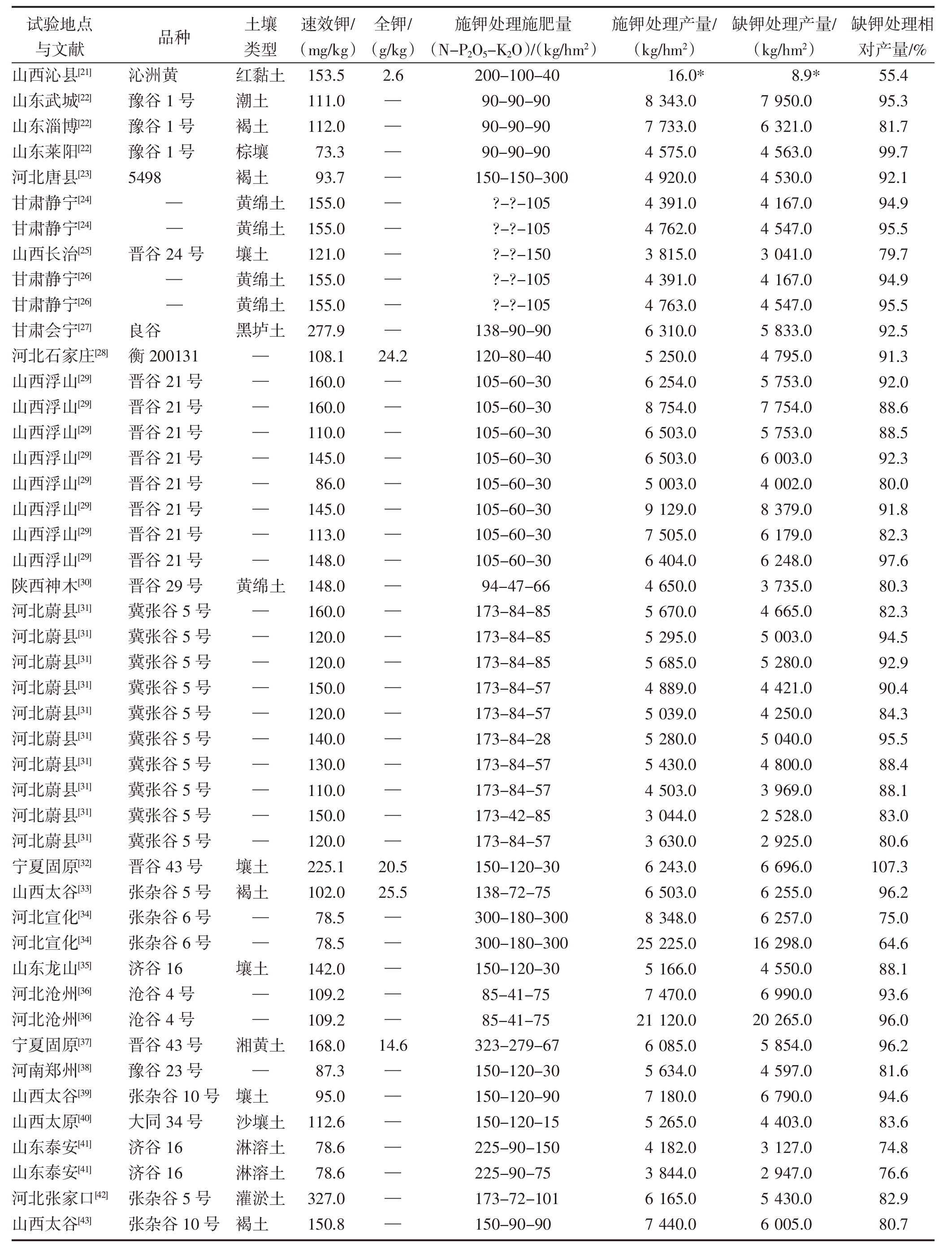
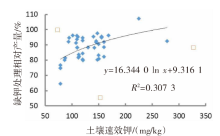
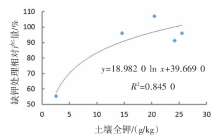
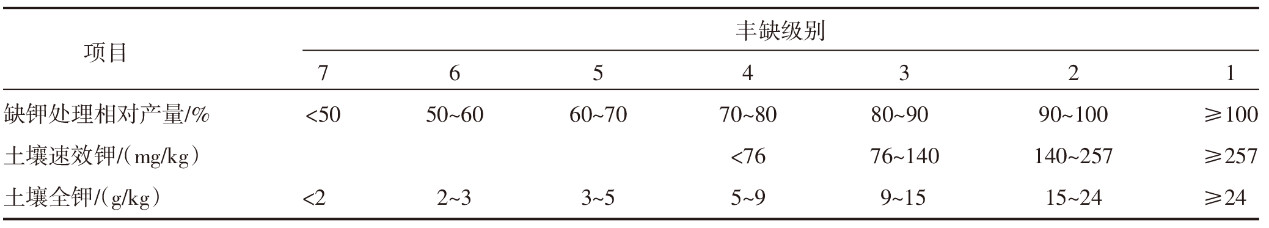
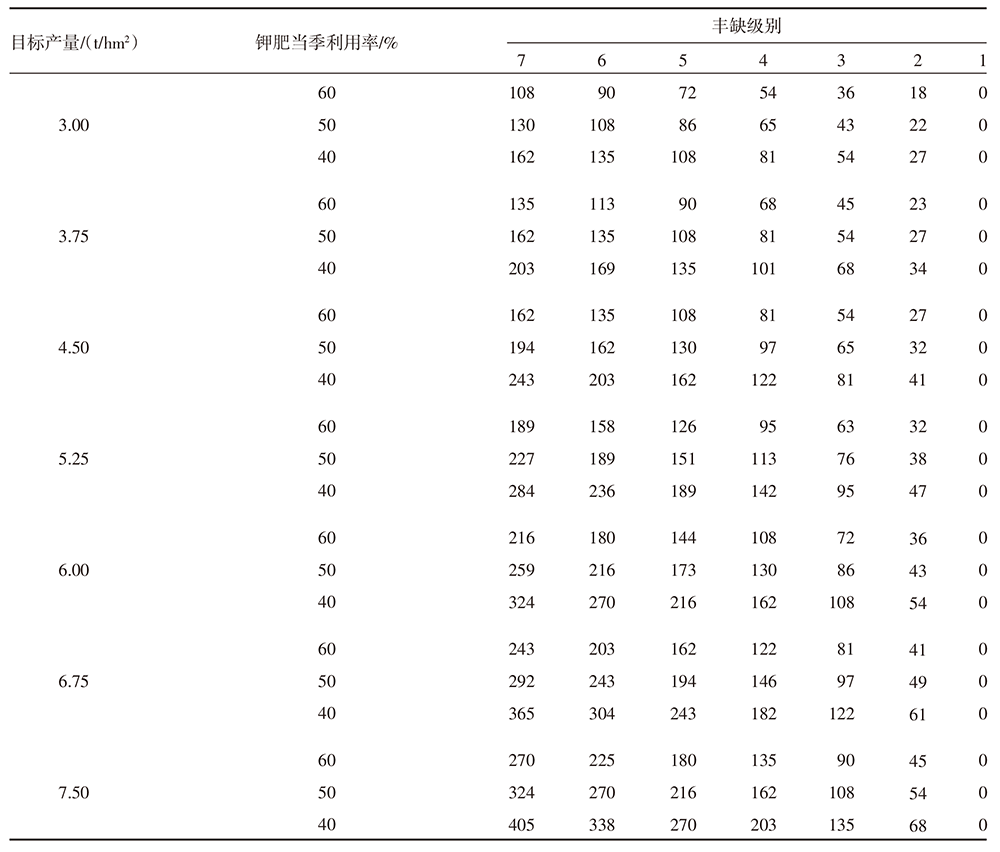
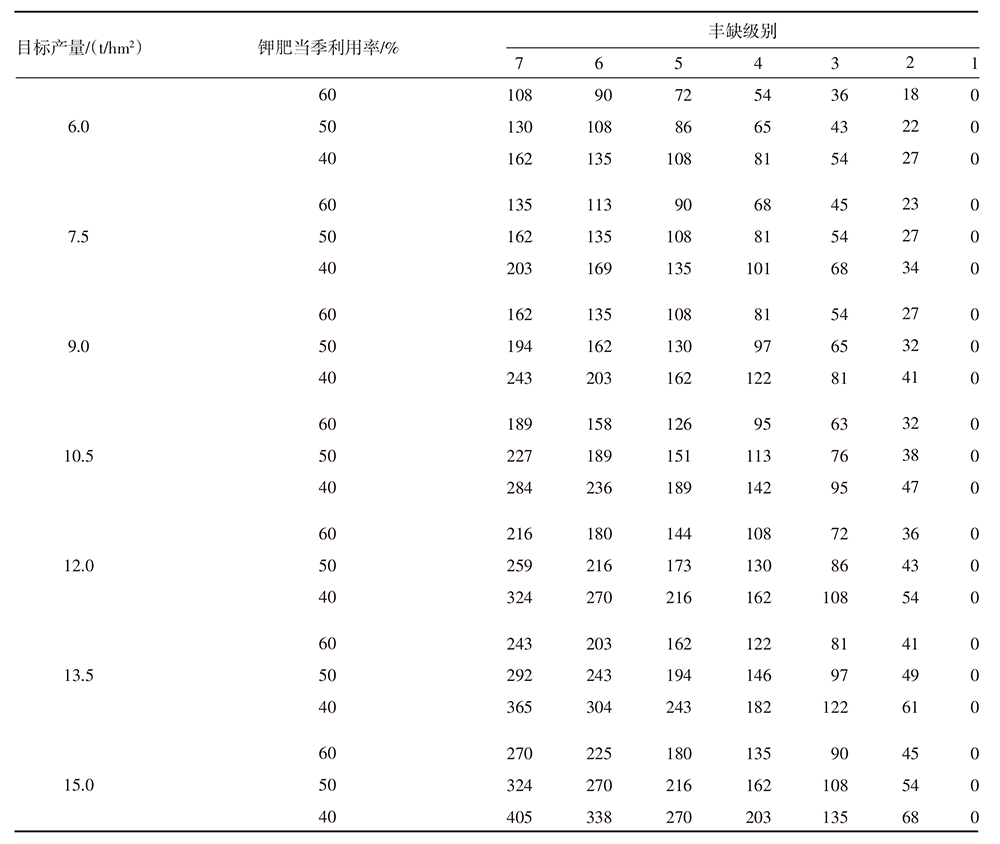
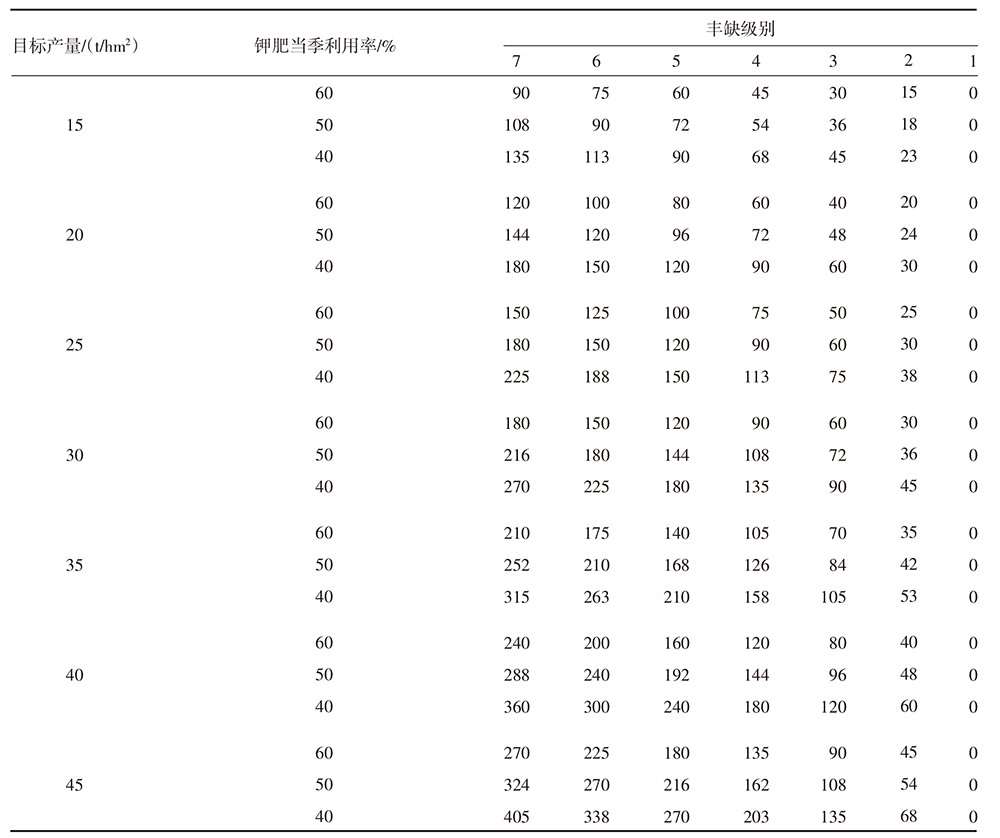
| [1] |
李顺国, 刘斐, 刘猛, 等. 中国谷子产业和种业发展现状与未来展望[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(3):459-470.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.03.001
|
| [2] |
BRAY R H. Soil-plant relations:Ⅰ.The quantitative relation of exchangeable potassium to crop yields and to crop response to potash additions[J]. Soil Science, 1944, 58:305-324.
doi: 10.1097/00010694-194410000-00007
|
| [3] |
周鸣铮. 中国的测土施肥[J]. 土壤通报, 1987(1):7-13.
|
| [4] |
黄德明. 我国农田土壤养分肥力状况及丰缺指标[J]. 华北农学报, 1988(2):46-53.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7091.1988.02.008
|
| [5] |
孙洪仁, 刘江扬, 赵雅晴, 等. 中国玉米土壤速效钾丰缺指标与适宜施钾量研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017(5):29-37.
|
| [6] |
孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 冮丽华, 等. 我国水稻土壤有效磷和速效钾丰缺指标与适宜磷钾施用量研究[J]. 中国稻米, 2018, 24(5):1-10.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8082.2018.05.001
|
| [7] |
孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 冮丽华, 等. 中国小麦土壤速效钾丰缺指标与适宜施钾量研究[J]. 土壤, 2019, 51(5):895-902.
|
| [8] |
王纪泽, 张学兰. 谷子建议施肥研究[J]. 土壤通报, 1985(4):158-161.
|
| [9] |
朱凯迪, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 等. 我国籽实和饲草谷子土壤氮素丰缺指标和推荐施氮量[J]. 草地学报, 2022, 30(8):2207-2216.
doi: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2022.08.033
|
| [10] |
孙洪仁, 王显国, 穆尼热·买买提, 等. 中国三大自然区域紫花苜蓿土壤速效钾丰缺指标和推荐施钾量[J]. 中国草地学报, 2021, 43(3):19-28.
|
| [11] |
孙洪仁, 曾红, 刘江扬, 等. 中国农牧交错带燕麦土壤氮素丰缺指标与适宜施氮量初步研究[J]. 北方农业学报, 2017, 45(5):22-27.
|
| [12] |
孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 吕玉才, 等. 中国北方甜菜土壤速效钾丰缺指标与适宜施钾量研究[J]. 中国糖料, 2020, 42(1):45-49.
|
| [13] |
钟培阁, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 等. 中国南方甘蔗土壤全氮丰缺指标与适宜施氮量初步研究[J]. 中国糖料, 2020, 42(3):43-48.
|
| [14] |
王彦, 朱凯迪, 孙洪仁, 等. 中国苹果土壤养分丰缺指标与适宜施肥量初步研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(5):69-78.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0292
|
| [15] |
吕志伟, 孙洪仁, 张吉萍, 等. 中国棉花土壤有效磷丰缺指标与适宜施磷量研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(2):197-206.
|
| [16] |
孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. 测土施肥土壤有效养分丰缺分级改良方案[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(19):1-5.
|
| [17] |
孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. “养分平衡-地力差减法”确定适宜施肥量的新应用公式[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(7):1-4.
|
| [18] |
孙洪仁, 曹影, 刘琳, 等. 测土施肥不同丰缺级别土壤的适宜施肥量[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(23):7-11.
|
| [19] |
高祥照, 马常宝, 杜森. 测土配方施肥技术[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2005:132.
|
| [20] |
张福锁, 陈新平, 陈清. 中国主要作物施肥指南[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2009:96-99.
|
| [21] |
张珠玉, 王文忠. 有机无机肥不同施肥量对谷子氨基酸的影响[J]. 山西农业大学学报, 1988(2):174-182.
|
| [22] |
赵镭, 程绍义, 隋方功, 等. 施用氮磷钾肥对夏谷品质的影响[J]. 莱阳农学院学报, 1990(1):34-38.
|
| [23] |
王殿武, 周大迈, 臧士国, 等. 太行山区旱地谷子推荐施肥量的确定及其水分利用效率研究[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 1997(4):16-20.
|
| [24] |
陈炳东. 新修梯田作物施肥与土壤培肥效果研究[J]. 甘肃农业科技, 2000(7):34-37.
|
| [25] |
窦桂梅, 王景盛, 刘巧英. 钾肥在农作物上的应用研究[J]. 山西农业科学, 2001(1):49-52.
|
| [26] |
王生录, 崔云玲, 张福武, 等. 陇中旱区新修梯田施肥效应研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2009, 27(1):47-52.
|
| [27] |
张小红, 王自忠. 会宁县谷子配方施肥试验初报[J]. 甘肃农业科技, 2009(9):23-25.
|
| [28] |
郝洪波, 李明哲. 配方施肥对成熟期谷子氮磷钾吸收及产量的影响[J]. 河北农业科学, 2010, 14(11):62-64.
|
| [29] |
杨淑霞, 黄金钟, 梁国爱. 谷子测土配方施肥校正试验研究[J]. 湖南农机, 2010, 37(7):19.
|
| [30] |
李志军, 贺丽瑜, 梁鸡保, 等. 不同氮磷钾配比对黄土丘陵沟壑区谷子产量及肥料利用率的影响[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2013, 59(5):107-109.
|
| [31] |
刘建平, 李龙江. 冀西北春谷子“3414”肥效试验研究[J]. 河北农业科学, 2013, 17(6):1-5.
|
| [32] |
罗世武, 王勇, 杨军学, 等. 宁南干旱区谷子肥料试验研究[J]. 陕西农业科学, 2013, 59(4):88-91.
|
| [33] |
杨艳君, 王宏富, 郭平毅, 等. 施肥和密度对张杂谷5号光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(3):566-576.
|
| [34] |
张亚琦.氮、 钾肥对杂交谷子产量及耗水规律的影响研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2014.
|
| [35] |
陈二影, 秦岭, 程炳文, 等. 夏谷氮、磷、钾肥的效应研究[J]. 山东农业科学, 2015, 47(1):61-65.
|
| [36] |
宋淑贤, 田伯红, 王建广, 等. 不同施钾量对谷子干物质及产量的影响[J]. 现代农业科技, 2015(19):9-10.
|
| [37] |
王晓军, 王勇, 张晓娟, 等. 氮磷钾平衡施肥对谷子产量及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 农业科学研究, 2015, 36(2):5-8.
|
| [38] |
代小冬, 徐心志, 朱灿灿, 等. 谷子氮、磷、钾肥的效应研究[J]. 作物杂志, 2016(5):147-151.
|
| [39] |
郝科星, 李娜娜, 侯富恩. 氮·磷·钾肥运筹对谷子品质与产量的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(13):51-55.
|
| [40] |
任月梅, 杨忠, 郭瑞锋, 等. 不同施肥水平对大同34号谷子产量的影响[J]. 北方农业学报, 2016, 44(4):27-30.
|
| [41] |
关瑞. 夏播谷子氮磷钾配比及控释氮肥一次性基施效应研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2018.
|
| [42] |
殷振琴. 测土配方施肥对谷子产量及经济效益的影响[J]. 农业开发与装备, 2018(11):136-137.
|
| [43] |
李永虎, 曹梦琳, 杜慧玲, 等. 施肥位置及施肥量对杂交谷子干物质累积、转运和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(22):4177-4190.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.22.021
|