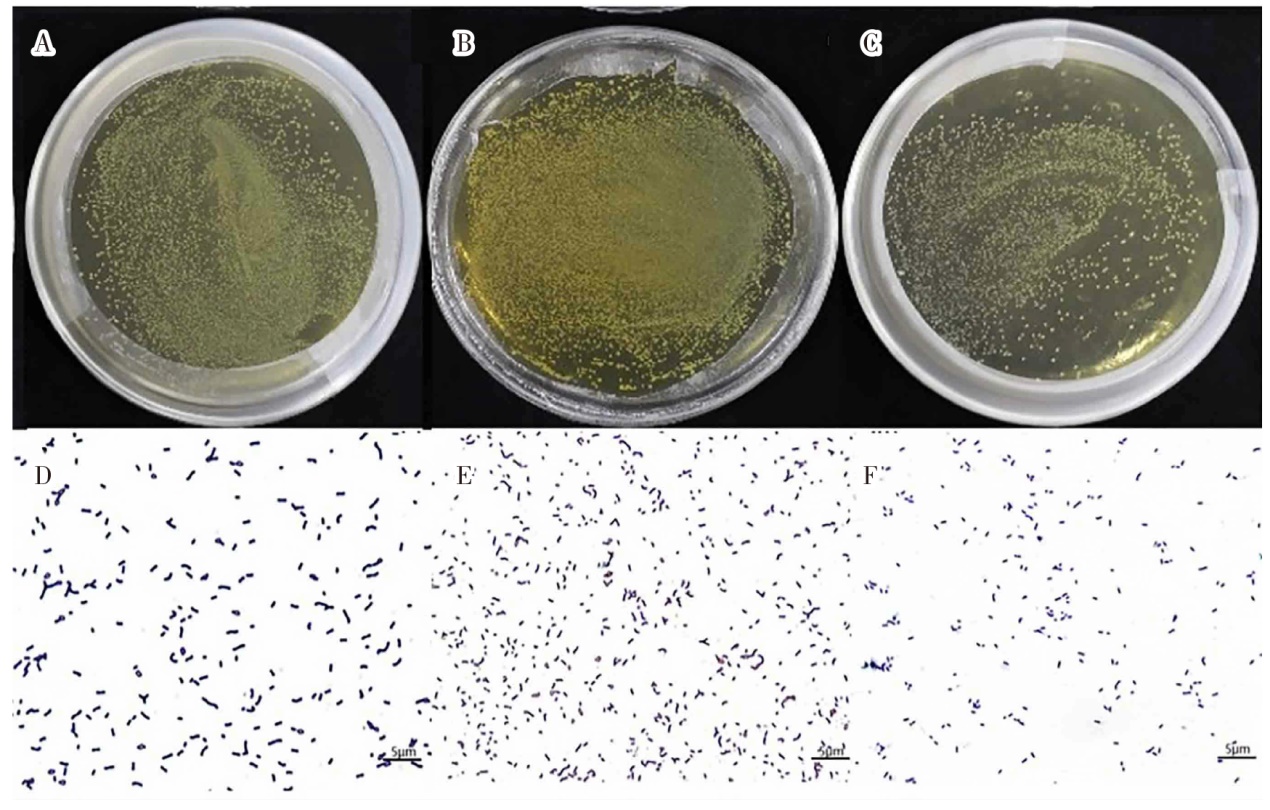
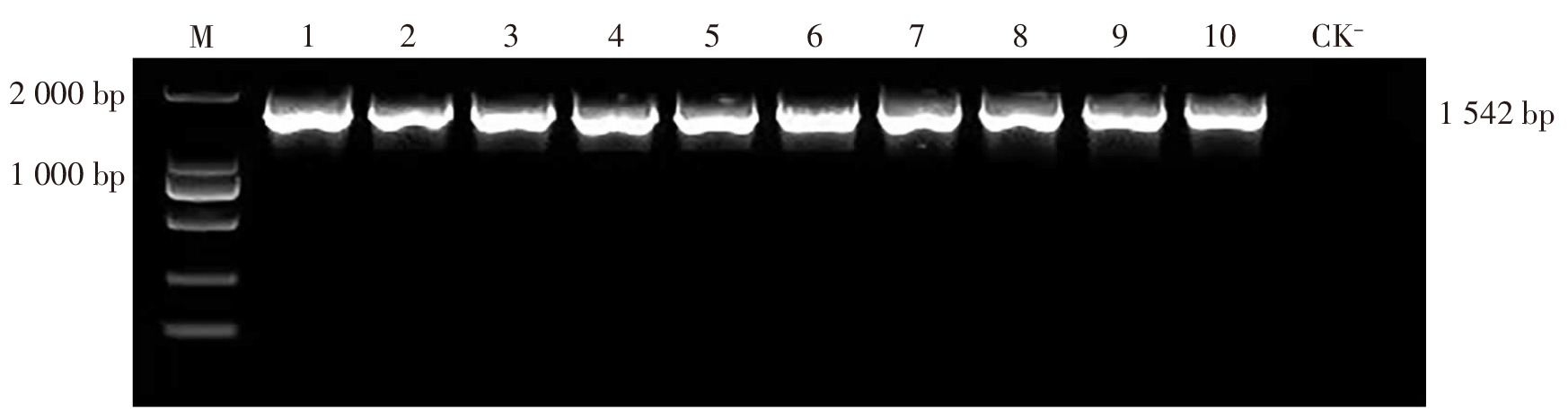
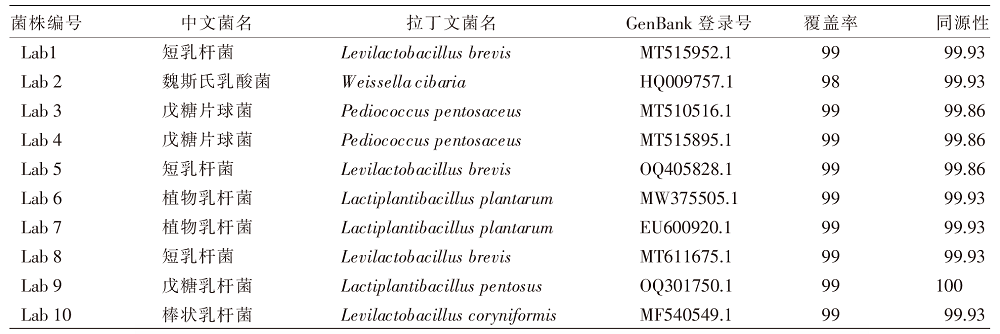
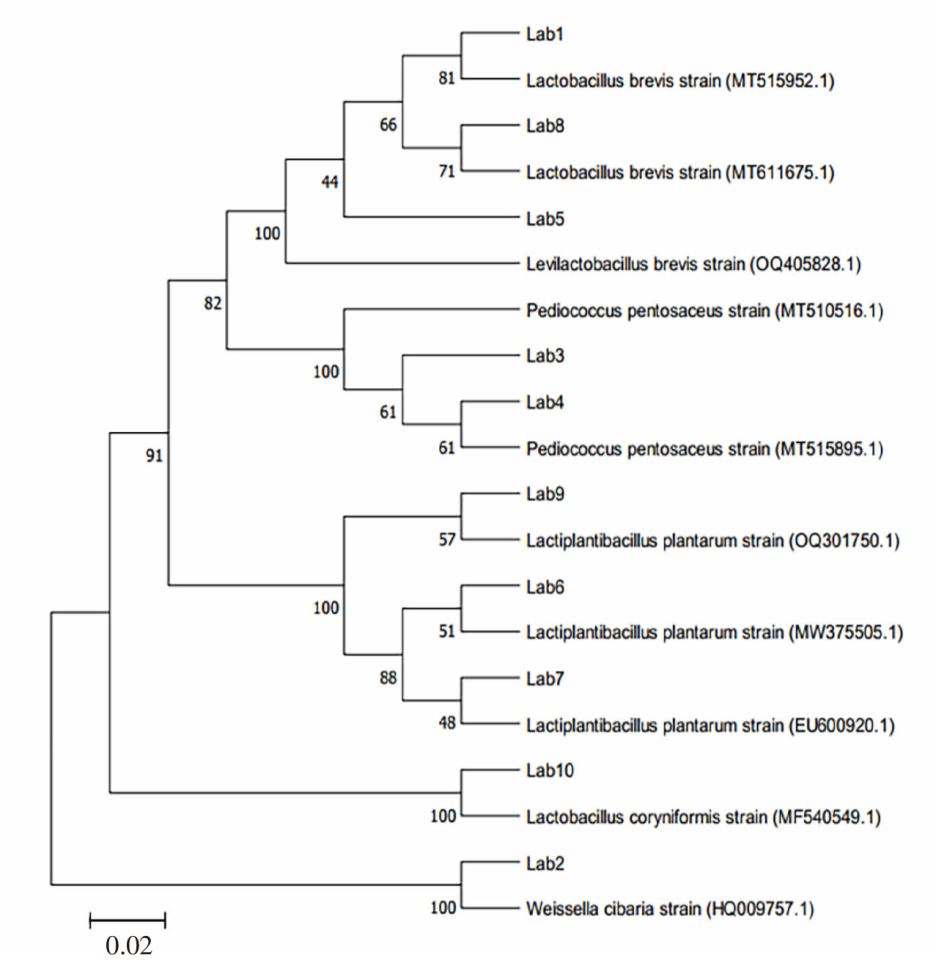
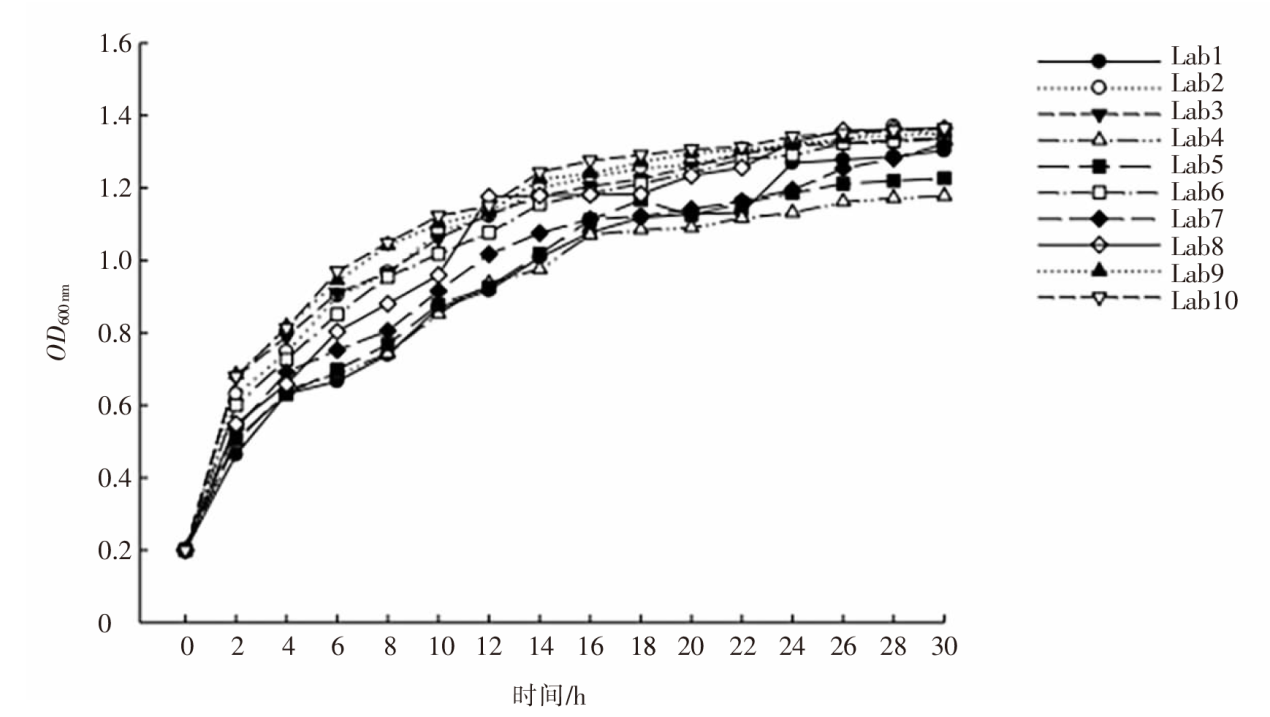
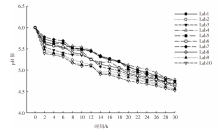
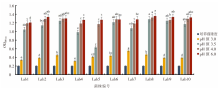
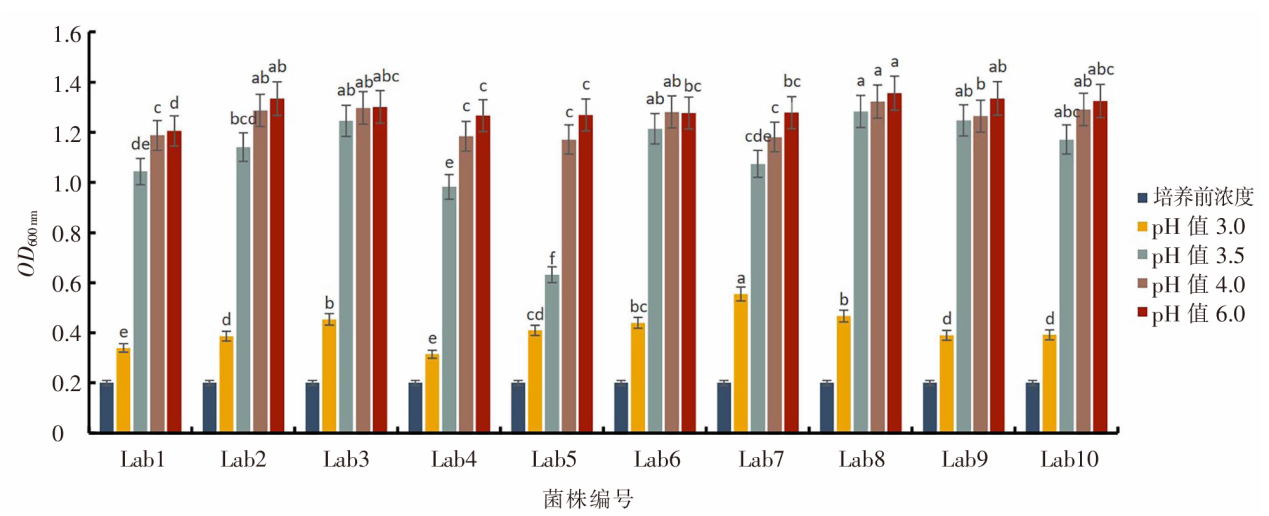
| [1] |
何轶群. 青贮用优良乳酸菌的分离筛选及其初步应用效果[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2013.
|
| [2] |
赵碧刚. 青贮饲料营养价值及其在反刍动物生产中的应用[J]. 畜牧兽医科学(电子版), 2019(13): 155-156.
|
| [3] |
张大伟, 陈林海, 朱海霞, 等. 青贮饲料中主要微生物对青贮品质的影响[J]. 饲料研究, 2007(3): 65-68.
|
| [4] |
杨文琦, 龙宣杞, 崔卫东. 玉米青贮中细菌多样性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2013, 50(8): 1424-1433.
|
| [5] |
崔棹茗, 郭刚, 原现军, 等. 青稞秸秆青贮饲料中优良乳酸菌的筛选及鉴定[J]. 草地学报, 2015, 23(3): 607-615.
doi: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2015.03.025
|
| [6] |
朱爱文, 殷洁鑫, 穆立然, 等. 微生态制剂对湖羊营养物质消化率、屠宰性能和肉质性状的影响[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2017, 23(20): 79-81.
|
| [7] |
ZHANG R, ZHOU M, TU Y, et al. Effect of oral administration of probiotics on growth performance, apparent nutrient digestibility and stress‐related indicators in Holstein calves[J]. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2016, 100(1): 33-38.
doi: 10.1111/jpn.2016.100.issue-1
|
| [8] |
王奇, 余成群, 李志华, 等. 添加酶和乳酸菌制剂对西藏苇状羊茅和箭筈豌豆混合青贮发酵品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2012, 21(4): 186-191.
|
| [9] |
YAHAYA M S, GOTO M, YIMITI W, et al. Evaluation of fermentation quality of a tropical and temperate forage crops ensiled with additives of fermented juice of epiphytic lactic acid bacteria (FJLB)[J]. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 2004, 17(7): 1011-2367.
|
| [10] |
WOOLFORD M K, SAWCZYC M K. An investigation into the effect of culture of lactic acid bacteria on fer-mentation in silage[J]. Grass and Forage Science, 1984, 39(2): 139-148.
doi: 10.1111/gfs.1984.39.issue-2
|
| [11] |
CAI Y. Identification and characterization of Enterococcus species isolated from forage crops and their influence on silage fermentation[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 1999, 82(11): 2466-2471.
doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(99)75498-6
|
| [12] |
张志飞, 王青兰. 牧草青贮乳酸菌研究进展[J]. 湖南生态科学学报, 2021, 8(1): 70-76.
|
| [13] |
KIM E, YANG S, LIM B, et al. Design of PCR assays to specifically detect and identify 37 Lactobacillus species in a single 96 well plate[J]. BMC Microbiology, 2020, 20(1): 96-110.
doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01781-z
|
| [14] |
高擎燏, 李平华, 黄瑞华, 等. 猪源乳酸菌的抗逆性及益生性研究[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2015, 47(10): 41-46.
|
| [15] |
韦庆旭, 张建鹏, 梁煜晨, 等. 青贮用乳酸菌的分离鉴定及生物学特性评价[J]. 动物营养学报, 2022, 34(7): 4737-4749.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2022.07.060
|
| [16] |
王红梅, 孙启忠, 屠焰, 等. 呼伦贝尔草原野生牧草青贮中优良乳酸菌的分离及鉴定[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8): 189-196.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2016092
|
| [17] |
LIN C, BOLSEN K K, BRENT B E, et al. Epiphytic microflora on alfalfa and whole-plant corn[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 1992, 75(9): 2484-2493.
pmid: 1452853
|
| [18] |
张红梅, 段珍, 李霞, 等. 青贮饲料乳酸菌添加剂的应用现状[J]. 草业科学, 2017, 34(12): 2575-2583.
|
| [19] |
袁洁, 马冉冉, 张文洁, 等. 自然青贮多花黑麦草优良乳酸菌的筛选及对多花黑麦草青贮品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(11): 132-143.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2021064
|
| [20] |
郑昕, 唐霄, 宫利宏, 等. 鸡源肠道乳酸菌的筛选及抑菌作用分析[J]. 养禽与禽病防治, 2020(12): 9-15.
|
| [21] |
付彤. 玉米青贮饲料中优势乳酸菌的筛选与青贮发酵调控技术研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2014.
|
| [22] |
SI H Z, LIU H L, LI Z P, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus buchneri addition on fermentation, bacterial community and aerobic stability in lucerne silage[J]. Animal Production Science, 2019, 59(8): 1528-1536.
doi: 10.1071/AN16008
|