畜牧与饲料科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 41-46.doi: 10.12160/j.issn.1672-5190.2023.04.006
藜麦秸秆微贮替代全株青贮玉米对西杂育肥牛生产性能、营养物质表观消化率及血清指标的影响
张俊丽1,摆世林2,侯鹏霞1,梁小军1
- 1.宁夏农林科学院动物科学研究所,宁夏 银川 750002
2.宁夏向丰农牧业有限公司,宁夏 固原 753400
Effects of Partly Replacing Whole-plant Corn Silage with Quinoa Straw Micro-silage on Production Performance, Nutrient Apparent Digestibility, and Serum Indexes of Fattening Simmental Crossbred Cattle
ZHANG Junli1,BAI Shilin2,HOU Pengxia1,LIANG Xiaojun1
- 1. Institute of Animal Science,Ningxia Academy of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences,Yinchuan 750002,China
2. Ningxia Xiangfeng Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Co.,Ltd., Guyuan 753400,China
摘要:
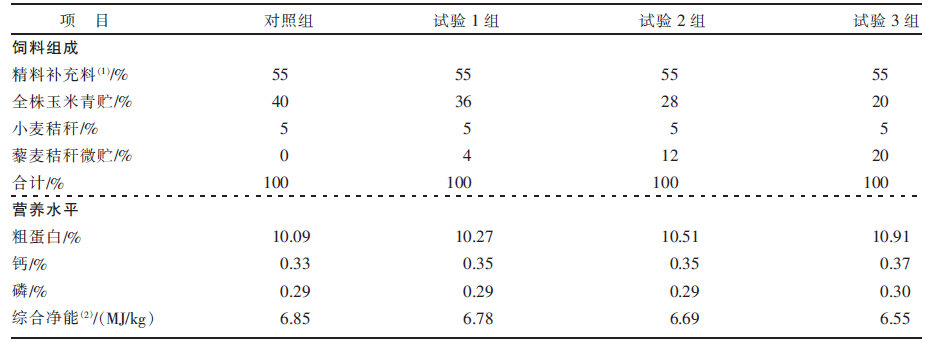
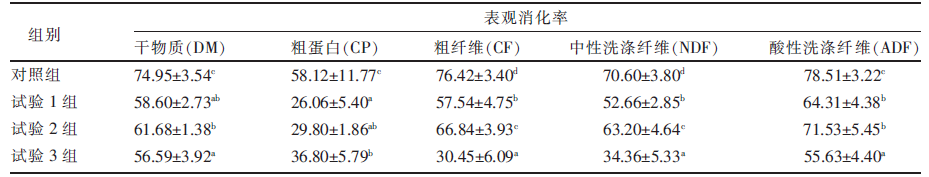
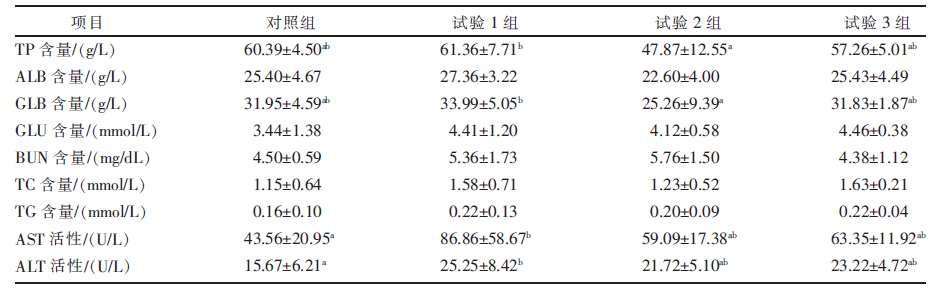
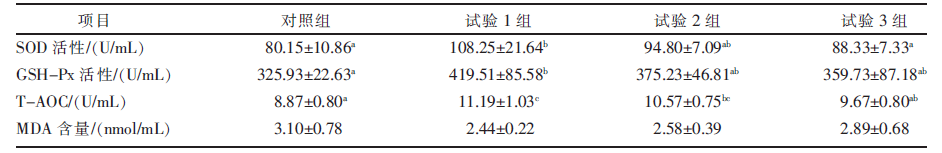
[目的]研究日粮中藜麦秸秆微贮替代全株玉米青贮对西杂育肥牛生产性能、营养物质表观消化率及血清指标的影响。[方法]选择体况良好、初始体重450 kg左右的西杂肉牛36头,随机分为4组,即对照组、试验1组、试验2组、试验3组,每组9头,每头为1个重复。对照组饲喂TMR基础日粮,试验1组、试验2组、试验3组在基础日粮中粗饲料的基础上分别用藜麦秸秆微贮替代10%、30%、50%的全株玉米青贮。预饲期15 d,正饲期60 d。记录各组肉牛在试验期间的体重及采食情况,计算平均日增重、平均日采食量、平均料重比;采集饲料样品及粪样,测定主要营养物质含量,计算营养物质表观消化率;试验结束时,采集血液样本制备血清,测定血清生化指标、抗氧化能力指标以及免疫指标。[结果]与对照组相比,试验1组肉牛的平均日增重显著(P<0.05)提高,平均料重比显著(P<0.05)降低。试验1组、试验2组、试验3组肉牛的干物质(DM)、粗蛋白(CP)、粗纤维(CF)、中性洗涤纤维(NDF)、酸性洗涤纤维(ADF)表观消化率均显著(P<0.05)低于对照组。试验1组肉牛的血清谷草转氨酶(AST)活性、谷丙转氨酶(ALT)活性、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)活性、总抗氧化能力(T-AOC),以及IgG和IgM含量显著(P<0.05)高于对照组,血清MDA含量低于对照组(P>0.05)。[结论]日粮中用藜麦秸秆微贮替代部分全株玉米青贮饲喂西杂育肥牛,可提高日增重,降低料重比,增强机体抗氧化能力和免疫能力,建议替代比例以10%为宜。
中图分类号: