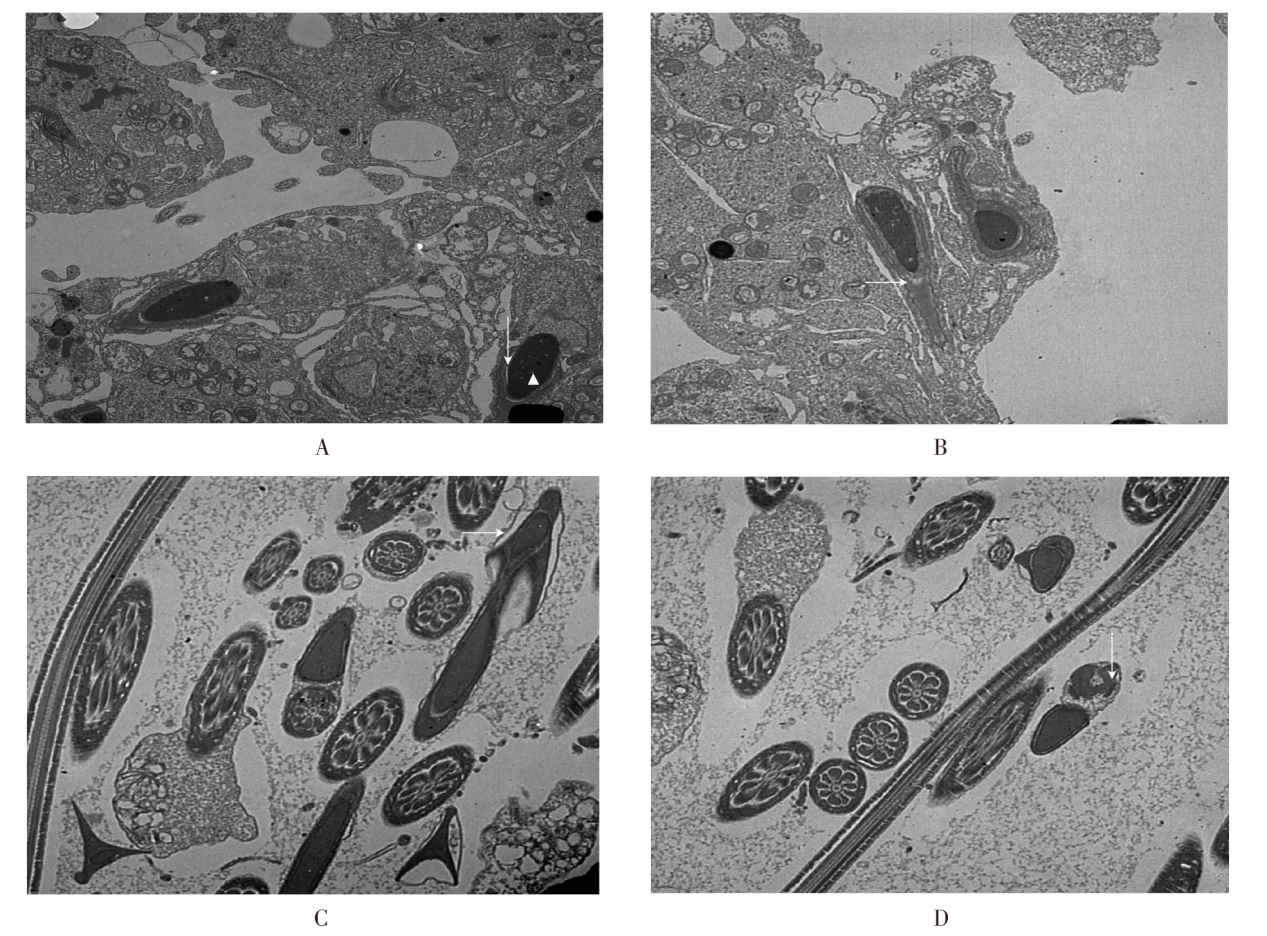
| [1] |
JALALUDEEN A M, RAN L, LEE W Y, et al. Ameliorating effect of selenium against arsenic induced male reproductive toxicity in rats[J]. Reproductive and Developmental Biology, 2014, 38(3):107-114.
doi: 10.12749/RDB.
|
| [2] |
王平, 戴研平, 杨薇, 等. 不育患者凋亡生精细胞与ACP超微结构的关系[J]. 检验医学, 2018, 33(6):472-475.
|
| [3] |
王随心, 张玉华, 李向阳, 等. 重金属生精细胞毒性研究进展[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2011, 28(4):367-372.
|
| [4] |
秦海霞, 高晓勤, 刘智, 等. 亚慢性砷中毒对大鼠睾丸间质细胞caspase-3表达及血清中睾酮含量的影响[J]. 中华地方病学杂志, 2016(1):14-17.
|
| [5] |
许小凤, 谈勇, 陈宣伊, 等. 补肾活血中药对雷公藤致卵巢储备下降大鼠颗粒细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2009, 38(12):123-125.
|
| [6] |
马惠芳, 任秀君, 图娅, 等. 针刺对高血脂合并脑缺血大鼠海马区Caspase-9蛋白表达及神经行为学的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2008, 33(6):382-386.
|
| [7] |
赵茹, 华亚军, 万俊. 杜仲水提液对幼鼠睾丸间质细胞睾酮合成和caspase-9的影响[J]. 儿科药学杂志, 2012, 18(6):11-14.
|
| [8] |
郭泳梅, 姚红, 童娟. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病膈肌形态学改变的机制探讨[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2012, 17(9):1675-1676.
|
| [9] |
KONG D, ZHENG T, ZHANG M, et al. Static mechanical stress induces apoptosis in rat endplate chondrocytes through MAPK and mitochondria-dependent caspase activation signaling pathways[J]. PLoS ONE, 2013, 8(7):e69403.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069403
|
| [10] |
朱筑霞, 潘玮炜, 易必达, 等. 砷致大鼠海马神经细胞凋亡对学习记忆功能的影响[J]. 贵州医药, 2010, 34(9):777-780.
|
| [11] |
李玉飞, 康朝胜, 臧贵勇, 等. SYNⅠ在慢性砷中毒大鼠海马CA3区的表达[J]. 当代医学, 2009(34):3-5.
|
| [12] |
范兴君, 马子媛, 杜宗花, 等. 低剂量亚慢性砷染毒对雄性大鼠生殖功能及子代的影响[J]. 中国生育健康杂志, 2012, 23(5):361-364.
|
| [13] |
李解生, 李纯颖, 李勇, 等. 甲醛对小鼠胚胎的发育毒性[J]. 实用预防医学, 2009, 16(4):1242-1244.
|
| [14] |
吴勇. 精索静脉曲张大鼠血清抑制素B、性激素及睾丸肿瘤坏死因子的变化[D]. 佳木斯: 佳木斯大学, 2007.
|
| [15] |
曹兴午, 林凯, 李翠英, 等. 睾丸生精小管界膜和管周肌样细胞调控睾丸功能[J]. 中国男科学杂志, 2011, 25(12):59-62.
|
| [16] |
杨春林, 王明, 邓远忠, 等. 雄性大鼠脊髓损伤对生殖系细菌感染及IL-1、TNF-α、SOD表达的影响[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2011, 36(11):1296-1299.
|
| [17] |
戴研平, 高晓勤, 丁贤胜. 盐酸利多卡因体外对精子功能及超微结构的影响[J]. 甘肃医药, 2020, 39(9):799-801.
|
| [18] |
胡京美, 许成岩, 李媛, 等. 不同冷冻保护剂对人类精子冷冻复苏后活动能力的影响[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2008(1):23-25.
|
| [19] |
郭海, 宋爽, 王国秀, 等. 染锰大鼠生精细胞凋亡中caspase-3 mRNA、凋亡蛋白酶活化因子-1及多聚ADP核糖聚合酶的表达变化[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2017, 40(3):254-257.
|
| [20] |
白彩军, 刘丹, 李冰. 砷的氧化应激分子机制研究进展[J]. 实用预防医学, 2012, 19(2):314-316.
|