畜牧与饲料科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 108-114.doi: 10.12160/j.issn.1672-5190.2023.05.015
牛粪与化肥配施对土壤及青贮玉米中铜、锌含量的影响
王振
- 黑龙江省农业科学院畜牧兽医分院,黑龙江 齐齐哈尔 161000
Effects of Combined Application of Cattle Manure with Chemical Fertilizer on Copper and Zinc Contents in Soil and Silage Maize
WANG Zhen
- Branch of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary,Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Qiqihar 161000,China
摘要:
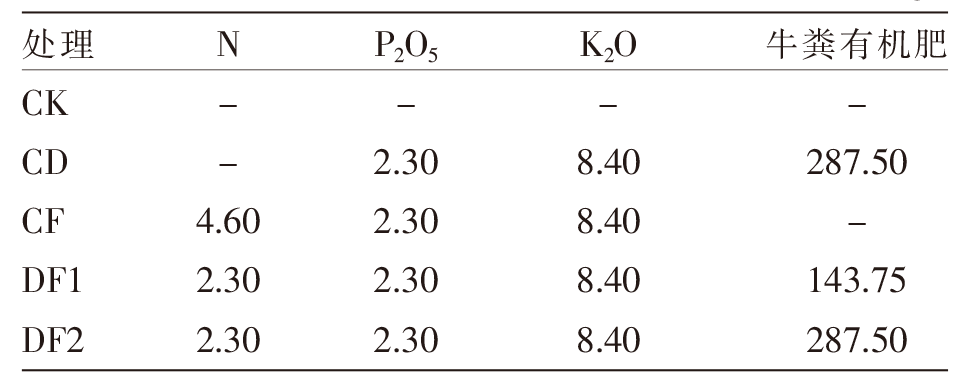
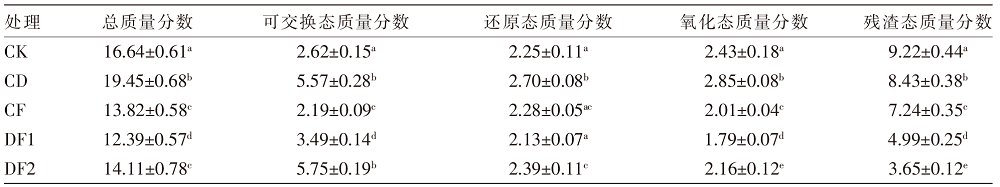
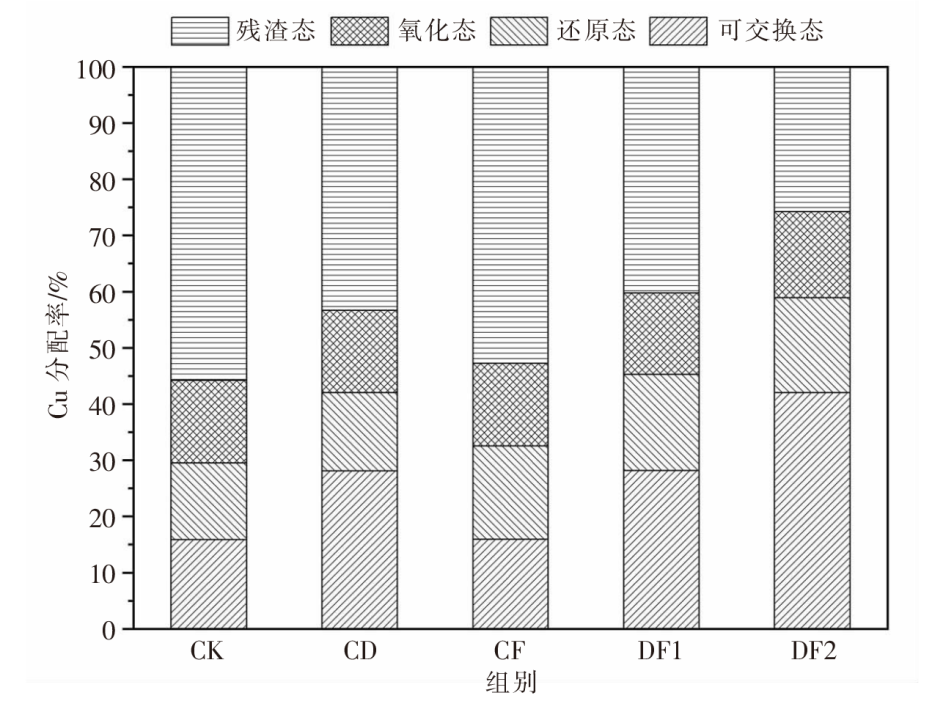
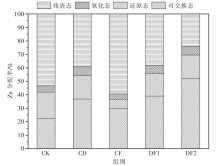
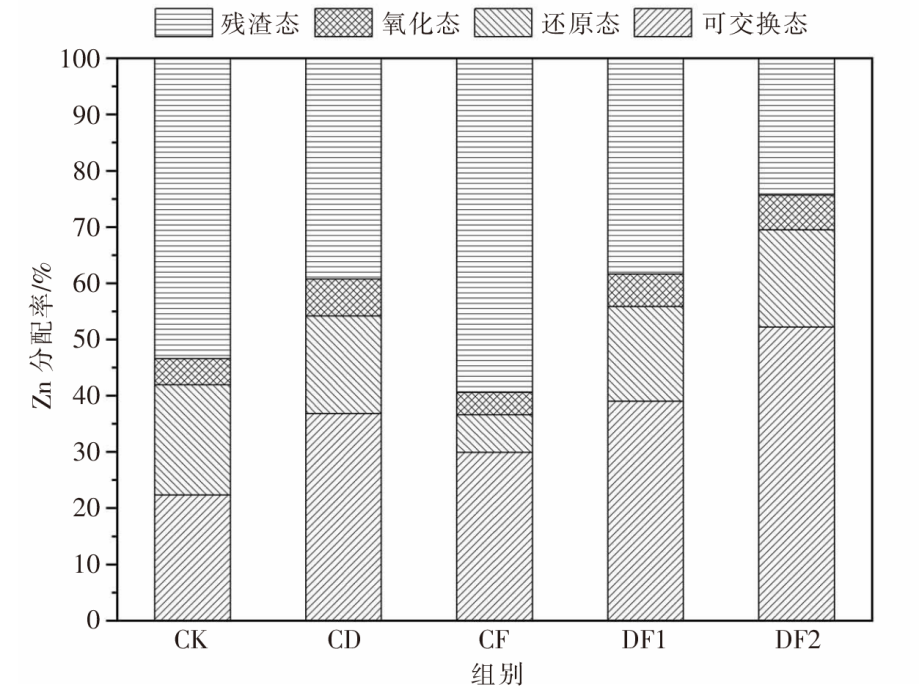
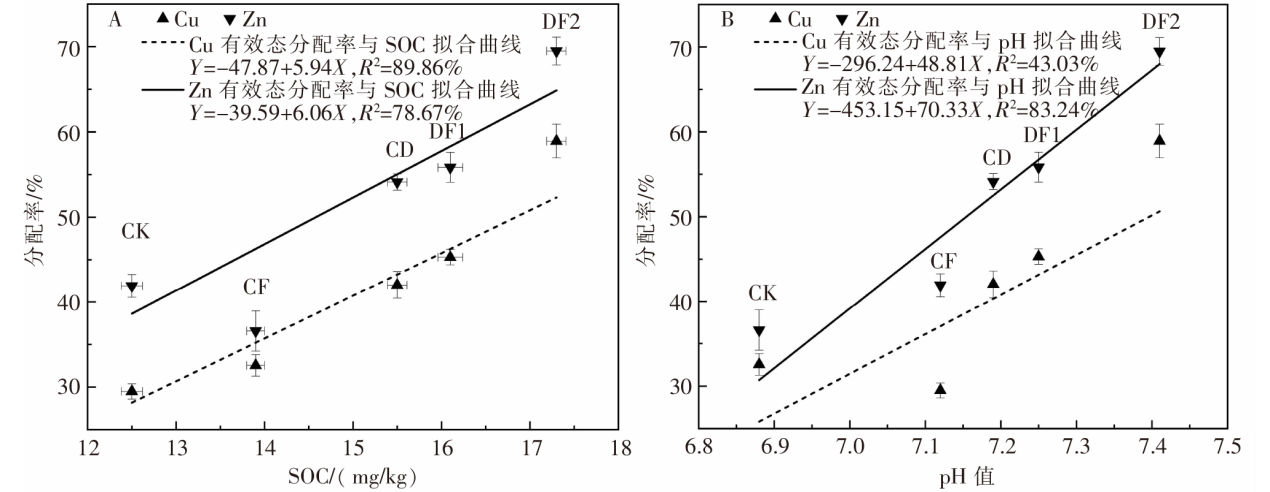
[目的]充分挖掘牛粪肥料化利用的潜力,避免过量施用牛粪给土壤-农作物生态系统带来的潜在重金属危害。[方法]根据牛粪有机肥和化肥的不同配施比例,设置5个处理,分别为空白对照组(CK)、单施牛粪有机肥组(CD)、单施化肥组(CF)、牛粪有机肥和化肥1∶1配施组(DF1)、牛粪有机肥和化肥2∶1配施组(DF2),以土壤和青贮玉米为研究对象进行盆栽试验。测定并计算不同配施处理下土壤重金属铜(Cu)、锌(Zn)的各形态质量分数,分析Cu、Zn有效态分配率与土壤pH值、有机碳质量分数的相关性;比较青贮玉米不同部位的Cu、Zn含量。[结果]牛粪有机肥与化肥配施对土壤中Cu、Zn的总质量分数及不同形态的质量分数影响显著(P<0.05),施用牛粪有机肥可以促进残渣态Cu向可交换态转化,CD和DF1处理的可交换态Cu分配率从CK处理的15.86%分别提高至28.12%、28.13%,与CK处理相比DF2处理的可交换态Cu分配率提高幅度最大,提高至42.02%;而CD和DF1处理的残渣态Zn分配率从CK处理的53.40%分别降低至39.27%、38.40%,与CK处理相比DF2处理的残渣态Zn分配率变化幅度最大,降低至24.33%。牛粪有机肥与化肥配施后,土壤pH值、有机碳质量分数呈上升趋势,其中,土壤有机碳质量分数与土壤中有效态Cu、Zn的分配率正相关,其相关性分别达到极显著(P<0.01)和显著(P<0.05)水平;同时土壤Zn的有效态分配率与土壤pH值的变化趋势显著(P<0.05)相关,但Cu的有效态分配率与土壤pH值的相关性不显著(P>0.05);施用牛粪有机肥提高了玉米植株内的Cu、Zn含量,与CK处理相比分别提高了45.50%~115.38%、44.99%~93.29%。[结论]牛粪有机肥与化肥配施在改善土壤理化性质的同时使得土壤中重金属Cu、Zn活化,提高了青贮玉米对其的富集能力,因此,施用牛粪有机肥时应严格遵循测土配方算出的实际需求量,以降低土壤环境的重金属污染风险和青贮玉米的饲用风险。
中图分类号: