北方农业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 18-25.doi: 10.12190/j.issn.2096-1197.2022.04.03
盐胁迫对不同盐敏感性向日葵幼苗生长和生理特性的影响
邬雪瑞, 李军, 武悦, 王刚, 陈阳, 杜超, 任志远, 张俊峰
- 巴彦淖尔市农牧业科学研究所,内蒙古 临河 015000
Effects of salt stress on seedling growth and physiological characteristics of salt tolerant and salt sensitive sunflower
WU Xuerui, LI Jun, WU Yue, WANG Gang, CHEN Yang, DU Chao, REN Zhiyuan, ZHANG Junfeng
- Bayannur Institute of Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Sciences,Linhe 015000,China
摘要:
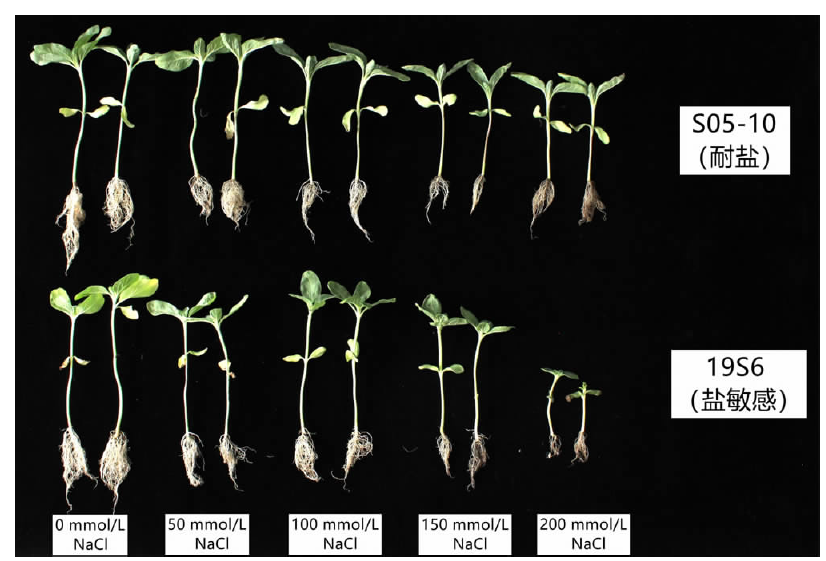
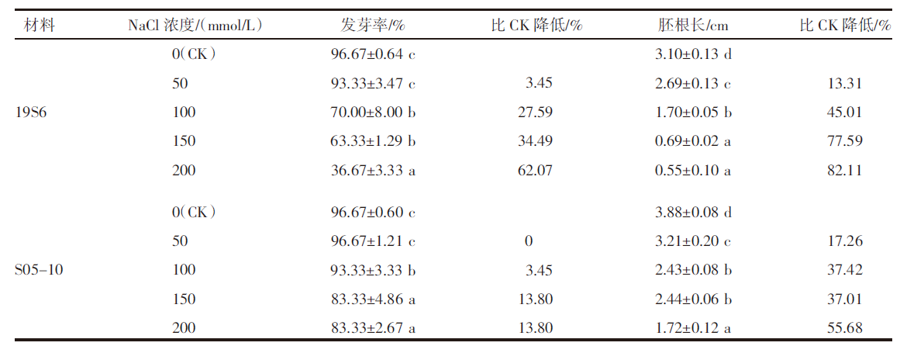
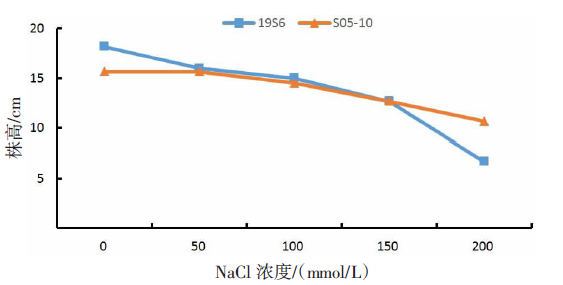
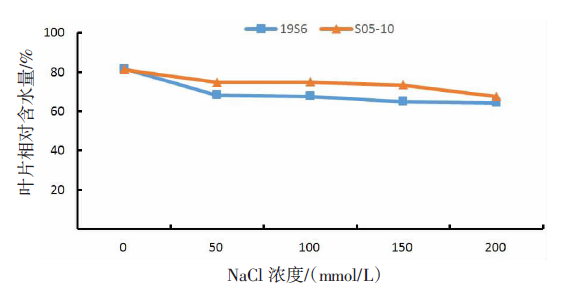
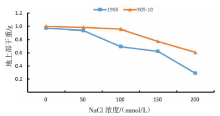
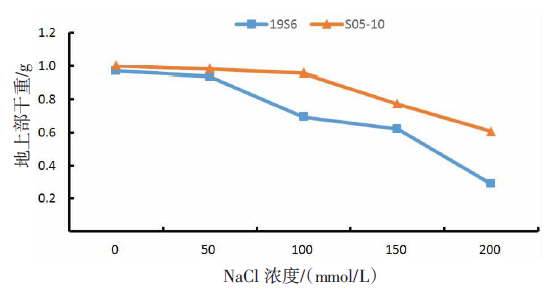
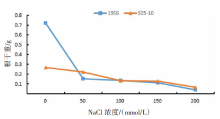
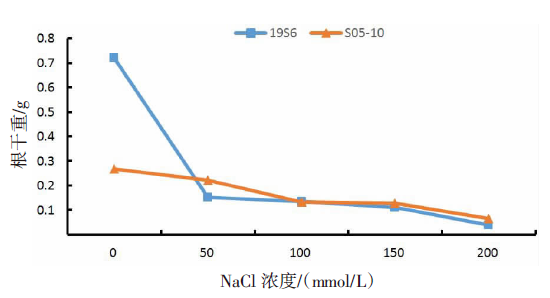
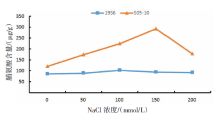
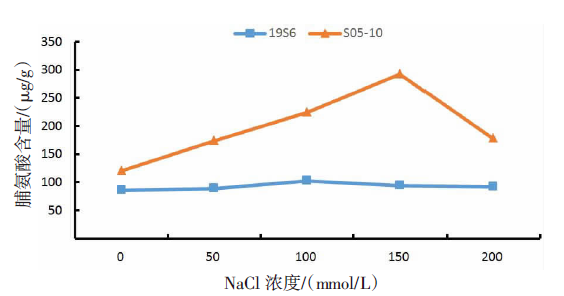
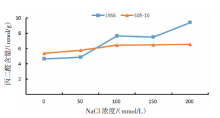
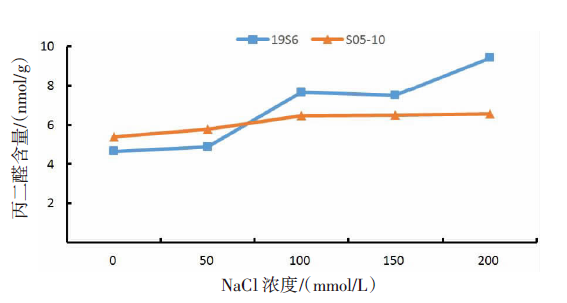
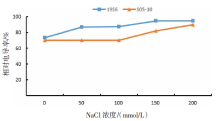
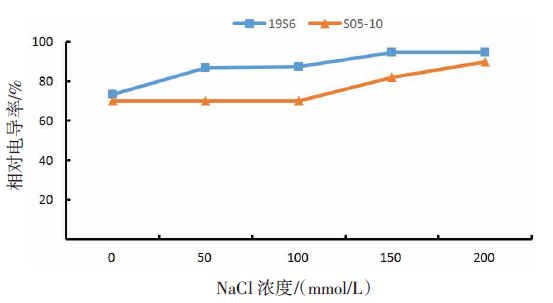
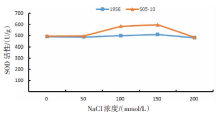
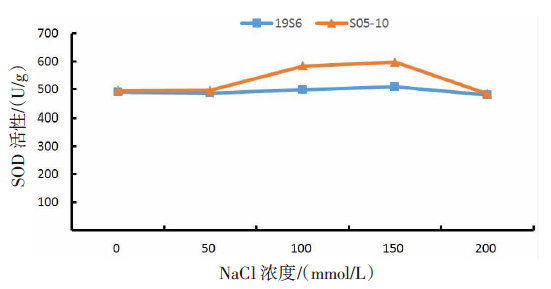
【目的】了解盐胁迫对耐盐和盐敏感向日葵种子发芽、幼苗生长和生理特性的影响,从生理生化角度解析向日葵的耐盐机制。【方法】采用50、100、150、200 mmol/L NaCl 溶液胁迫2份不同盐敏感性向日葵自交系S05-10(耐盐)和19S6(盐敏感),以蒸馏水处理为对照(CK),测定发芽率、株高、脯氨酸含量、丙二醛含量、相对电导率和SOD活性等,分析盐胁迫对向日葵种子发芽、幼苗生长和生理特性的影响。【结果】100、150、200 mmol/L NaCl胁迫下,S05-10和19S6发芽率受抑制明显,与CK相比,最高分别降低55.68%和82.11%,差异显著(P<0.05)。200 mmol/L NaCl胁迫下,S05-10和19S6株高分别比CK降低31.93%、63.31%。50~200 mmol/L NaCl胁迫下,与CK相比,S05-10脯氨酸含量增加44.38%~142.62%,丙二醛含量增加7.12%~21.36%,叶片相对电导率增加0.04%~28.52%;19S6脯氨酸含量增加4.01%~19.74%,丙二醛含量增加5.00%~102.50%,叶片相对电导率增加18.24%~28.96%。100、150 mmol/L NaCl胁迫下,S05-10 SOD活性分别比CK增加17.77%、20.43%;50~200 mmol/L NaCl胁迫下,19S6 SOD活性较稳定,比CK增加1.86%~3.73%。【结论】100~200 mmol/L NaCl胁迫下向日葵种子发芽、幼苗生长受抑制明显,19S6受抑制程度明显大于S05-10。19S6在NaCl胁迫后受盐害较重,叶片细胞膜脂过氧化严重,电解质严重泄露,丙二醛含量和叶片相对电导率增加幅度明显高于S05-10;S05-10受NaCl胁迫后通过积累更多的渗透调节物质(脯氨酸)、提高抗氧化酶(SOD)活性来缓解逆境压力,增强耐盐能力;19S6在NaCl胁迫下脯氨酸含量和SOD活性变化不明显,耐盐能力明显不足。
中图分类号:
- S565.5