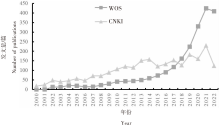
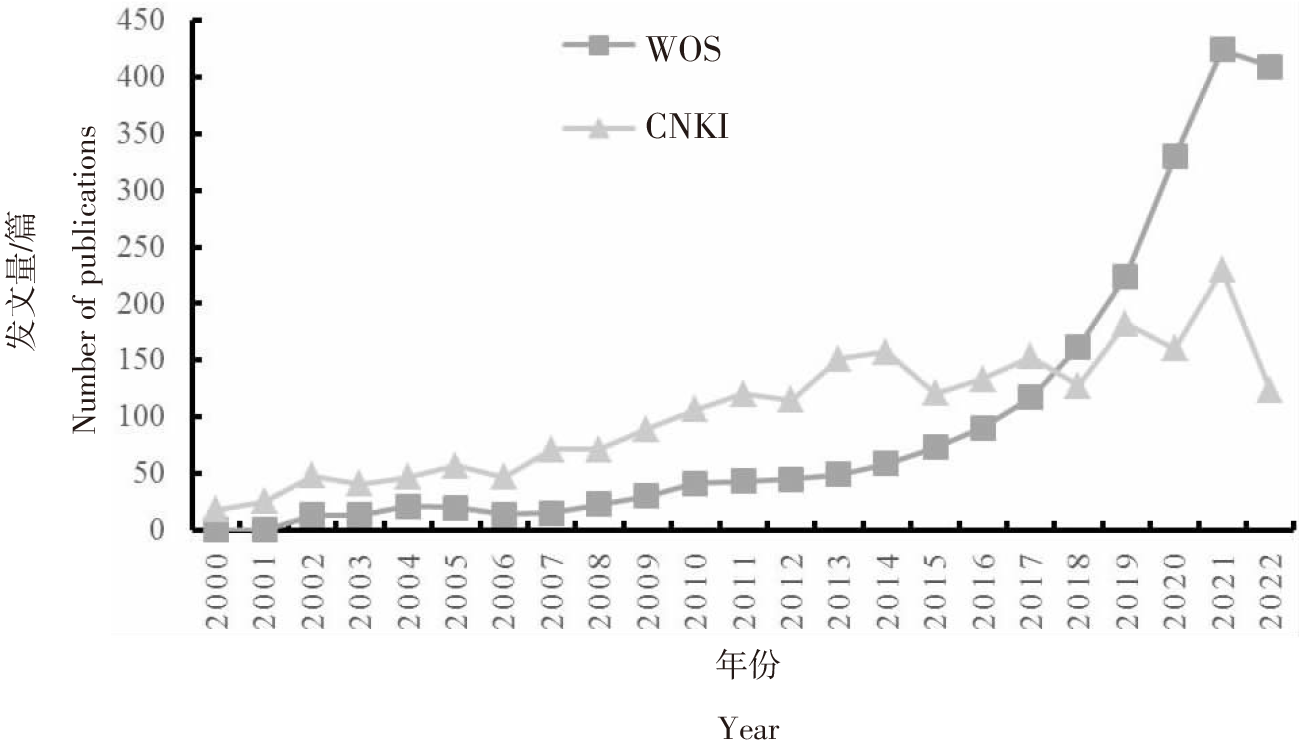
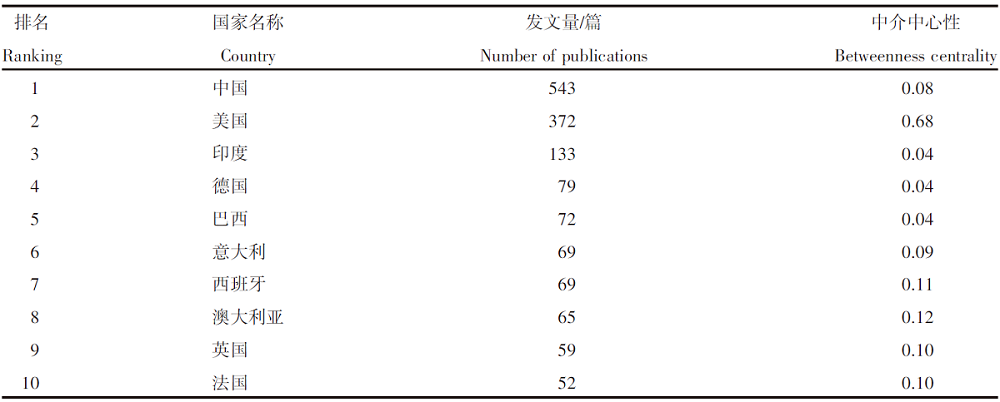
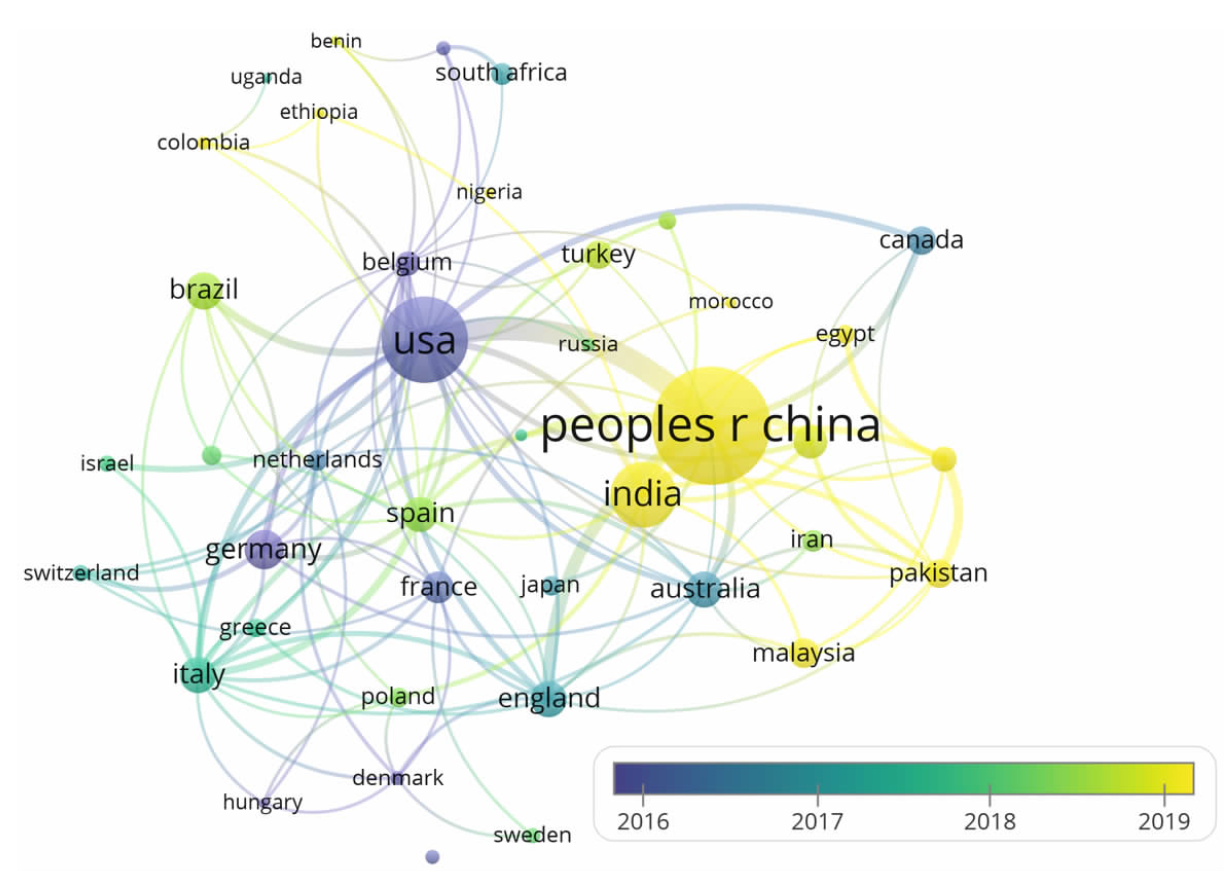
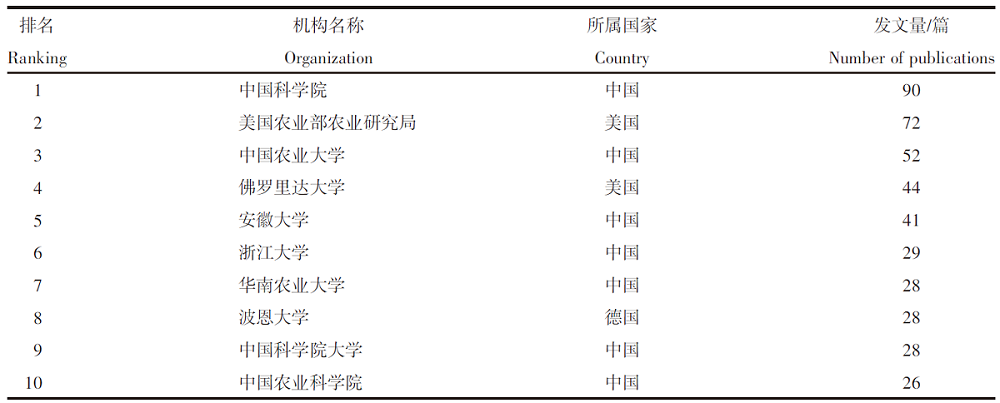
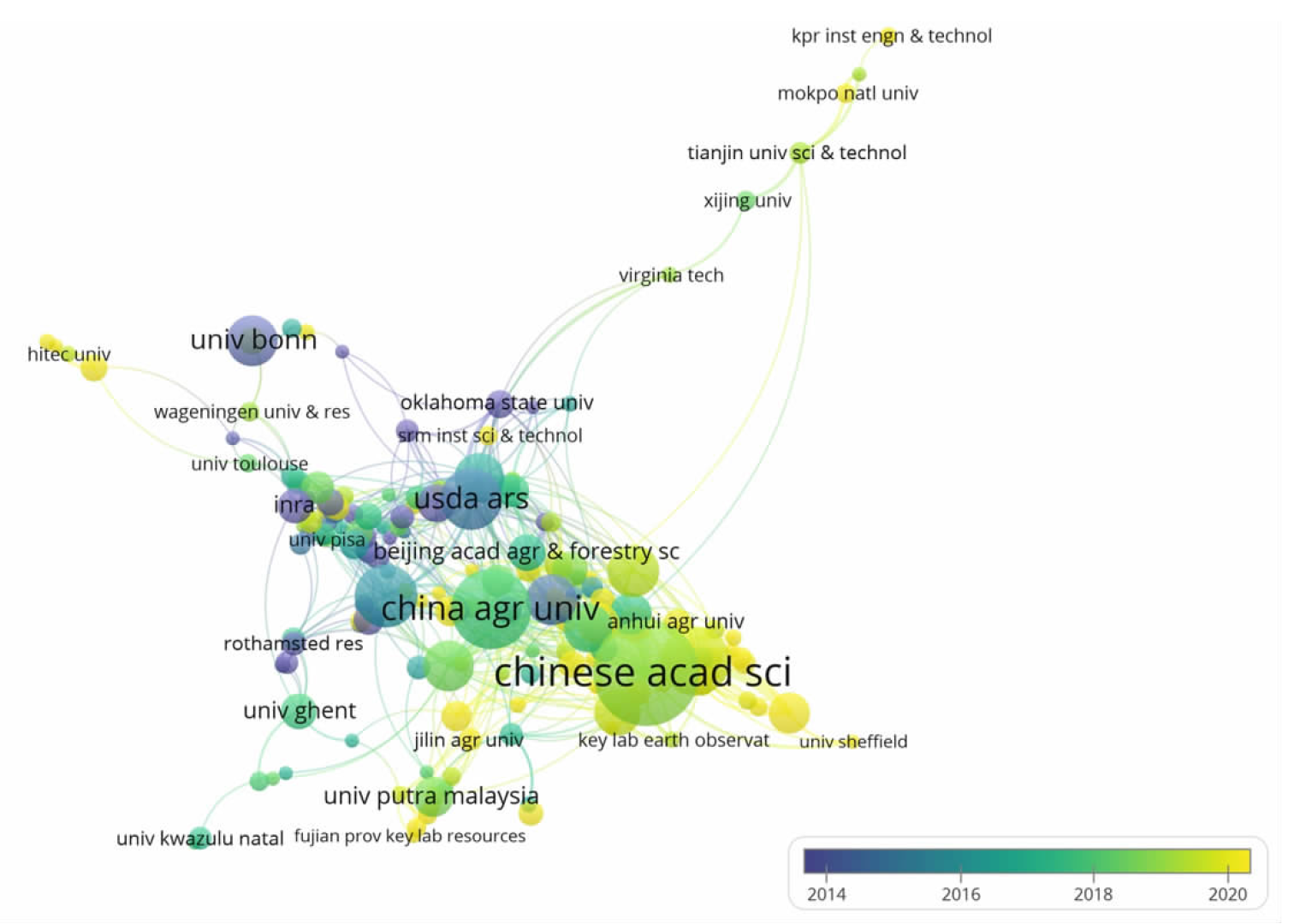
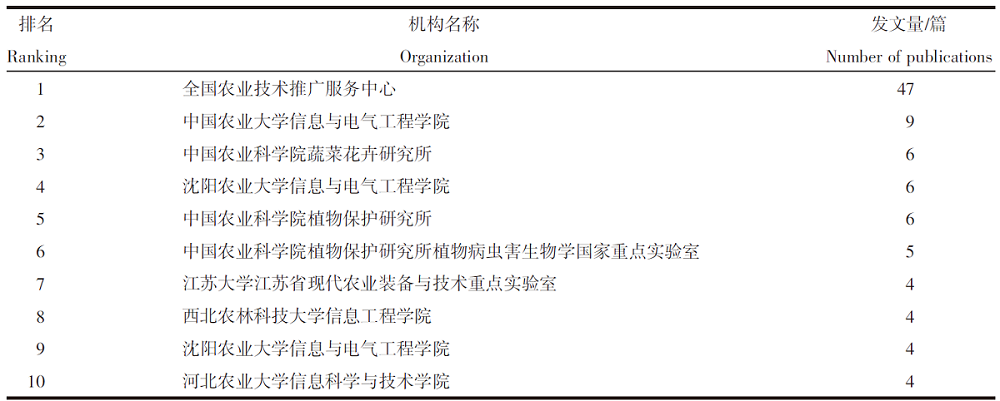
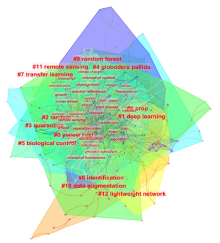
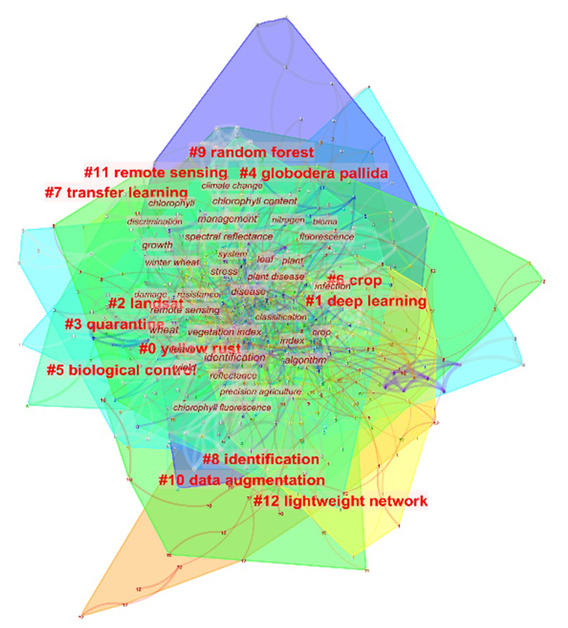
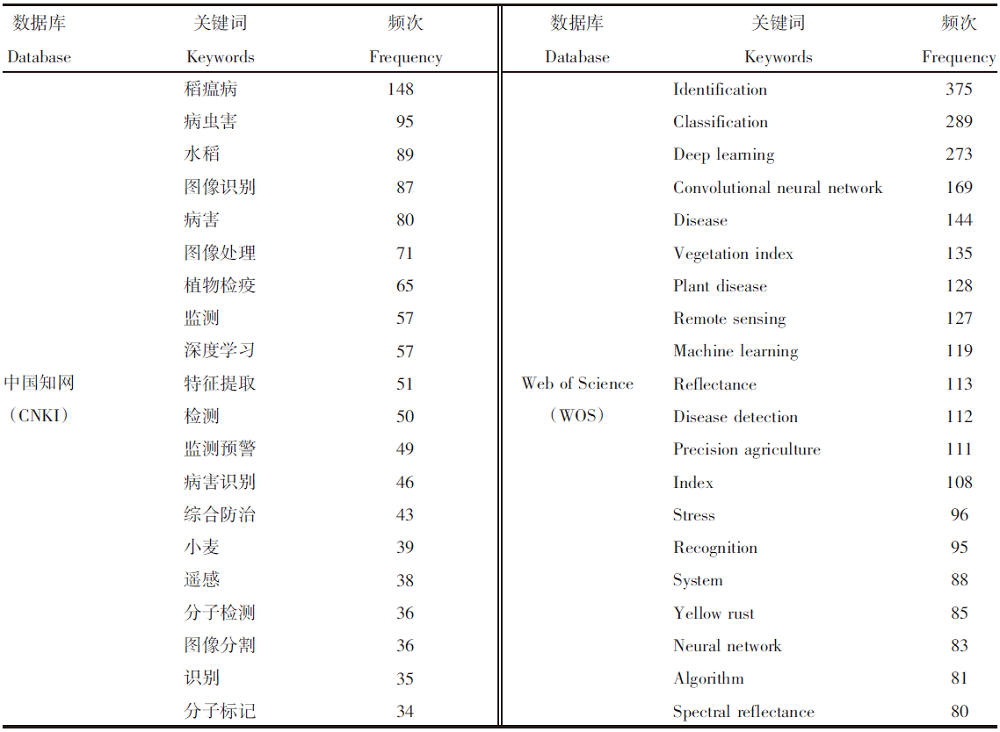
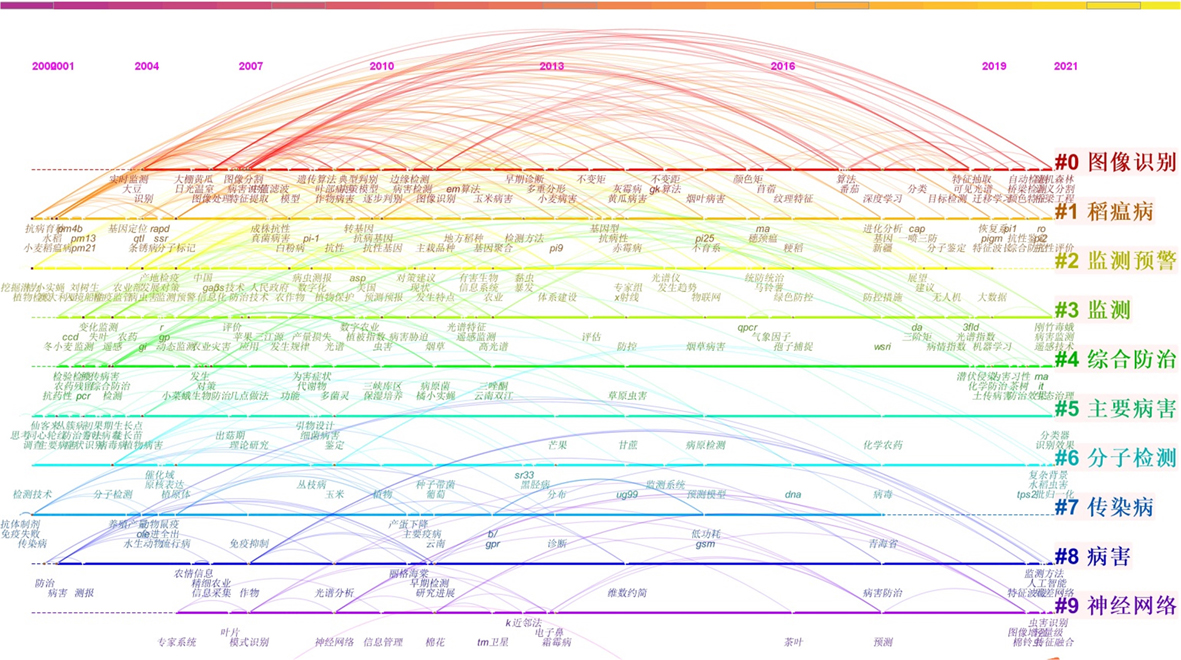
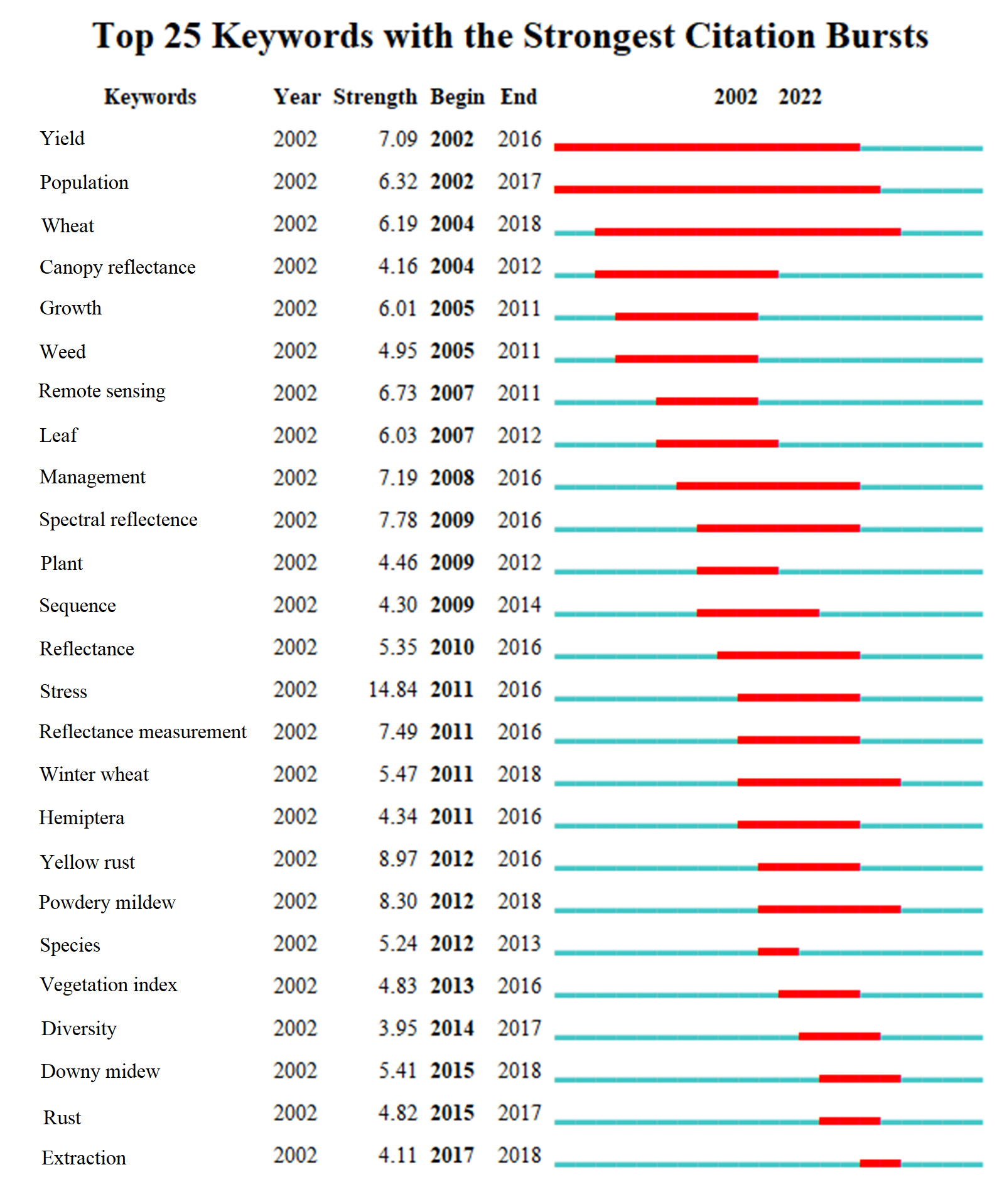
| [1] |
SAVARY S, WILLOCQUET L, PETHYBRIDGE S J, et al. The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2019, 3(3):430-439.
|
| [2] |
刘杰帆, 林铭佳, 张建桃, 等. 基于CiteSpace可视化分析的柑橘黄龙病研究进展[J]. 果树学报, 2023, 40(4):771-787.
|
| [3] |
曹丽英, 邸玉琦, 陈帅. 基于知识图谱的玉米病虫害研究可视化分析[J]. 东北农业科学, 2022, 47(1):145-150.
|
| [4] |
ZHU L J, MA Q, CHEN J, et al. Current progress on innovative pest detection techniques for stored cereal grains and thereof powders[J]. Food Chemistry, 2022, 396:133706.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133706
|
| [5] |
翟肇裕, 曹益飞, 徐焕良, 等. 农作物病虫害识别关键技术研究综述[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(7):1-18.
|
| [6] |
温艳兰, 陈友鹏, 王克强, 等. 基于机器视觉的病虫害检测综述[J]. 中国粮油学报, 2022, 37(10):271-279.
|
| [7] |
THELWALL M. Bibliometrics to webometrics[J]. Journal of Information Science, 2008, 34(4):605-621.
doi: 10.1177/0165551507087238
|
| [8] |
ROCCHI L, BOGGIA A, PAOLOTTI L. Sustainable agricultural systems:A bibliometrics analysis of ecological modernization approach[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(22):9635.
doi: 10.3390/su12229635
|
| [9] |
TAKEDA Y, KAJIKAWA Y. Tracking modularity in citation networks[J]. Scientometrics, 2010, 83(3):783-792.
doi: 10.1007/s11192-010-0158-z
|
| [10] |
MEKHA J, PARTHASARATHY V. An automated pest identification and classification in crops using artificial intelligence a state of art review[J]. Automatic Control and Computer Sciences, 2022, 56(3):283-290.
doi: 10.3103/S0146411622030038
|
| [11] |
HUANG M L, CHUANG T C, LIAO Y C. Application of transfer learning and image augmentation technology for tomato pest identification[J]. Sustainable Computing:Informatics and Systems, 2022, 33:100646.
doi: 10.1016/j.suscom.2021.100646
|
| [12] |
MOHANTY S P, HUGHES D P, SALATHÉ M. Using deep learning for image-based plant disease detection[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7:1419.
pmid: 27713752
|
| [13] |
CHENG X, ZHANG Y H, CHEN Y Q, et al. Pest identification via deep residual learning in complex background[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2017, 141:351-356.
doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2017.08.005
|
| [14] |
LIU J, WANG X W. Plant diseases and pests detection based on deep learning:A review[J]. Plant Methods, 2021, 17(1):1-18.
doi: 10.1186/s13007-020-00700-7
|
| [15] |
WANG K L, CHEN K Y, DU H Y, et al. New image dataset and new negative sample judgment method for crop pest recognition based on deep learning models[J]. Ecological Informatics, 2022, 69:101620.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoinf.2022.101620
|
| [16] |
XIAO Z T, YIN K, GENG L, et al. Pest identification via hyperspectral image and deep learning[J]. Signal,Image and Video Processing, 2022, 16(4):873-880.
doi: 10.1007/s11760-021-02029-7
|
| [17] |
WANG B. Identification of crop diseases and insect pests based on deep learning[J]. Scientific Programming, 2022, 2022:1-10.
|
| [18] |
CARDIM FERREIRA LIMA M, DAMASCENA DE ALMEIDA LEANDRO M E, VALERO C, et al. Automatic detection and monitoring of insect pests:A review[J]. Agriculture, 2020, 10(5):161.
doi: 10.3390/agriculture10050161
|
| [19] |
ABD EL-GHANY N M, ABD EL-AZIZ S E, MAREI S S. A review:Application of remote sensing as a promising strategy for insect pests and diseases management[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(27):33503-33515.
doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09517-2
|
| [20] |
CALOU V B C, DOS SANTOS TEIXEIRA A, MOREIRA L C J, et al. The use of UAVs in monitoring yellow sigatoka in banana[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2020, 193:115-125.
doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2020.02.016
|
| [21] |
DU X, LI Q Z, SHANG J L, et al. Detecting advanced stages of winter wheat yellow rust and aphid infection using RapidEye data in North China Plain[J]. GIScience & Remote Sensing, 2019, 56(7):1093-1113.
|
| [22] |
YANG N, YU J J, WANG A Y, et al. A rapid rice blast detection and identification method based on crop disease spores′ diffraction fingerprint texture[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2020, 100(9):3608-3621.
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.v100.9
|
| [23] |
章艺, 马新焱, 余红瑞, 等. 十字花科作物根肿病综合防治研究进展[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2022(10):27-37.
|
| [24] |
牛学德, 高丙朋, 任荣荣, 等. 基于轻量级CNN的作物病虫害识别及安卓端应用[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 40(6):59-68.
|
| [25] |
周维, 牛永真, 王亚炜, 等. 基于改进的YOLOv4-GhostNet水稻病虫害识别方法[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2022, 38(3):685-695.
|
| [26] |
赵海岚, 蒙继华, 纪云鹏. 遥感技术在苹果园精准种植管理中的应用现状及展望[J]. 自然资源遥感, 2022, 35(2):1-15.
|
| [27] |
邓小玲, 曾国亮, 朱梓豪, 等. 基于无人机高光谱遥感的柑橘患病植株分类与特征波段提取[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2020, 41(6):100-108.
|
| [28] |
孙瑞琳, 孙全, 孙成明, 等. 基于不同平台的小麦病虫害遥感监测研究进展[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2021, 42(3):142-150.
doi: 10.13733/j.jcam.issn.2095-5553.2021.03.020
|
| [29] |
USHA K, SINGH B. Potential applications of remote sensing in horticulture:A review[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2013, 153:71-83.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2013.01.008
|
| [30] |
AHMAD LOTI N N, MOHD NOOR M R, CHANG S W. Integrated analysis of machine learning and deep learning in chili pest and disease identification[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2021, 101(9):3582-3594.
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10987
pmid: 33275806
|
| [31] |
ZHAO J, CHENG X P. Field pest identification by an improved Gabor texture segmentation scheme[J]. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research, 2007, 50(5):719-723.
doi: 10.1080/00288230709510343
|
| [32] |
THENMOZHI K, SRINIVASULU REDDY U. Crop pest classification based on deep convolutional neural network and transfer learning[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2019, 164:104906.
doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2019.104906
|
| [33] |
杨田堂, 刘琳. 保护地辣椒主要病害症状识别及综合防治[J]. 北方园艺, 2003(2):64-65.
|
| [34] |
刘琳. 大棚春番茄主要病害的识别与防治[J]. 北方园艺, 2003(6):16-17.
|
| [35] |
高灵旺, 陈继光, 于新文, 等. 农业病虫害预测预报专家系统平台的开发[J]. 农业工程学报, 2006, 22(10):154-158.
|
| [36] |
王婧, 路宗海, 李会平, 等. 基于Web的园林植物病虫害诊断系统框架构建[J]. 北方园艺, 2016(7):205-208.
|
| [37] |
邓晓璐, 王培, 马宁, 等. 基于物联网的寒地玉米大斑病预警系统的设计与实现[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2016, 37(7):166-170.
|
| [38] |
秦彩杰, 李勇. 作物病虫害自动识别技术研究:基于视频监控和无人机平台[J]. 农机化研究, 2021, 43(10):42-45.
|
| [39] |
伏荣桃, 陈诚, 王剑, 等. 植保无人机对水稻病虫害防治条件与防效的研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(4):103-109.
doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2019.0682
|
| [40] |
王兴旺, 郑汉垣, 王素青. 基于CSJMM-AS-GAC的马陆葡萄病虫害识别研究[J]. 河南农业科学, 2022, 51(6):154-163.
|
| [41] |
彭红星, 何慧君, 高宗梅, 等. 基于改进ShuffleNetV2模型的荔枝病虫害识别方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2022, 53(12):290-300.
|
| [42] |
彭红星, 徐慧明, 刘华鼐. 融合双分支特征和注意力机制的葡萄病虫害识别模型[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(10):156-165.
|
| [43] |
刘斌, 贾润昌, 朱先语, 等. 面向移动端的苹果叶部病虫害轻量级识别模型[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(6):130-139.
|