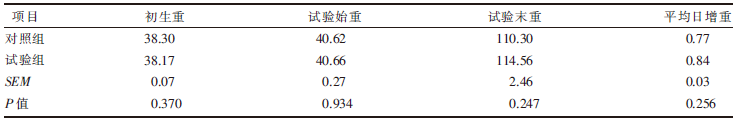
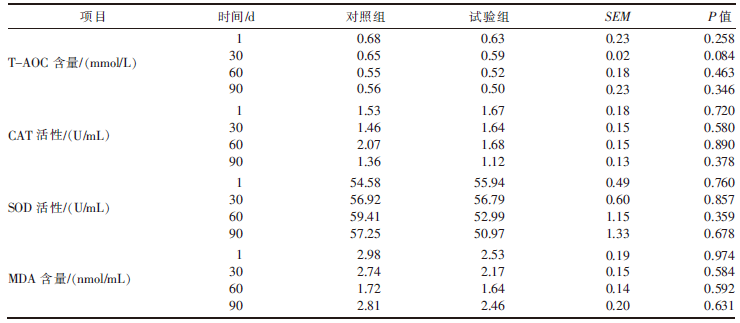
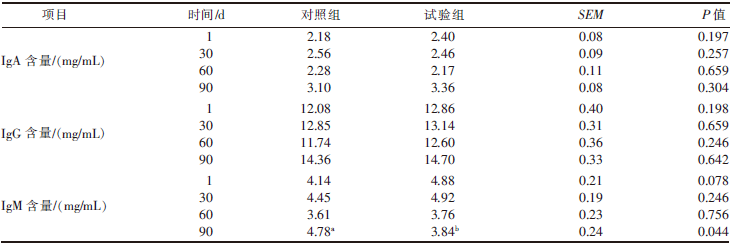
| [1] |
胡兴义, 张双翔, 冯旭芳, 等. 复合益生菌制剂对哺乳仔猪生长性能和免疫水平的影响研究[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2017, 38(8):24-28.
|
| [2] |
卢佳伟, 王金刚, 高琴, 等. 不同益生菌对断奶山羊生长性能、血清生化指标以及粪便菌群的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(5):2752-2764.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.05.034
|
| [3] |
MARKOWIAK P, SLIZEWSKA K. The role of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in animal nutrition[J]. Gut Pathogens, 2018, 10(1):21.
doi: 10.1186/s13099-018-0250-0
|
| [4] |
林建和, 陈张华, 张娟. 乳酸菌在畜禽生产中应用的研究进展[J]. 吉林畜牧兽医, 2021, 42(1):65.
|
| [5] |
吕全云, 陈仕强, 武玉华, 等. 乳酸菌对畜禽的作用及其应用[J]. 山东畜牧兽医, 2013, 34(4):23.
|
| [6] |
王晓伟, 高鹏飞, 姚国强, 等. 乳酸菌发酵饲料的优势及其在畜禽养殖中的应用[J]. 粮食与饲料工业, 2015(7):47-50,55.
|
| [7] |
杨学林, 林峰, 潘捷科, 等. 一种抗腹泻型仔猪专用复合微生态制剂的制备及其应用:CN106721260A[P]. 2017-05-31.
|
| [8] |
DE REZENDE A S C, TRIGO P, LANA A M Q, et al. Yeast as a feed additive for training horses[J]. Ciência e Agrotecnologia, 2012, 36(3):354-362.
doi: 10.1590/S1413-70542012000300012
|
| [9] |
ZHAO Y L, JIANG L F, LIU T, et al. Construction and immunogenicity of the recombinant Lactobacillus acidophilus pMG36e-E0-LA-5 of bovine viral diarrhea virus[J]. Journal of Virological Methods, 2015, 225:70-75.
doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2015.09.007
|
| [10] |
吕利军, 季海峰, 黄建国, 等. 菊粉在断奶仔猪中的研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2007, 4(7):29-31.
|
| [11] |
PETERSON R E, KLOPFENSTEIN T J, ERICKSON G E, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus strain NP51 on Escherichia coil O157: H7 fecal shedding and finishing performance in beef feedlot cattle[J]. Journal of Food Protection, 2007, 70(2):287-291.
doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-70.2.287
|
| [12] |
BAYATKOUHSAR J, TAHMASEBI A M, NASERIAN A A, et al. Effects of supplementation of lactic acid bacteria on growth performance, blood metabolites and fecal coliform and lactobacilli of young dairy calves[J]. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2013, 186(1/2):1-11.
doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2013.04.015
|
| [13] |
KOBIERECKA P A, WYSZYNSKA A K, ALEKSANDRZAK-PIEKARCZYK T, et al. In vitro characteristics of Lactobacillus spp. strains isolated from the chicken digestive tract and their role in the inhibition of Campylobacter colonization[J]. Microbiology Open, 2017, 6(5):e00512.
doi: 10.1002/mbo3.512
|
| [14] |
李春生. 微生态活菌制剂防治初生犊牛腹泻的效果试验[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2010(22):109-110.
|
| [15] |
单婕, 邵孝侯. 有效微生物与调理剂在奶牛粪堆肥中的保氮与除臭效应[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(2):646-648.
|
| [16] |
郭欣怡, 张曼, 韩飞, 等. 不同益生菌制剂对肉鸡生产性能、免疫功能和肠道菌群的影响[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2016, 37(11):79-83.
|
| [17] |
陈文辉, 周映华, 李秋云, 等. 复合益生菌制剂对断奶仔猪生产性能和腹泻率的影响[J]. 湖南畜牧兽医, 2007(3):14-15.
|
| [18] |
崔一喆, 王秋菊, 苏景, 等. 复合益生菌制剂对离乳梅花鹿生长性能、粪便菌群及血液生化指标的影响[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2017, 37(1):129-133.
|
| [19] |
COLLINGTON G K, PARKER D S, ARMSTRONG D G. The influence of inclusion of either an antibiotic or a probiotic in the diet on the development of digestive enzyme activity in the pig[J]. The British Journal of Nutrition, 1990, 64(1):59-70.
doi: 10.1079/BJN19900009
|
| [20] |
陈鲜鑫, 王金全, 王春阳, 等. 乳酸菌发酵液体饲料对生长猪生长性能和粪中微生物区系的影响[J]. 饲料工业, 2010, 31(4):40-42.
|
| [21] |
李清定, 彭立秋, 王德昌, 等. 消效TM微生物发酵饲料对生长猪生长性能和粪中微生物区系的影响[J]. 湖南饲料, 2011(3):43-45.
|
| [22] |
肖海霞, 托乎提·阿及德, 石国庆, 等. 不同月龄断奶应激对马驹血清指标和体增重的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2015, 46(11):2010-2019.
|
| [23] |
JANG J Y, KIM S, KWON M S, et al. Rotavirus-mediated alteration of gut microbiota and its correlation with physiological characteristics in neonatal calves[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2019, 57(2):113-121.
doi: 10.1007/s12275-019-8549-1
|
| [24] |
杨海英, 杨在宾, 杨维仁, 等. 益生素和低聚木糖对断奶仔猪生产性能、消化酶活性、血液指标和肠道微生物的影响[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2009, 29(7):914-919.
|
| [25] |
滕颖, 陈先国. 动物微生态制剂的研究进展[J]. 中国兽药杂志, 2005, 39(11):43-46.
|
| [26] |
ALIPOUR M J, JALANKA J, PESSA-MORIKAWA T, et al. The composition of the perinatal intestinal microbiota in cattle[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1):10437.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28733-y
pmid: 29993024
|
| [27] |
伍革民, 柳小春, 施启顺, 等. 血浆酶活性与猪生产性状及其杂种优势的相关研究[J]. 甘肃畜牧兽医, 1999, 29(5):3-5.
|
| [28] |
殷溪沙, 李伟, 赵鑫, 等. 乳酸菌素对犊牛血液指标影响的研究[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2014, 26(5):44-47.
|
| [29] |
王惠影, 刘毅, 王翠, 等. 乳酸菌对朗德鹅填饲效果的影响[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2015, 42(5):1152-1157.
|
| [30] |
汪丹. 代乳粉饲喂时间对奶公犊生长性能、血清生化和免疫相关指标的影响[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2016.
|
| [31] |
董佳琦, 金三俊, 汪晶晶, 等. 复合益生菌发酵液对哺乳母猪生产性能、血清生化及免疫指标的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2018, 30(1):343-349.
|
| [32] |
罗小华, 刘臻, 肖克宇, 等. 饲料酵母及其在水产动物营养中的应用[J]. 北京水产, 2008(2):49-53.
|
| [33] |
FOMENKY B E, DO D N, TALBOT G, et al. Direct-fed microbial supplementation influences the bacteria community composition of the gastrointestinal tract of pre- and post-weaned calves[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8:14147.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32375-5
pmid: 30237565
|