畜牧与饲料科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 17-25.doi: 10.12160/j.issn.1672-5190.2023.02.003
腹泻型肠易激综合征大鼠炎症因子与肠道微生物的相关性研究
张儒奇1,朱炳旭2,孙金鹏1,王荣1,孙闵1
- 1.济宁医学院中西医结合学院,山东 济宁 272067
2.济宁医学院基础医学院,山东 济宁 272067
Correlation between Inflammatory Factors and Intestinal Microbiota in Rats with Diarrhea-predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome
ZHANG Ruqi1,ZHU Bingxu2,SUN Jinpeng1,WANG Rong1,SUN Min1
- 1. College of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine,Jining Medical University,Jining 272067,China
2. College of Basic Medicine,Jining Medical University,Jining 272067,China
摘要:
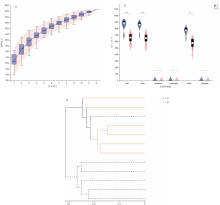
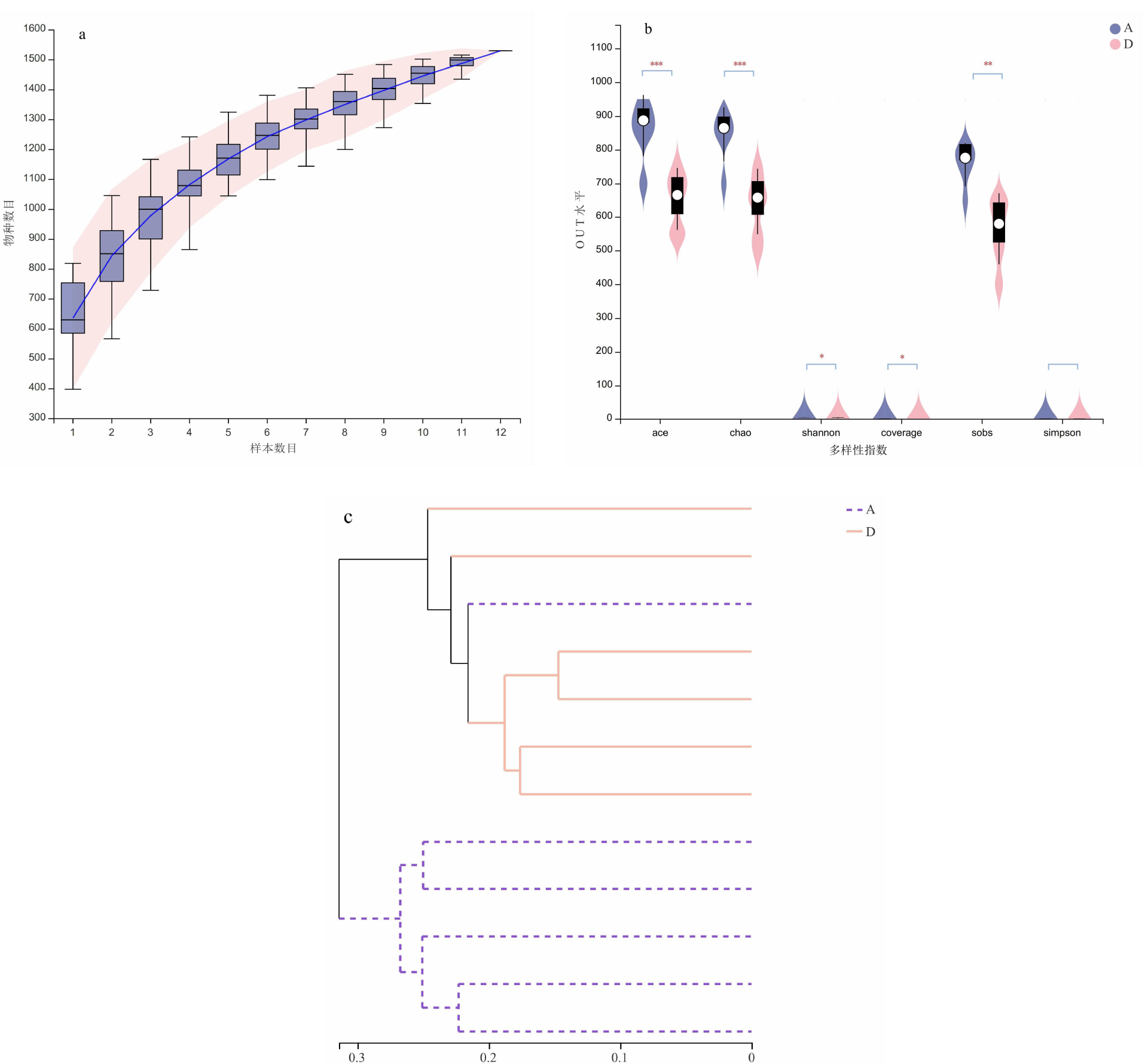
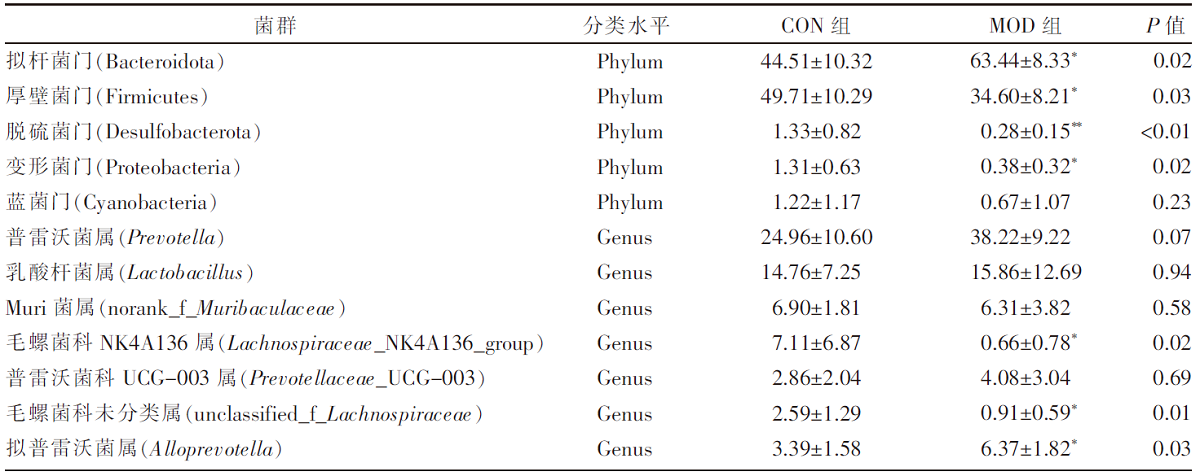
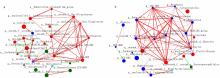
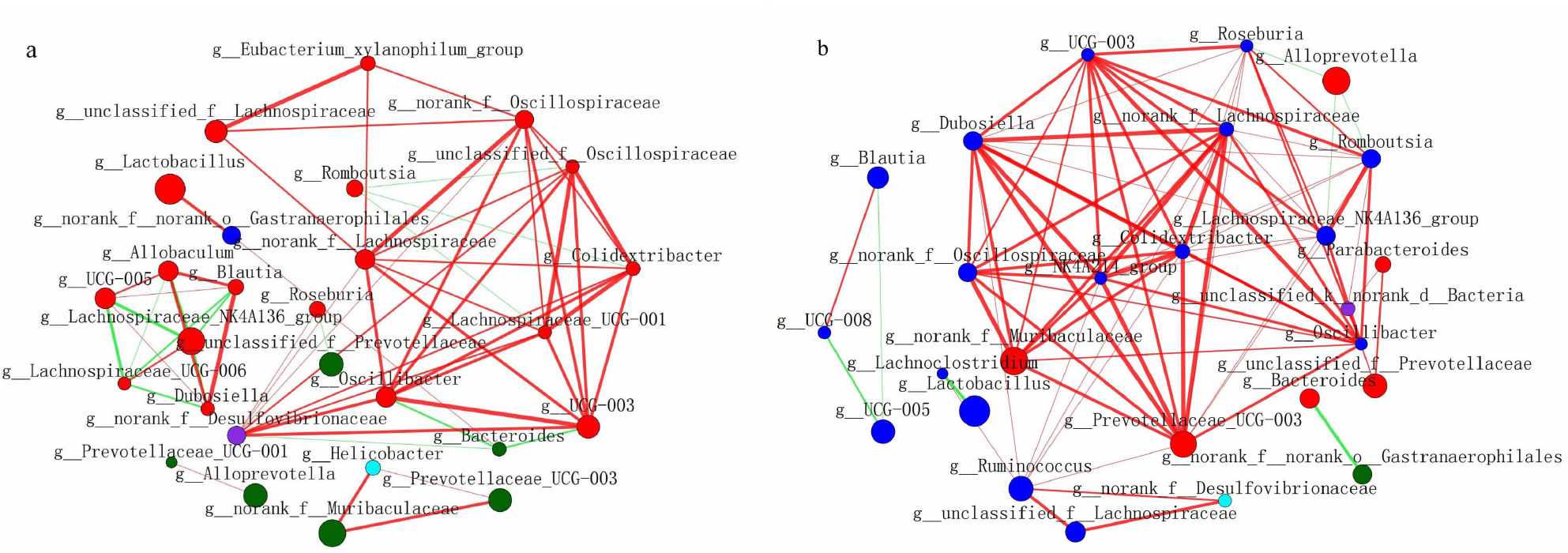
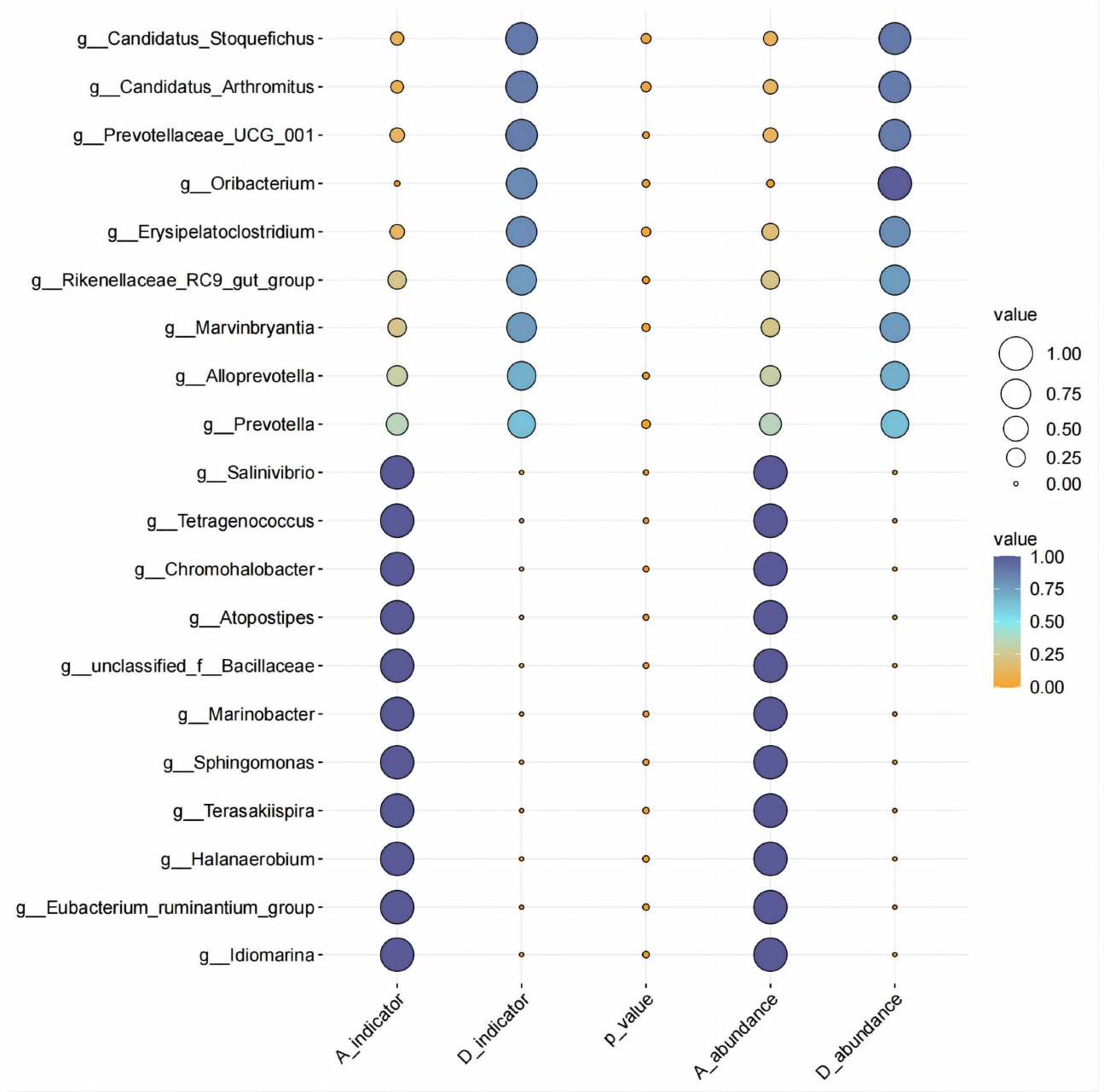
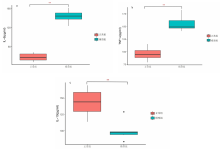
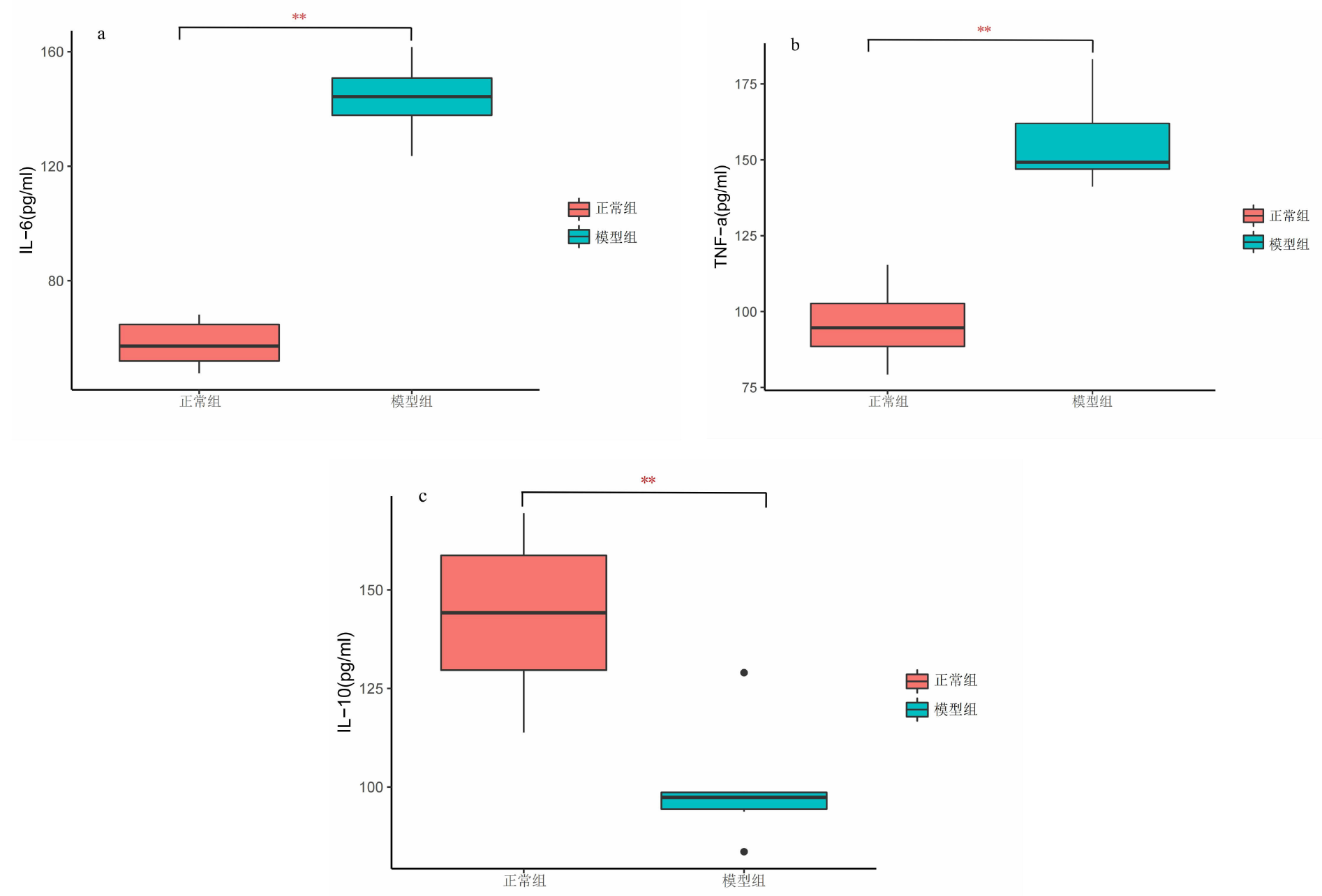
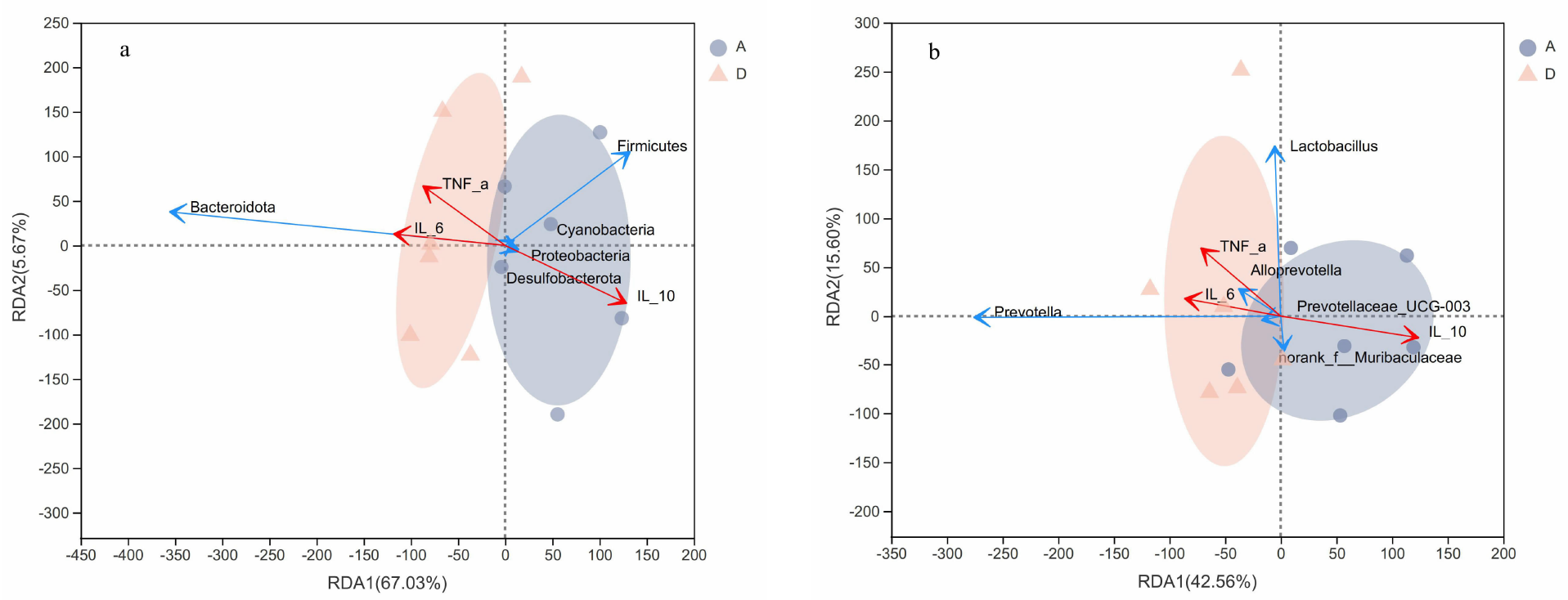
[目的]探讨腹泻型肠易激综合征(diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome,IBS-D)大鼠肠道菌群组成与血清炎症因子变化及两者相关性。[方法]选取12只雄性SD大鼠按随机数字表法分为正常组与模型组,每组6只。模型组依照“乙酸结肠灌注联合束缚刺激法”构建IBS-D大鼠模型。正常组、模型组大鼠均通过灌胃给予蒸馏水10 mL/(kg·BW),1次/d,连续干预8 d后进行样本采集。应用ELISA法检测血清中IL-10、IL-6、TNF-α含量,并利用16S rDNA测序结果对2组大鼠肠道菌群物种组成、单因素网络以及与血清炎症因子的相关性等进行分析。[结果]与正常组相比,模型组IL-10水平降低(P<0.01),而IL-6、TNF-α水平提高(P<0.01)。物种组成比较显示,2组肠道菌群在门和属水平上存在差异,与正常组相比,在门水平上,模型组拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota)相对丰度增加,厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)等相对丰度降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);在属水平上,模型组拟普雷沃菌属(Alloprevotella)等相对丰度增加,Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group等相对丰度降低(P<0.05)。肠道菌群指示物种分析显示,模型组Candidatus_Stoquefichus、Candidatus_Arthromitus等具有显著效应(P<0.05)。单因素网络分析结果显示,模型组的差异菌群Alloprevotella与罗氏菌属(Roseburia)、罗姆布茨菌属(Romboutsia)、Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group呈负相关,而Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group与Romboutsia、UCG-003、Oscillibacter、Roseburia呈正相关。相关性分析结果显示,门水平上,梭杆菌门(Fusobacteriota)、黏菌门(Myxococcota)、变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、盐厌氧菌门(Halanaerobiaeota)与IL-10水平呈正相关,Bacteroidota与IL-10水平呈负相关,Bacteroidota与IL-6水平呈正相关,Campilobacterota、Halanaerobiaeota与IL-6水平呈负相关,脱硫菌门(Desulfobacterota)、Campilobacterota、Halanaerobiaeota与TNF-α呈负相关;在属水平上,Alloprevotella、Prevotellaceae_UCG-001、普雷沃菌属(Prevotella)与IL-10呈正相关,而Alloprevotella、Prevotellaceae_UCG-001与IL-6、TNF-α呈负相关,Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group、UCG-003、Oscillibacter与IL-10呈负相关,与IL-6、TNF-α水平呈正相关,上述结果差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05或P<0.01或P<0.001)。[结论]IBS-D大鼠与健康大鼠相比,肠道菌群组成与血清炎症因子均存在差异,并且肠道菌群与血清炎症因子具有一定关联性。研究结果为临床检测炎症因子以指导益生菌或抗生素选用提供了有益参考。
中图分类号: