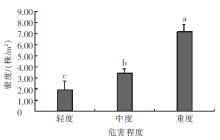
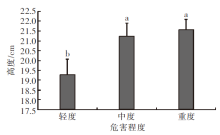
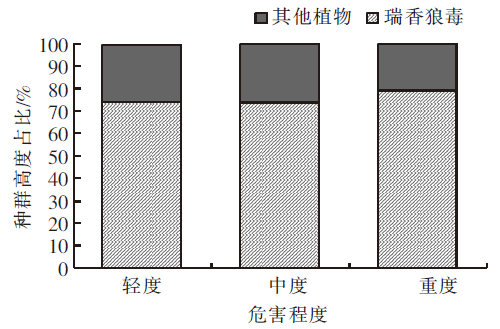
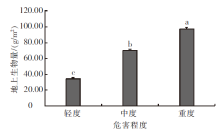
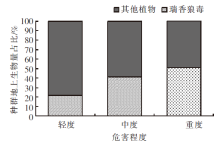
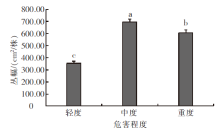
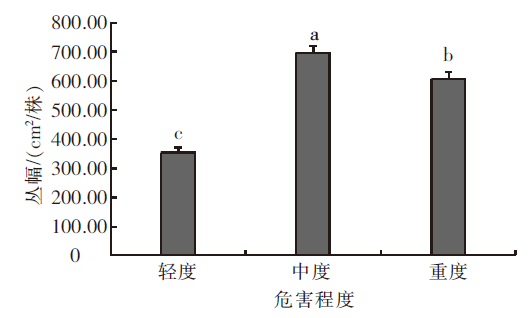
| [1] |
赵宝玉, 刘忠艳, 万学攀, 等. 中国西部草地毒草危害及治理对策[J]. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(10):3094-3103.
|
| [2] |
刘晓学, 冯柯, 严杜建, 等. 西藏天然草原有毒植物危害与防控技术研究进展[J]. 中国草地学报, 2015, 37(3):104-111.
|
| [3] |
严杜建, 周启武, 路浩, 等. 新疆天然草地毒草灾害分布与防控对策[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(3):565-582.
|
| [4] |
张庚, 郭亚洲, 张水平, 等. 甘肃天祝县天然草地毒草危害状况调查与防控[J]. 动物医学进展, 2019, 40(3):123-128.
|
| [5] |
马成武. 青海草地毒草狼毒的发生及防治对策[J]. 新农业, 2018(21):9-10.
|
| [6] |
严杜建, 吴晨晨, 赵宝玉. 中国天然草地毒草灾害分布与防控技术的研究进展[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2016, 44(1):104-109.
|
| [7] |
陆阿飞. 青海草地有毒植物及综合防治浅议[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2010(11):104-105.
|
| [8] |
郭亚洲, 张睿涵, 孙暾, 等. 甘肃天然草地毒草危害、防控与综合利用[J]. 草地学报, 2017, 25(2):243-256.
doi: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2017.02.004
|
| [9] |
王欢, 马青成, 耿朋帅, 等. 天然草地瑞香狼毒研究进展[J]. 动物医学进展, 2015, 36(12):154-160.
|
| [10] |
李秀萍, 马利青. 青海省草地狼毒的研究进展[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2014, 44(6):47-48.
|
| [11] |
吴国林, 魏有海. 青海草地毒草狼毒的发生及防治对策[J]. 青海农林科技, 2006(2):63-64.
|
| [12] |
高福元, 赵成章. 高寒退化草地狼毒种群株丛间格局控制机理[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(10):3114-3121.
|
| [13] |
高福元, 赵成章, 石福习, 等. 祁连山北坡高寒草地狼毒种群格局[J]. 生态学杂志, 2011, 30(6):1312-1316.
|
| [14] |
谢红旗, 杨廷勇, 赵磊, 等. 48%盖灌能乳油对草地狼毒的防治效果及牧草产量的影响[J]. 草学, 2018(3):38-40.
|
| [15] |
宋梅玲, 王玉琴, 鲍根生, 等. 不同草地管理措施对狼毒型退化草地群落结构及牧草品质的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2018, 35(10):2318-2326.
|
| [16] |
马玉寿, 尚占环, 施建军, 等. 黄河源区“黑土滩”退化草地群落类型多样性及其群落结构研究[J]. 草业科学, 2006, 23(12):6-11.
|
| [17] |
靳瑰丽, 朱习雯, 魏秀红, 等. 不同方法对醉马草防控效果的比较[J]. 草地学报, 2017, 25(3):625-632.
doi: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2017.03.025
|
| [18] |
王宏生, 鲍根生, 宋梅玲, 等. 应用“清橐1号”防除黄帚橐吾对草地群落及生产力的影响[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2018, 48(5):1-5.
|
| [19] |
尚占环, 龙瑞军, 马玉寿. 江河源区“黑土滩”退化草地特征、危害及治理思路探讨[J]. 中国草地学报, 2006, 28(1):69-74.
|
| [20] |
赵成章, 樊胜岳, 殷翠琴, 等. 毒杂草型退化草地植被群落特征的研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2004, 24(4):507-512.
|
| [21] |
周静, 袁媛, 孙承业, 等. 2004—2013年全国有毒动植物中毒事件分析[J]. 疾病监测, 2015, 30(5):403-407.
|
| [22] |
林丽, 赵成章, 龙瑞军, 等. 石羊河上游两种退化草地植物群落特征分析[J]. 草原与草坪, 2007, 27(4): 23-26.
|
| [23] |
樊胜岳, 赵成章, 殷翠琴, 等. 化学药剂灭杀棘豆技术研究与试验示范[J]. 中国沙漠, 2003, 23(2):205-208.
|
| [24] |
姚拓, 寇建村, 刘英. 狼毒栅锈病调查及其用于控制狼毒的初步研究[J]. 中国生物防治, 2004, 20(2):142-144.
|
| [25] |
黄玺, 李春杰, 南志标. 紫花苜蓿与醉马草的竞争效应[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(1):59-65.
|
| [26] |
李学森, 任继周, 冯克明, 等. 醉马草生态控制的研究[J]. 草业学报, 1996, 5(2):14-17.
|
| [27] |
李春杰, 姚祥, 南志标. 醉马草内生真菌共生体研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(8):793-805.
doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2018.0001
|
| [28] |
李娜娜, 赵玉凤, 夏超, 等. 甲基托布津对醉马草种带内生真菌的灭菌活性[J]. 草业科学, 2016, 33(7):1306-1314.
|
| [29] |
赵宝玉, 王保海, 莫重辉, 等. 西藏阿里地区牲畜冰川棘豆中毒灾害状况调查[J]. 西北农业学报, 2011, 20(4):40-46.
|