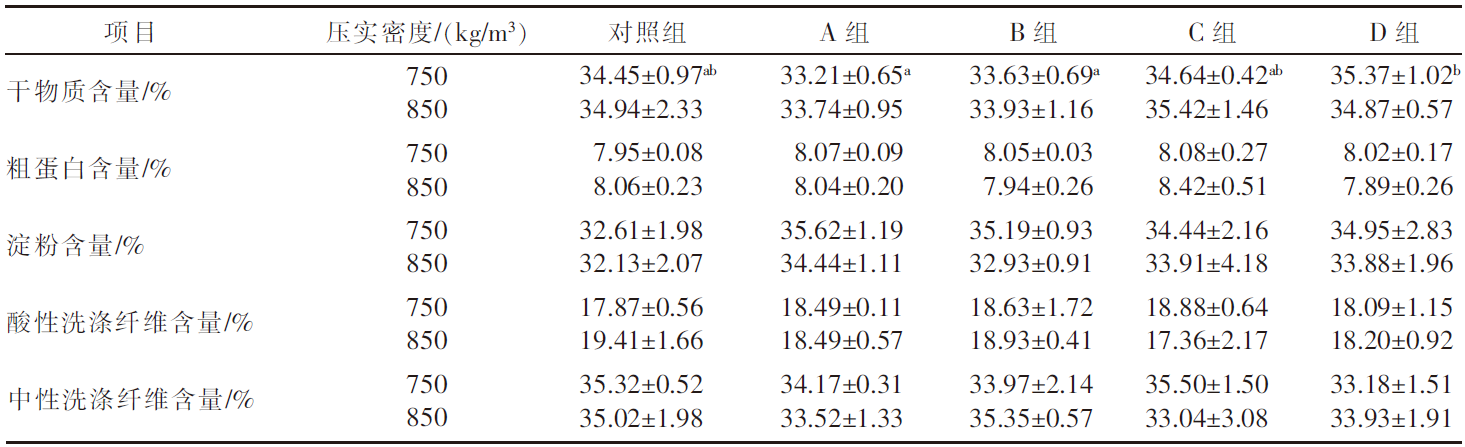
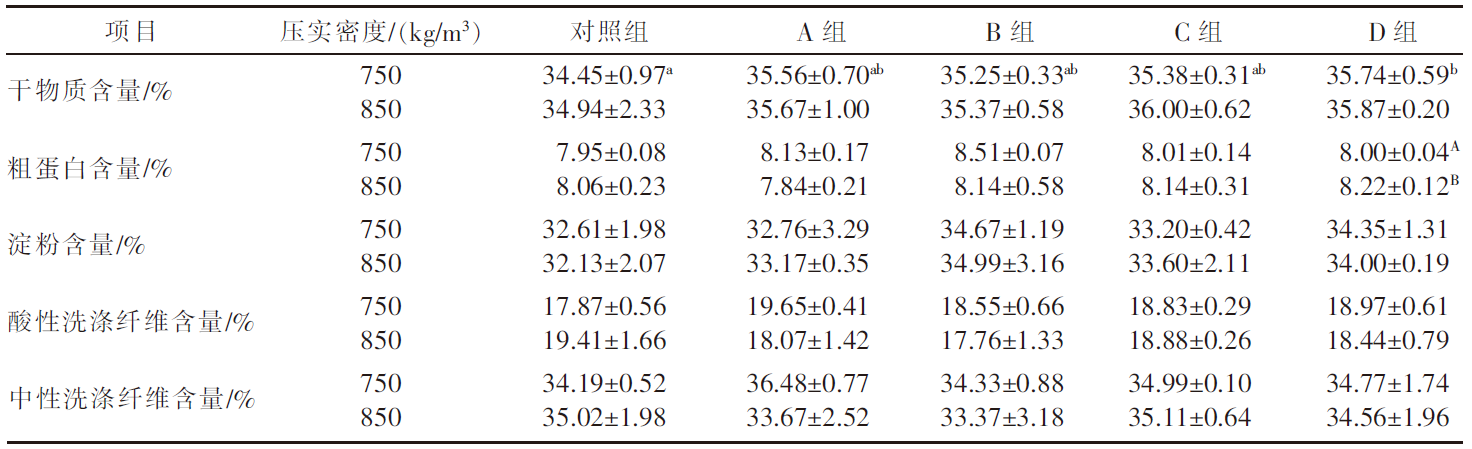
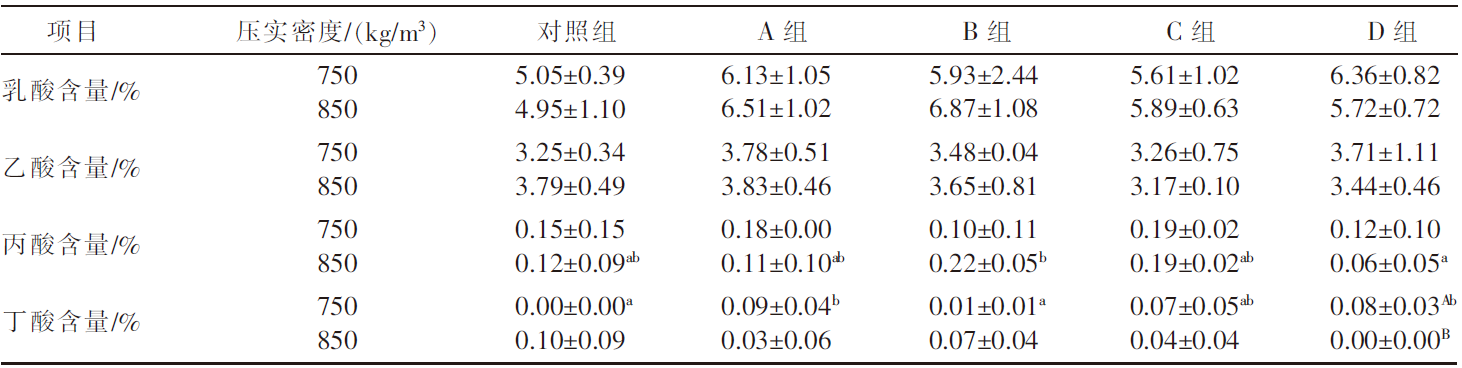
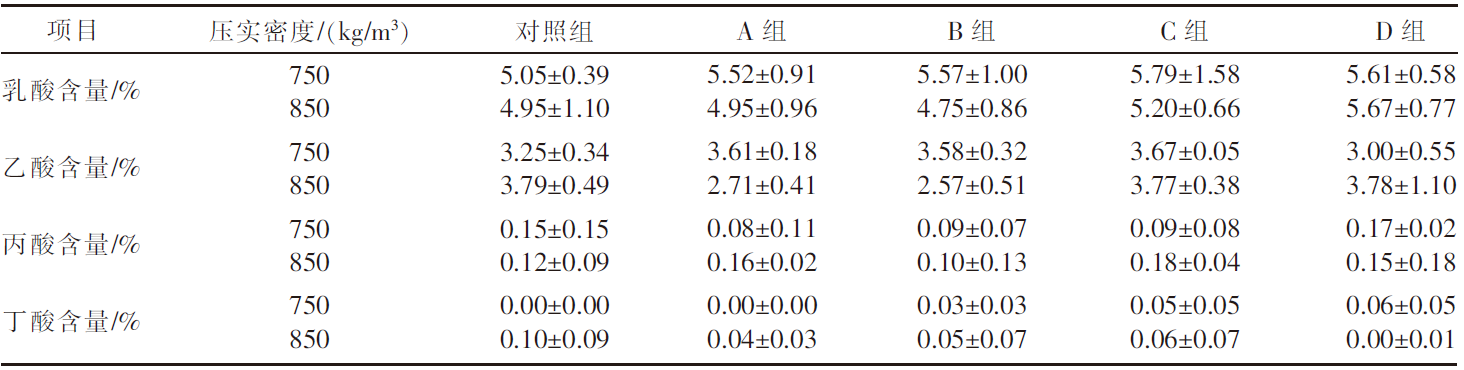
| [1] |
GOLLOP N, ZAKIN V, WEINBERG Z G. Antibacterial activity of lactic acid bacteria included in inoculants for silage and in silages treated with these inoculants[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2005, 98(3):662-666.
pmid: 15715869
|
| [2] |
钱寅森, 武启迪, 季中亚, 等. 我国青贮玉米生产与加工研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2021, 49(23):41-46.
|
| [3] |
陈凤梅. 复合微生态制剂对全株玉米青贮发酵品质及营养成分的影响[J]. 饲料研究, 2021, 44(15):92-95.
|
| [4] |
ADESOGAN A T, SALAWU M B, ROSS A B, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus buchneri, L. fermentum or Leuconostoc mesenteroides inoculants or a chemical additive on the fermentation, aerobic stability and nutritive value of crimped wheat grains[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2003, 86(5):1789-1796.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(03)73764-3
|
| [5] |
付薇, 陈伟, 韩永芬, 等. 添加不同乳酸菌对玉米秸秆青贮有氧稳定性影响的研究[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2019, 40(9):45-49.
|
| [6] |
JOO Y H, KIM D H, LEE H J, et al. Effects of microbial and organic additives on fermentation quality and aerobic stability of barley silage[J]. Journal of Agriculture and Life Science, 2020, 54(1):35-44.
|
| [7] |
付薇, 陈伟, 王小利, 等. 不同发酵乳酸菌剂及组合添加对甜高粱青贮营养价值、微生物数量及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(11):6245-6256.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.11.025
|
| [8] |
米筱. 压实密度和二次发酵对全株玉米青贮品质的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2022.
|
| [9] |
BRÜNING D, GERLACH K, WEIß K, et al. Effect of compaction, delayed sealing and aerobic exposure on maize silage quality and on formation of volatile organic compounds[J]. Grass and Forage Science, 2018, 73(1):53-66.
doi: 10.1111/gfs.2018.73.issue-1
|
| [10] |
VAN SOEST P J, ROBERTSON J B, LEWIS B A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 1991, 74(10):3583-3597.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(91)78551-2
pmid: 1660498
|
| [11] |
李松泽, 陈雪, 毋昊, 等. 2019年不同地区全株玉米青贮品质的分析[J]. 饲料工业, 2021, 42(5):60-64.
|
| [12] |
BURNS P, CUFFIA F, MILESI M, et al. Technological and probiotic role of adjunct cultures of non-starter lactobacilli in soft cheeses[J]. Food Microbiology, 2012, 30(1):45-50.
doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2011.09.015
pmid: 22265282
|
| [13] |
MUCK R E, NADEAU E, MCALLISTER T A, et al. Recent advances and future uses of silage additives[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2018, 101(5):3980-4000.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13839
|
| [14] |
王诚, 刘德娟, 何荣彦, 等. 植物乳杆菌和布氏乳杆菌对全株玉米青贮发酵品质影响[J]. 山东畜牧兽医, 2022, 43(1):15-18.
|
| [15] |
孙向丽, 菅复春, 许来鹏, 等. 布氏乳杆菌和植物乳杆菌对高粱青贮品质的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2021, 57(9):159-163.
|
| [16] |
成娟丽, 林金水. 布氏乳杆菌与不同乳酸菌联用对玉米青贮发酵、干物质回收率和营养价值的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2018(20):17-21.
|
| [17] |
RANJIT N K, KUNG L. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri, Lactobacillus plantarum, or a chemical preservative on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silage[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2000, 83(3):526-535.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(00)74912-5
|
| [18] |
ARRIOLA K G, QUEIROZ O C M, ROMERO J J, et al. Effect of microbial inoculants on the quality and aerobic stability of bermudagrass round-bale haylage[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2015, 98(1):478-485.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2014-8411
pmid: 25465545
|
| [19] |
ARRIOLA K G, OLIVEIRA A, JIANG Y, et al. Meta-analysis of effects of inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri, with or without other bacteria, on silage fermentation, aerobic stability, and performance of dairy cows[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2021, 104(7):7653-7670.
doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-19647
|
| [20] |
刘高坤, 王思, 刘少兴, 等. 不同微生物添加剂组合对全株玉米青贮品质的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2021, 57(8):215-218.
|
| [21] |
宋十妹, 吴春会, 李运起, 等. 青贮条件对天然牧草青贮发酵品质的影响[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2021(19):102-107.
|
| [22] |
王旭哲. 紧实度及收获期对全株玉米青贮品质及霉菌毒素的影响研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2019.
|
| [23] |
李松泽. 基于不同收获期和压实密度研究植物乳杆菌对全株玉米青贮品质的影响[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2021.
|