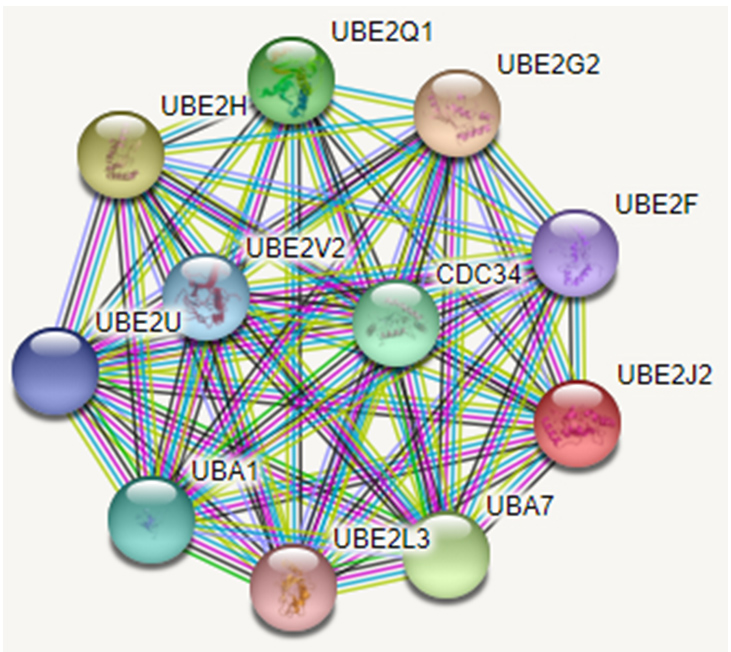
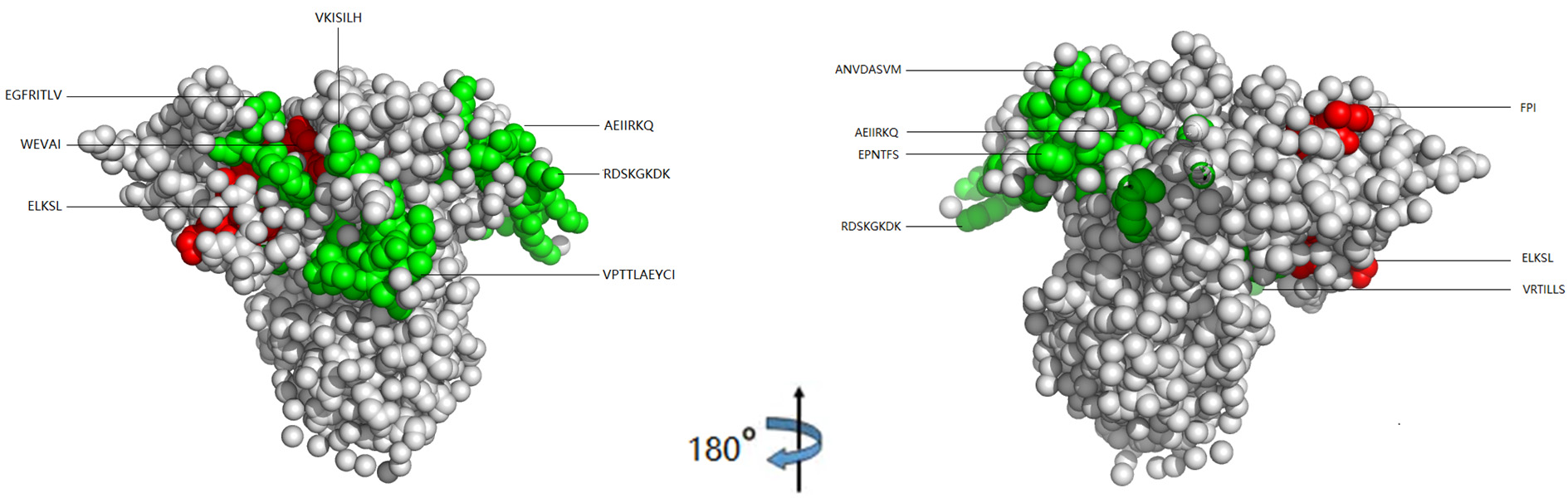
| [1] |
GAUDREAULT N N, MADDEN D W, WILSON W C, et al. African swine fever virus:An emerging DNA arbovirus[J]. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2020, 7:215.
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00215
|
| [2] |
URBANO A C, FERREIR F. Role of the DNA-binding protein pA104R in ASFV genome packaging and as a novel target for vaccine and drug development[J]. Vaccines, 2020, 8(4):585.
doi: 10.3390/vaccines8040585
|
| [3] |
ALONSO C, BORCA M, DIXON L, et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile:Asfarviridae[J]. The Journal of General Virology, 2018, 99(5):6s13-614.
|
| [4] |
WANG F, ZHANG H, HOU L, et al. Advance of African swine fever virus in recent years[J]. Research in Veterinary Science, 2021, 136:535-539.
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2021.04.004
pmid: 33882382
|
| [5] |
欧云文, 刘俐君, 贾宁, 等. 非结构蛋白在非洲猪瘟病毒感染中作用[J]. 病毒学报, 2021, 37(4):910-921.
|
| [6] |
王涛, 孙元, 罗玉子, 等. 非洲猪瘟防控及疫苗研发:挑战与对策[J]. 生物工程学报, 2018, 34(12):1931-1942.
|
| [7] |
WANG N, ZHAO D, WANG J, et al. Architecture of African swine fever virus and implications for viral assembly[J]. Science, 2019, 366(6465):640-644.
doi: 10.1126/science.aaz1439
pmid: 31624094
|
| [8] |
LIU S, LUO Y, WANG Y, et al. Cryo-EM structure of the African swine fever virus[J]. Cell Host and Microbe, 2019, 26(6):836-843.
doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.11.004
|
| [9] |
朱利敏, 邹兴启, 赵启祖. 非洲猪瘟病毒多样性[J]. 病毒学报, 2021, 37(3):719-725.
|
| [10] |
孙茂文, 王涛, 孙元, 等. 非洲猪瘟病毒的免疫逃逸策略[J]. 微生物学报, 2021, 61(2):249-262.
|
| [11] |
JANCOVICH J K, CHAPMAN D, HANSEN D T, et al. Immunization of pigs by DNA prime and recombinant vaccinia virus boost to identify and rank African swine fever virus immunogenic and protective proteins[J]. Journal of Virology, 2018, 92(8):e02219-17.
|
| [12] |
KEBLER C, FORTH J H, KEIL G M, et al. The intracellular proteome of African swine fever virus[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1):14714.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32985-z
pmid: 30279544
|
| [13] |
蒋思文, 房立春, 冯泽新, 等. 非洲猪瘟病毒UBCv1的原核表达及多抗制备[J]. 北京农学院学报, 2021, 36(4):1-6.
|
| [14] |
何健, 石建州, 刘阳坤, 等. 非洲猪瘟病毒研究进展[J]. 南阳师范学院学报, 2022, 21(1):55-62.
|
| [15] |
FREITAS F B, FROUCO G, MARTINS C, et al. African swine fever virus encodes for an E2-ubiquitin conjugating enzyme that is mono-and di-ubiquitinated and required for viral replication cycle[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1):3471.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21872-2
|
| [16] |
BARRADO-GIL L, GALIND O, MARTINEZ-ALONSO D, et al. The ubiquitin-proteasome system is required for African swine fever replication[J]. PLoS ONE, 2017, 12(12):1-20.
|
| [17] |
BARRADO-GIL L, DEL PUERTO A, MUÑOZ-MORENO R, et al. African swine fever virus ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme interacts with host translation machinery to regulate the host protein synthesis[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2020, 11:1-15.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00001
|
| [18] |
杨易霖. 非洲猪瘟病毒I215L蛋白参与泛素结合的结构基础与分子机制[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2021.
|
| [19] |
王俊娟, 李欣芮, 陈成, 等. 花生主要过敏原Ara h 1线性B细胞表位的预测及鉴定[J]. 食品科学, 2021, 42(17):106-112.
|
| [20] |
KARGER A, PEREZ-NUNEZ D, URQUIZA J, et al. An update on african swine fever virology[J]. Viruses, 2019, 11(9):864.
doi: 10.3390/v11090864
|
| [21] |
HUANG L, XU W, LIU H, et al. African swine fever virus pI215L negatively regulates cGAS-STING signaling pathway through recruiting RNF138 to inhibit K63-linked ubiquitination of TBK1[J]. Journal of Immunology, 2021, 207(11):2754-2769.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100320
pmid: 34759016
|