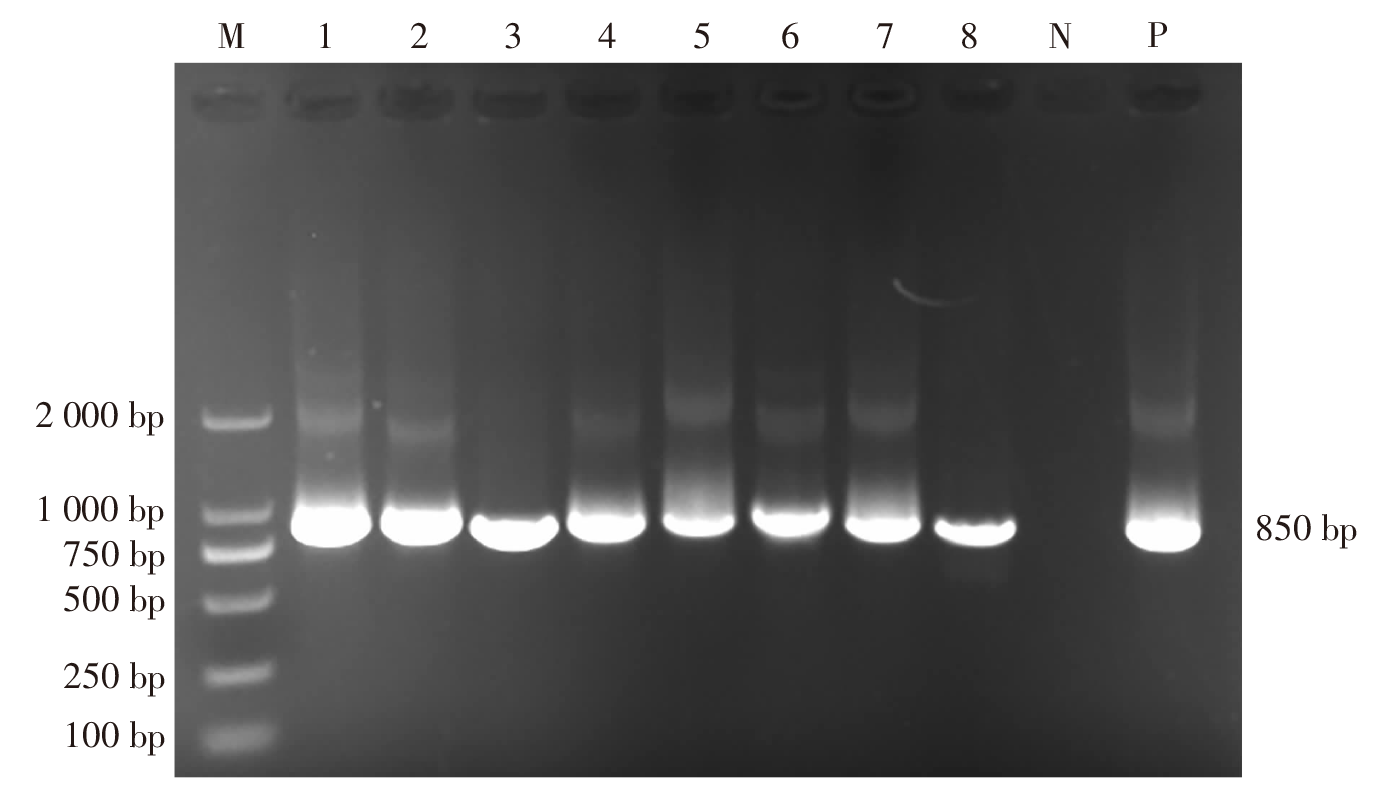
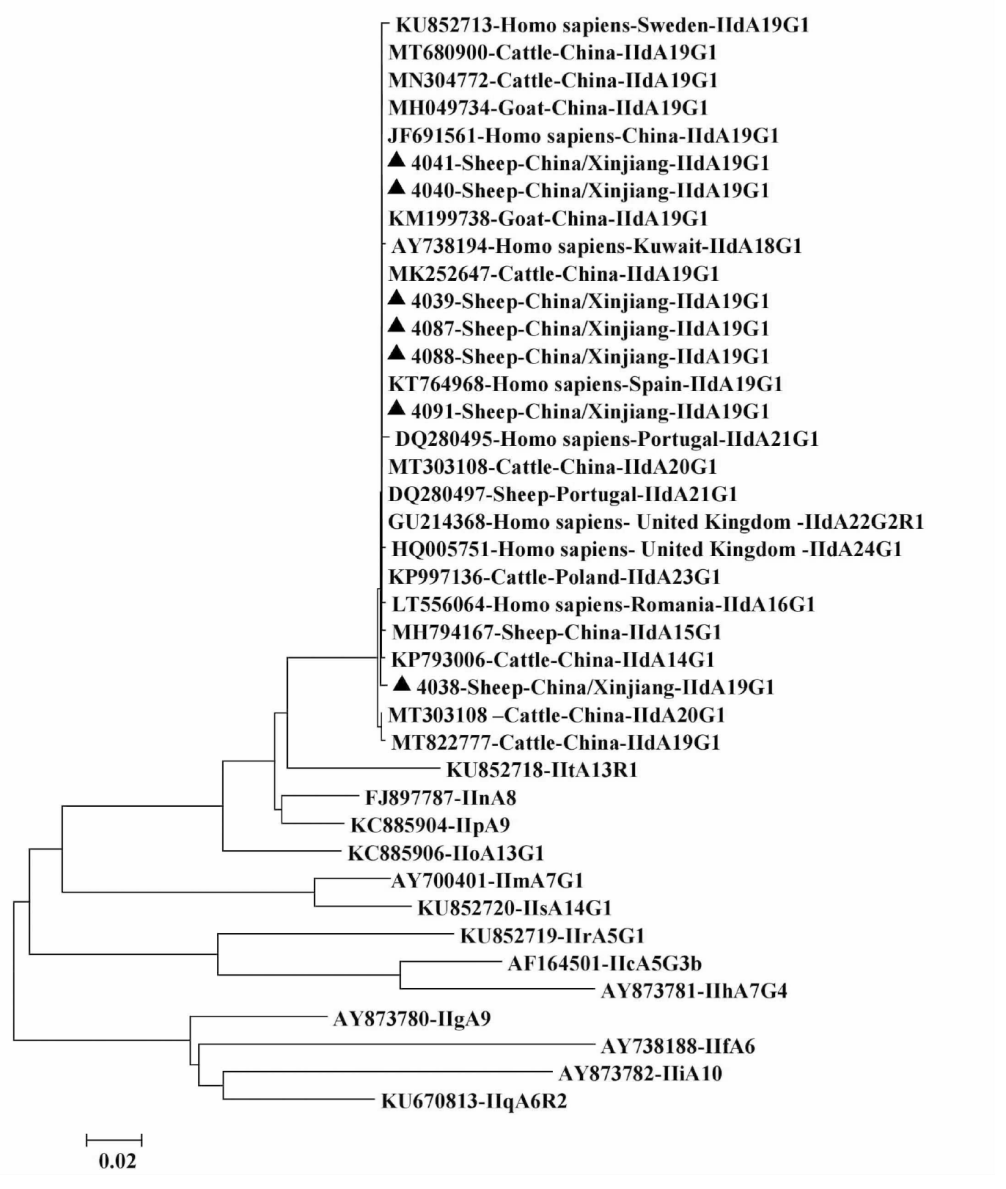
| [1] |
RYAN U, ZAHEDI A, PAPARINI A. Cryptosporidium in humans and animals-A one health approach to prophylaxis[J]. Parasite Immunology, 2016, 38(9): 535-547.
doi: 10.1111/pim.2016.38.issue-9
|
| [2] |
YANG X, GONG Q, ZHAO B, et al. Prevalence of Cryptosporidium infection in sheep and goat flocks in China during 2010—2019:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 2021, 21(9): 692-706.
doi: 10.1089/vbz.2020.2713
|
| [3] |
RYAN U M, FENG Y, FAYER R, et al. Taxonomy and molecular epidemiology of Cryptosporidium and Giardia-A 50 year perspective (1971—2021)[J]. International Journal for Parasitology, 2021, 51(13/14): 1099-1119.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2021.08.007
|
| [4] |
MI R, WANG X, HUANG Y, et al. Sheep as a potential source of zoonotic Cryptosporidiosis in China[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(18): e00868-18.
|
| [5] |
杨佳冰, 米荣升, 张烨华, 等. 宁夏吴忠市羊隐孢子虫感染情况调查及虫种鉴定[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2019, 27(6): 72-78.
|
| [6] |
XIAO L, FENG Y. Molecular epidemiologic tools for waterborne pathogens Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis[J]. Food and Waterborne Parasitology, 2017(8/9): 14-32.
|
| [7] |
李文超, 汪凯, 唐莉, 等. 安徽及周边省份绵羊和山羊隐孢子虫分子特性分析[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2019, 31(5): 474-478.
|
| [8] |
QI M, ZHANG Z, ZHAO A, et al. Distribution and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis, and Enterocytozoon bieneusi amongst grazing adult sheep in Xinjiang, China[J]. Parasitology International, 2019, 71:80-86.
doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2019.04.006
|
| [9] |
YE J, XIAO L, WANG Y, et al. Periparturient transmission of Cryptosporidium xiaoi from ewes to lambs[J]. Veterinary Parasitology, 2013, 197(3/4): 627-633.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.07.021
|
| [10] |
李治国, 徐春艳, 侯旻昱, 等. 新疆部分地区牧马肠道寄生虫感染情况调查[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2019, 51(9): 87-90.
|
| [11] |
RYAN U, XIAO L, READ C, et al. Identification of novel Cryptosporidium genotypes from the Czech Republic[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(7): 4302-4307.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.7.4302-4307.2003
|
| [12] |
ALVES M, XIAO L, SULAIMAN I, et al. Subgenotype analysis of Cryptosporidium isolates from humans,cattle,and zoo ruminants in Portugal[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 2003, 41(6): 2744-2747.
doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.6.2744-2747.2003
|
| [13] |
CONNELLY L, CRAIG B H, JONES B, et al. Genetic diversity of Cryptosporidium spp. within a remote population of soay sheep on St. Kilda Islands, Scotland[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2013, 79(7): 2240-2246.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.02823-12
|
| [14] |
CHEN Y, QIN H, HUANG J, et al. The global prevalence of Cryptosporidium in sheep:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Parasitology, 2022, 149(12): 1652-1665.
doi: 10.1017/S0031182022001196
|
| [15] |
TAKO S, FLEIDEROVITZ L, MARKOVICH M P, et al. Cryptosporidium parvum gp60 subtypes in diarrheic lambs and goat kids from Israel[J]. Parasitology Research, 2023, 122(9): 2237-2241.
doi: 10.1007/s00436-023-07925-0
|
| [16] |
IMRE K, LUCA C, COSTACHE M, et al. Zoonotic Cryptosporidium parvum in Romanian newborn lambs (Ovis aries)[J]. Veterinary Parasitology, 2013, 191(1/2): 119-122.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.08.020
|
| [17] |
DÍAZ P, NAVARRO E, PRIETO A, et al. Cryptosporidium species in post-weaned and adult sheep and goats from N.W. Spain: Public and animal health significance[J]. Veterinary Parasitology, 2018, 254:1-5.
doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2018.02.040
|
| [18] |
PAPANIKOLOPOULOU V, BAROUDI D, GUO Y, et al. Genotypes and subtypes of Cryptosporidium spp. in diarrheic lambs and goat kids in northern Greece[J]. Parasitology International, 2018, 67(4): 472-475.
doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2018.04.007
|
| [19] |
KAUPKE A, MICHALSKI M M, RZEZUTKA A. Diversity of Cryptosporidium species occurring in sheep and goat breeds reared in Poland[J]. Parasitology Research, 2017, 116(3): 871-879.
doi: 10.1007/s00436-016-5360-3
|
| [20] |
PAZ E SILVA F M, LOPES R S, BRESCIANI K D, et al. High occurrence of Cryptosporidium ubiquitum and Giardia duodenalis genotype E in sheep from Brazil[J]. Acta Parasitologica, 2014, 59(1): 193-196.
|