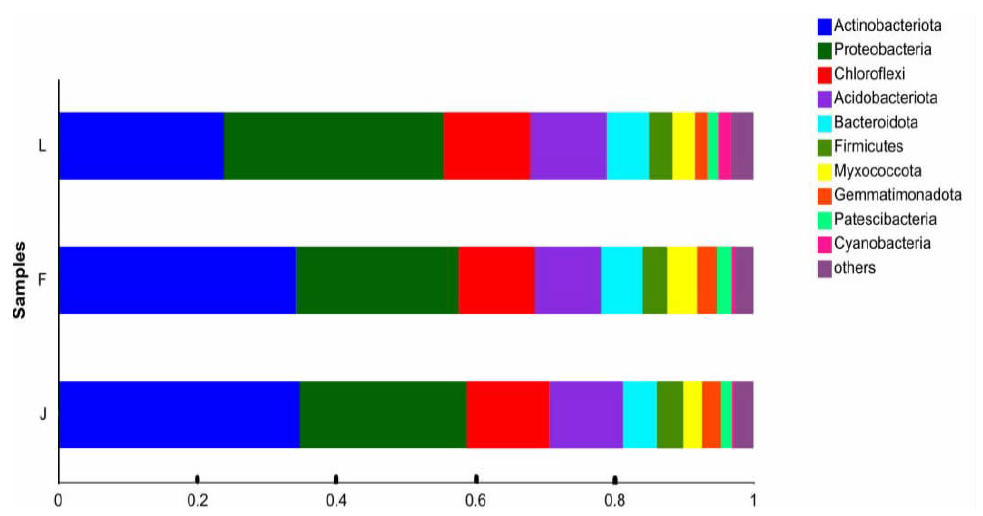
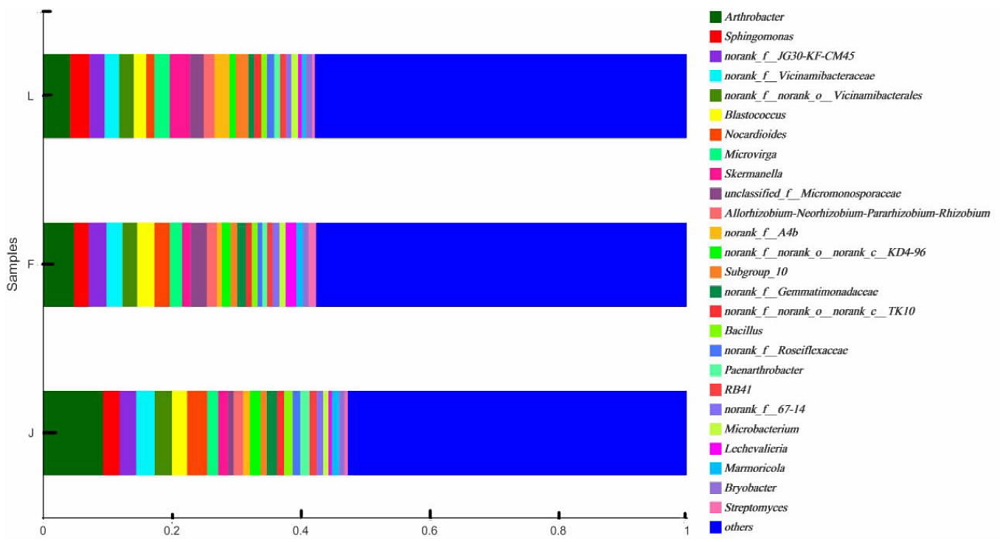
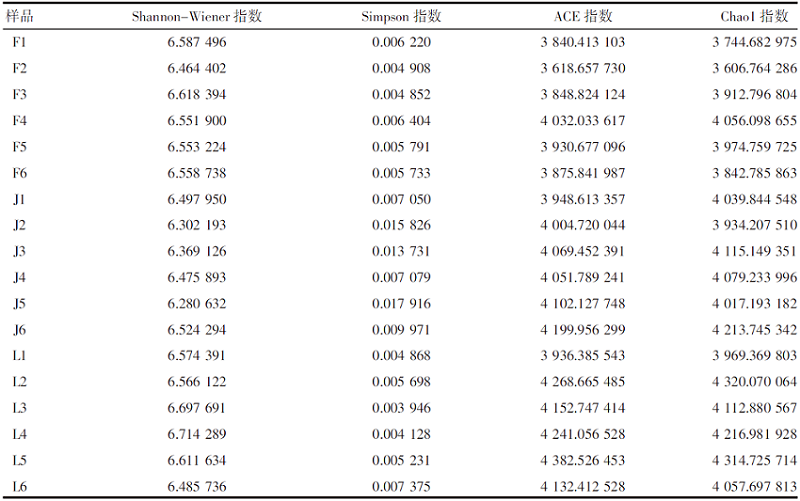
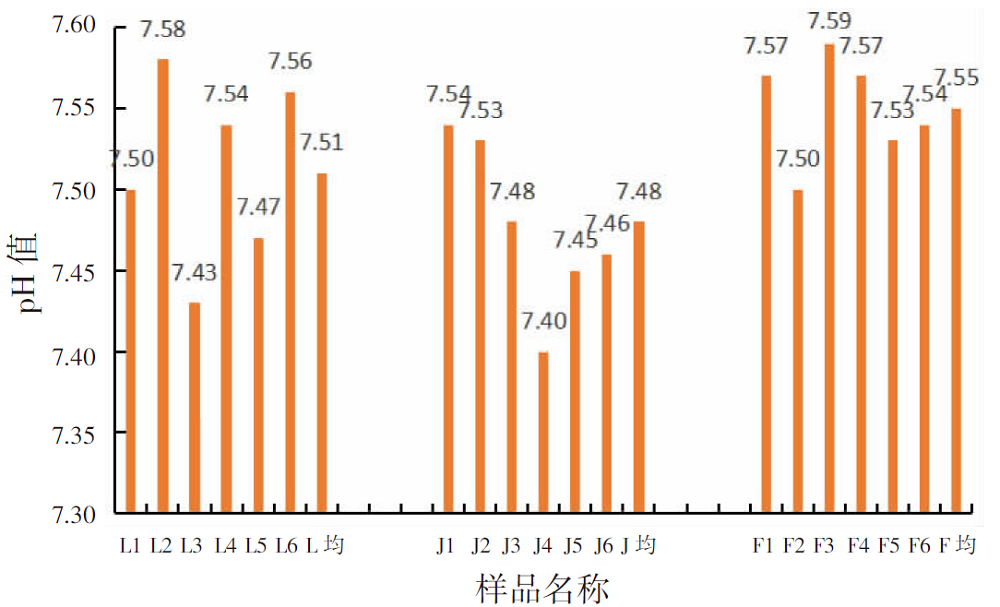
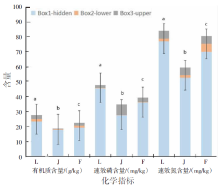
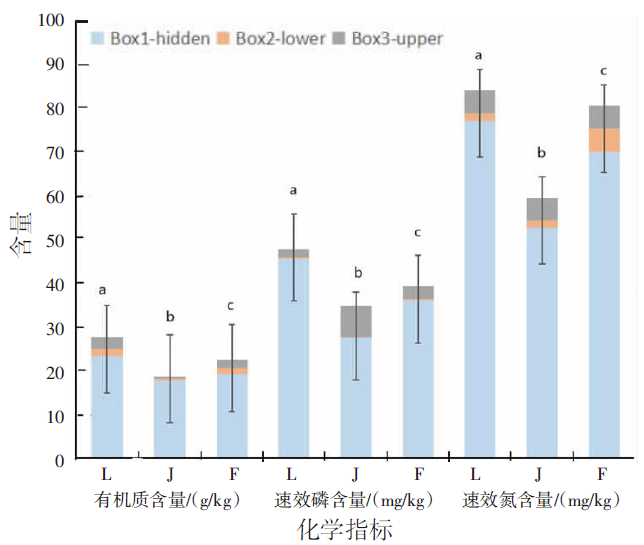
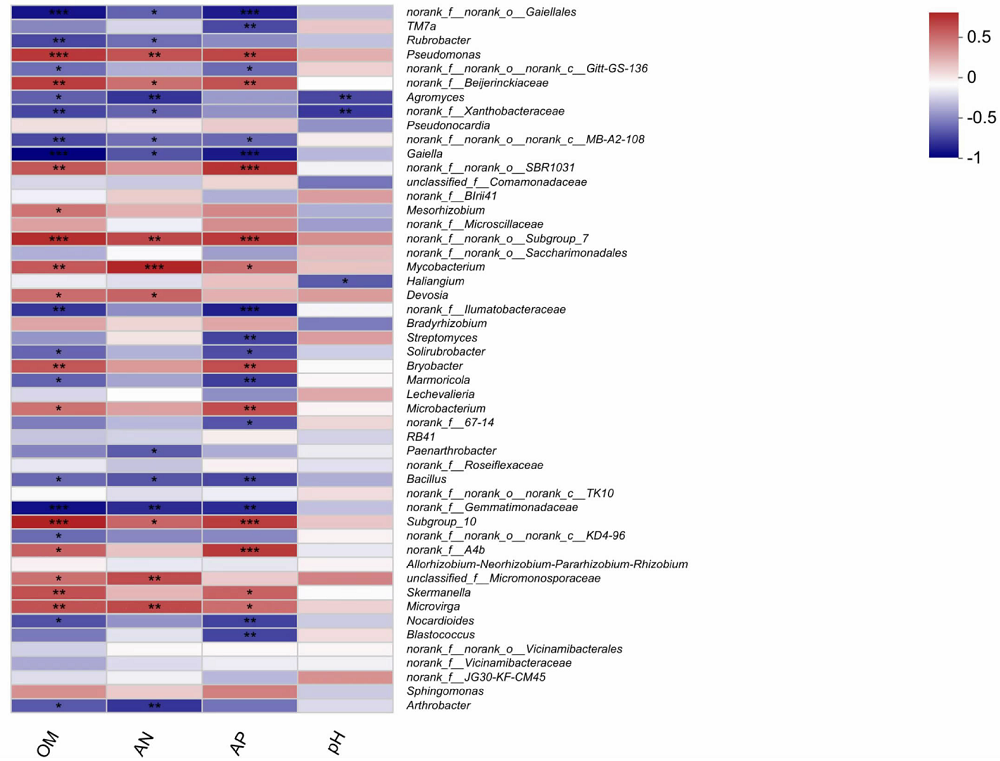
【目的】明确内蒙古沙壤质暗栗钙土上种植老芒麦(Elymus sibiricus Linn.)、加拿大披碱草(Elymus canadensis L.)和老芒麦(父本)×加拿大披碱草(母本)杂交一代根际土壤细菌群落结构和多样性的差异,阐明环境因子与其互作机制。【方法】采用Illumina MiSeq测序平台对老芒麦、加拿大披碱草和老芒麦(父本)×加拿大披碱草(母本)杂交一代根际土壤细菌群落16S rRNA基因进行高通量测序,通过生物信息学分析方法对这3种植物根际土壤的细菌群落结构和多样性进行比较,并对细菌组成与土壤化学指标进行相关性分析。【结果】老芒麦根际土壤细菌群落的Shannon-Wiener指数、ACE指数和Chao1指数均最高,而加拿大披碱草根际土壤细菌群落的Simpson指数最高。3种植物根际土壤细菌群落的共同优势门为放线菌门(Actinobacteria)、变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)和酸杆菌门(Acidobacteria),老芒麦和杂交一代根际土壤细菌群落的单独优势门均为拟杆菌门(Bacteroidete);3种植物根际土壤细菌群落的共同优势属为节细菌属(Arthrobacter),老芒麦、加拿大披碱草、杂交一代根际土壤细菌群落的单独优势属分别为希瓦氏菌属(Shewanella)、类诺卡氏菌属(Nocardioides)、norank-f-JG30-KF-CM45。3种植物根际土壤中,加拿大披碱草根际土壤的pH值最低,老芒麦根际土壤的速效氮、速效磷和有机质含量最高。土壤有机质与Pseudomonas、norank-f-norank-o-Subgroup-7、Subgroup-10,速效氮与Mycobacterium,速效磷与norank-f-norank-o-SBR1031、norank-f-norank-o-Subgroup-7、Subgroup-10、norank-f-A4b呈极显著正相关;土壤有机质与norank-f-norank-o-Gaiellales、Gaiella和norank-f-Gemmatimonadacea,速效磷与norank-f-norank-o-Gaiellales、Gaiella和norank-f-Ilumatobacteraceae呈极显著负相关。【结论】老芒麦×加拿大披碱草杂交一代与加拿大披碱草根际土壤的细菌群落结构更相似,与老芒麦根际土壤的细菌群落结构差异较大;土壤细菌群落结构多样性会受到土壤化学指标和种植植物种类的影响。
中图分类号:
- S154.3