北方农业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 34-40.doi: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2022.05.05
不同施肥处理对谷子光合特性及产量的影响
张彪1,2,3, 赵沛义1,2,3, 任永峰2,3, 张鹏2,3, 高宏艳2,3, 韩云飞2,3, 杜二小2,3, 罗素菊1, 王宣茗1
- 1.内蒙古农业大学 农学院,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010019
2.内蒙古自治区农牧业科学院,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010031
3.内蒙古旱作农业重点实验室,内蒙古 呼和浩特 010031
Effects of different fertilization treatments on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of millet
ZHANG Biao1,2,3, ZHAO Peiyi1,2,3, REN Yongfeng2,3, ZHANG Peng2,3, GAO Hongyan2,3, HAN Yunfei2,3, DU Erxiao2,3, LUO Suju1, WANG Xuanming1
- 1. College of Agriculture,Inner Mongolia Agricultural University,Hohhot 010019,China
2. Inner Mongolia Academy of Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Sciences,Hohhot 010031,China
3. Inner Mongolia Key Laboratory of Dryland Agriculture,Hohhot 010031,China
摘要:
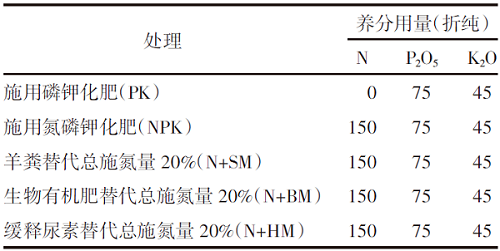
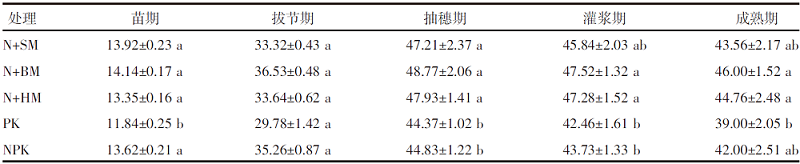
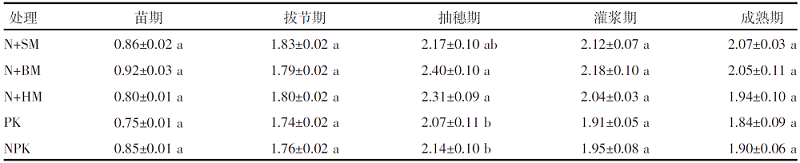
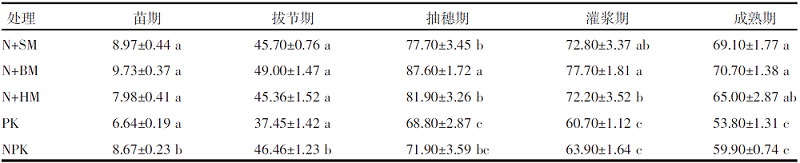
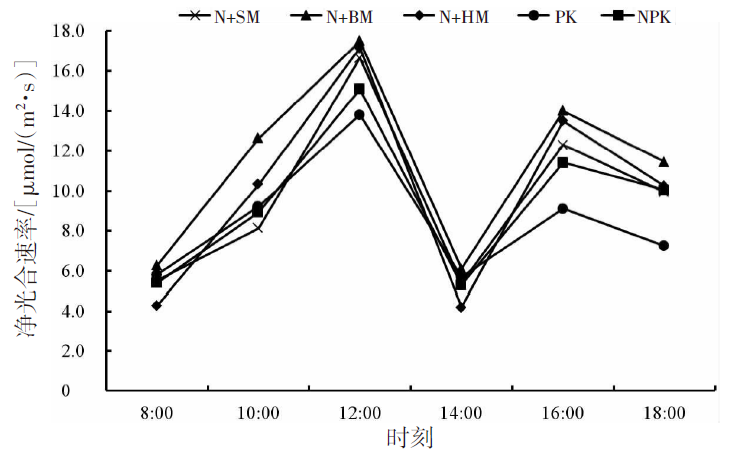
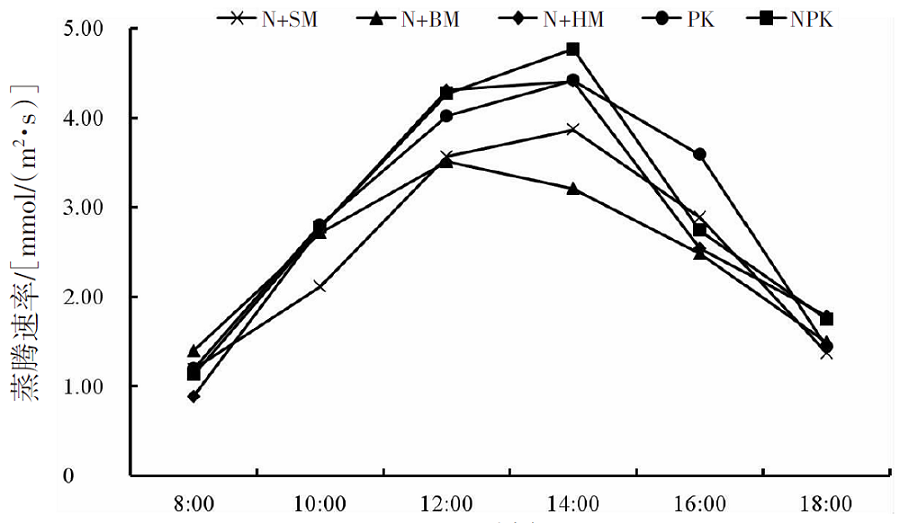
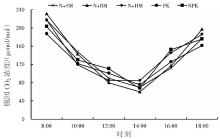
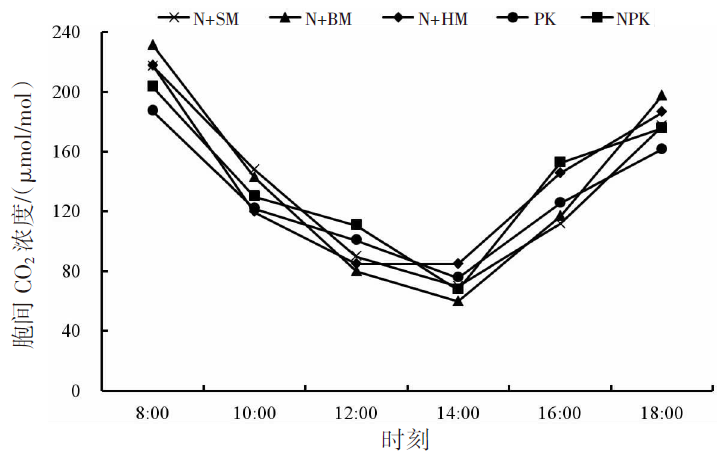
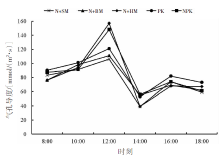
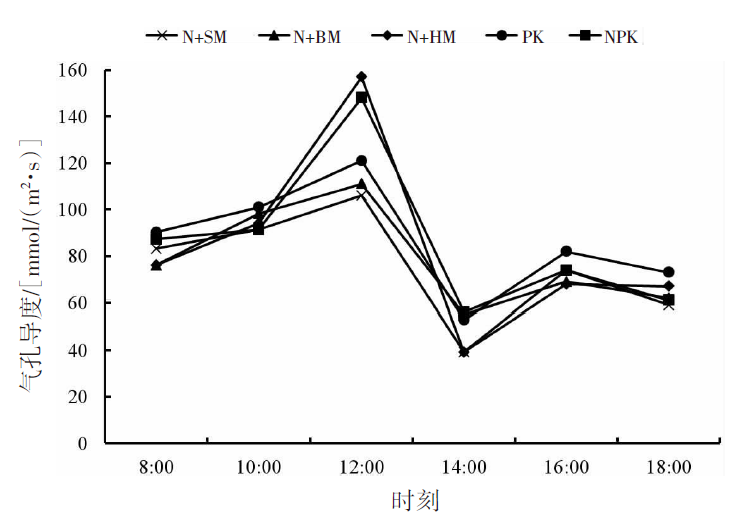
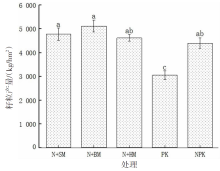
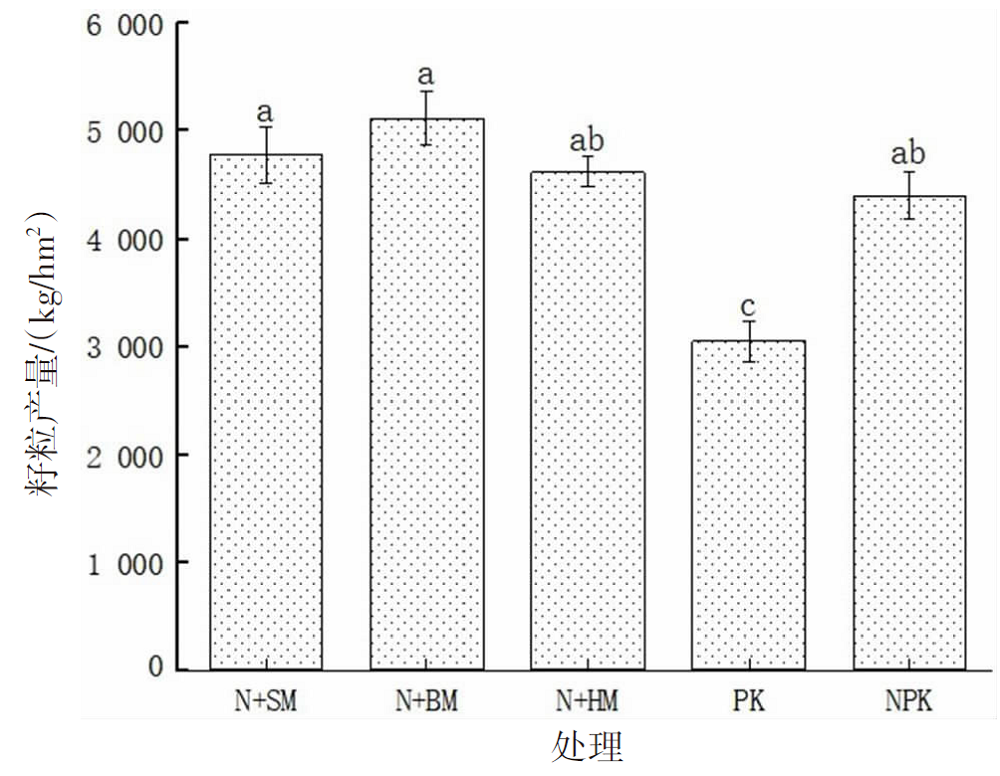
【目的】通过对谷子灌浆期光合特性日变化的研究,寻找最优施肥处理,为推动内蒙古鄂尔多斯市小杂粮生产和产业发展提供参考。【方法】试验地位于准格尔旗沙圪堵镇,选用金苗K1为试验品种,设置施用磷钾化肥(PK,空白)、氮磷钾化肥(NPK,对照)、羊粪替代总施氮量20%(N+SM)、生物有机肥替代总施氮量20%(N+BM)、缓释复合肥替代总施氮量20%(N+HM)5个施肥处理,采用膜侧播种方式,分析谷子叶面积和灌浆期光合特性日变化及产量的差异。【结果】N+BM处理金苗K1叶面积在拔节期后均高于其他处理;不同处理净光合速率日变化均呈双峰曲线变化规律,存在光合午休现象,N+BM处理净光合速率最高,为17.5 μmol/(m2·s);各处理蒸腾速率最高值均出现在12:00—14:00;胞间CO2浓度日变化呈“V”字形变化趋势,N+BM处理胞间CO2浓度最低,为39.2 mmol/(m2·s);各处理气孔导度和净光合速率变化趋势相同,最低值均出现在12:00—14:00,在12:00时N+BM处理气孔导度比NPK处理低33.3%。净光合速率与蒸腾速率存在显著正相关关系,与气孔导度存在极显著正相关关系。N+BM处理籽粒产量达到了5 122 kg/hm2,较NPK处理提高16.2%。【结论】生物有机肥替代总施氮量20%可以提高谷子后期光合能力和干物质积累能力,增加产量,是鄂尔多斯市适宜的施肥方式。
中图分类号:
- S515